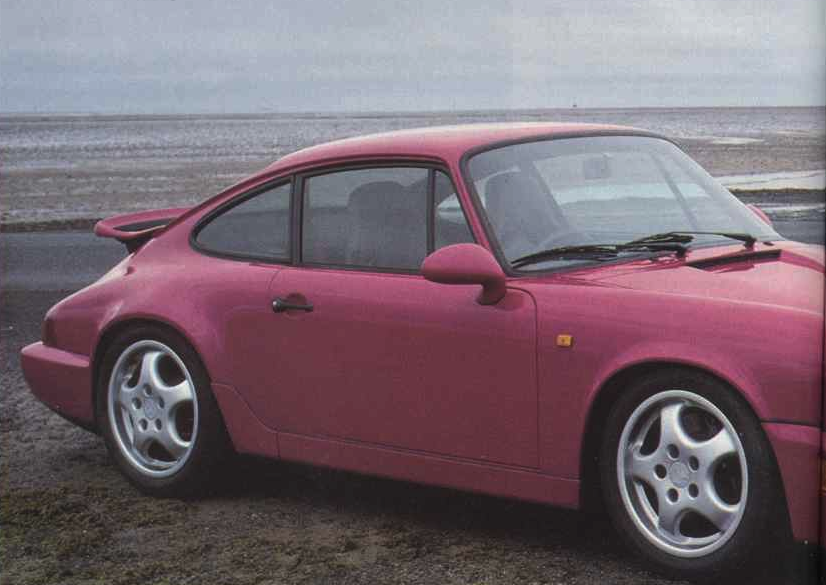
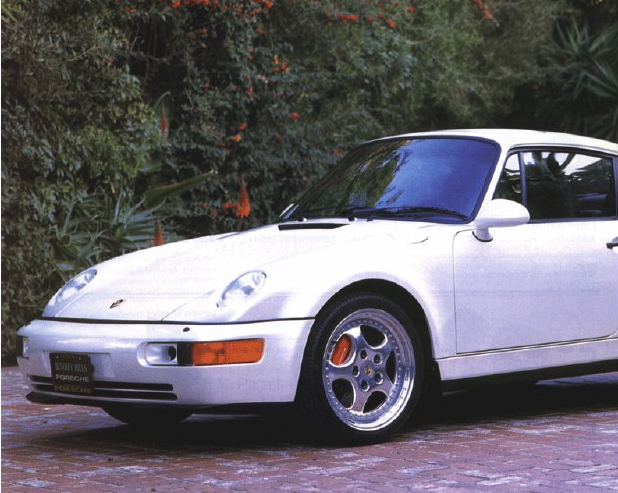
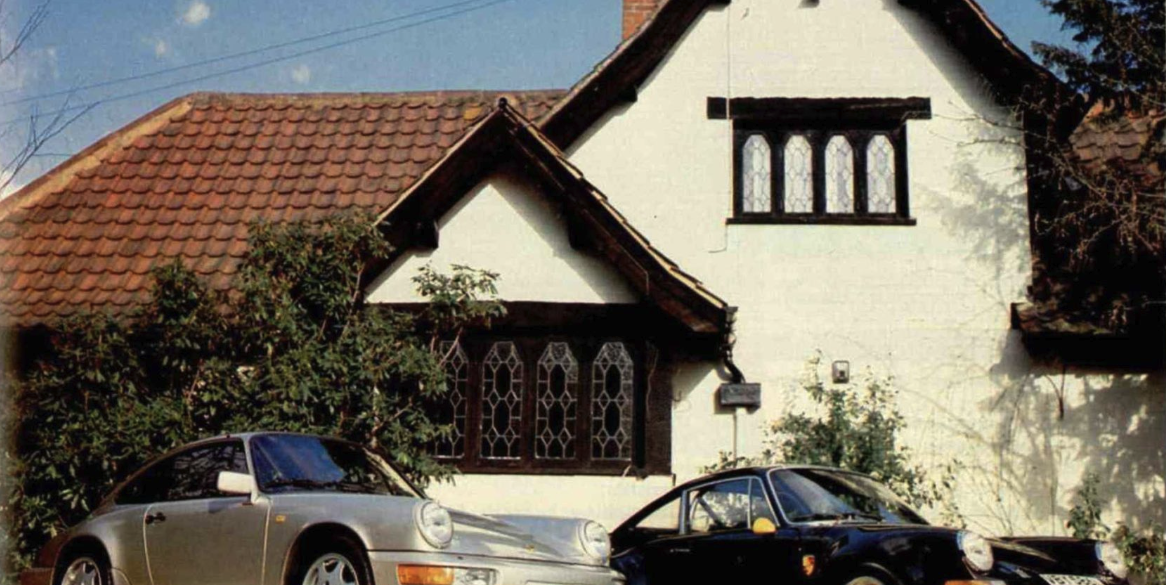
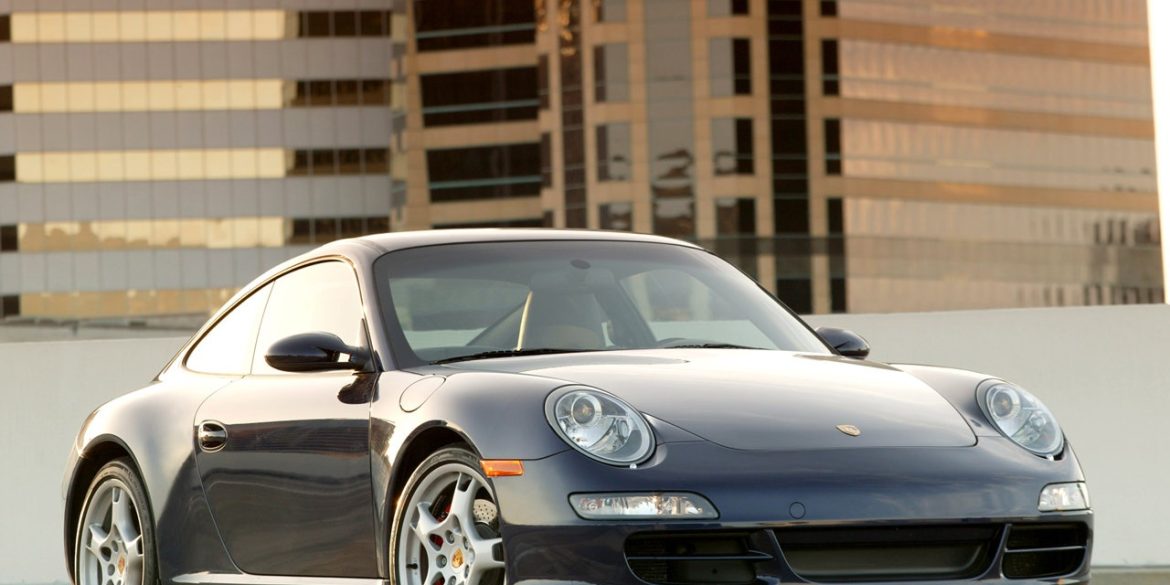
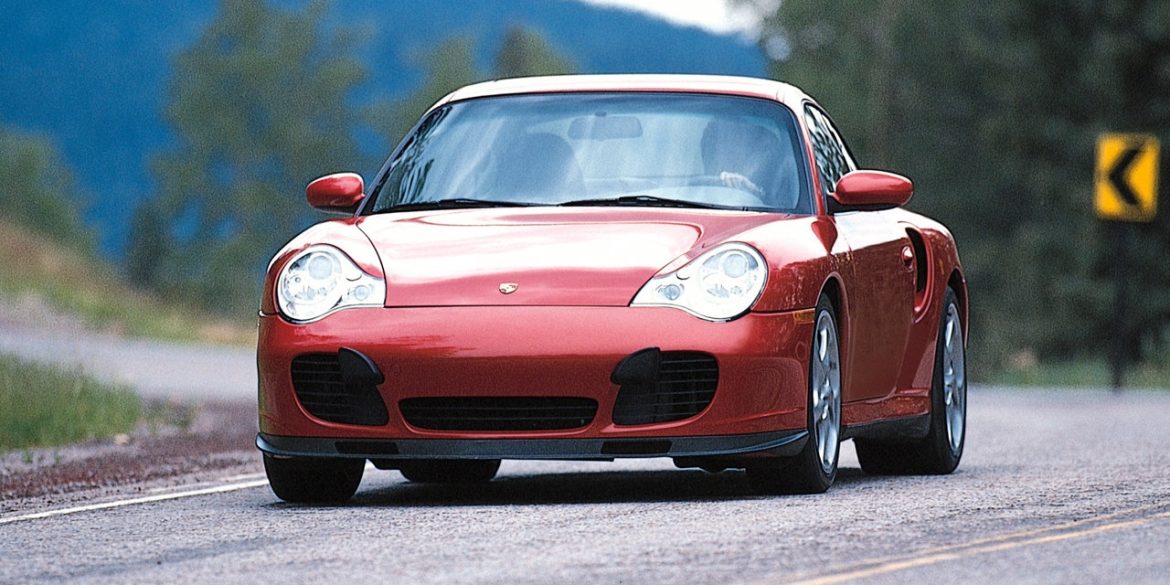
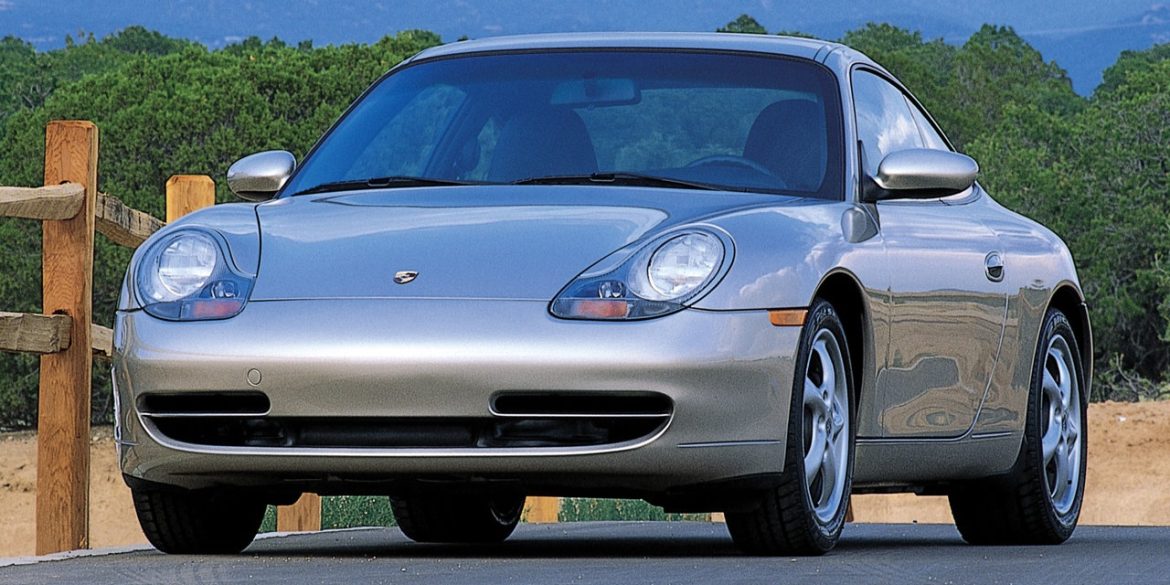
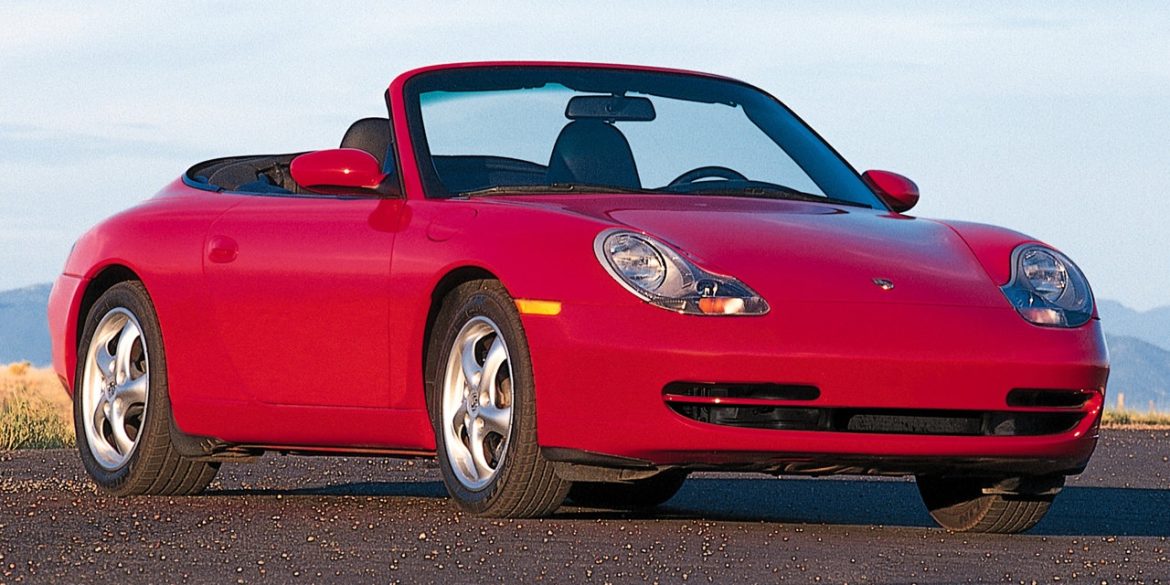
Porsche Models
All
- Porsche 911
- Porsche 914
- Porsche 917K
- Porsche 918
- Porsche 924
- Porsche 928
- Porsche 944
- Porsche 959
- Porsche 962
- Porsche Boxster Concept
- Porsche Carrera GT
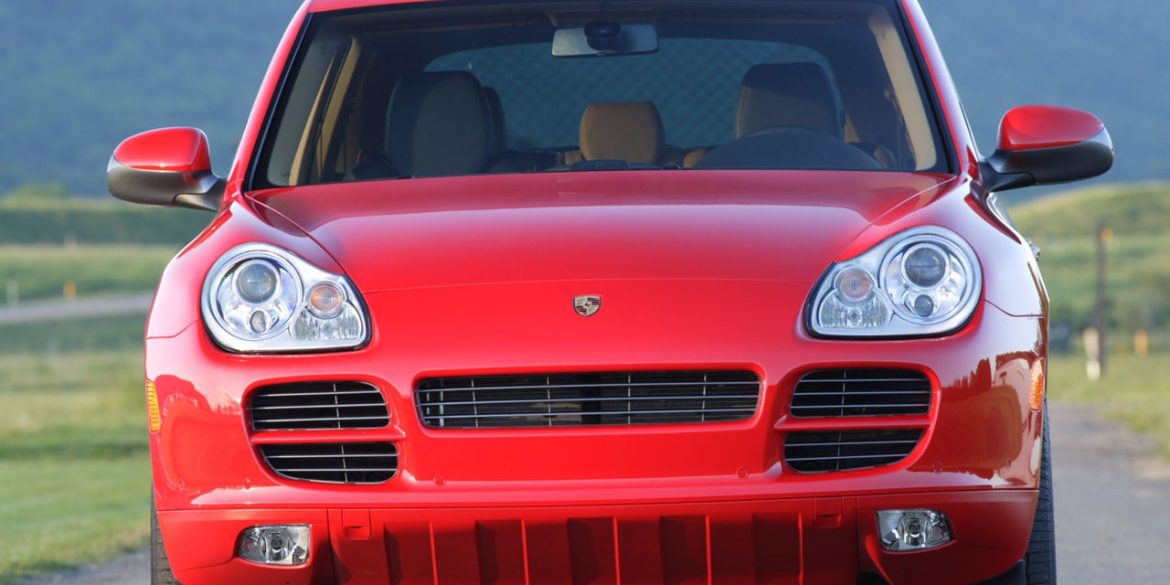
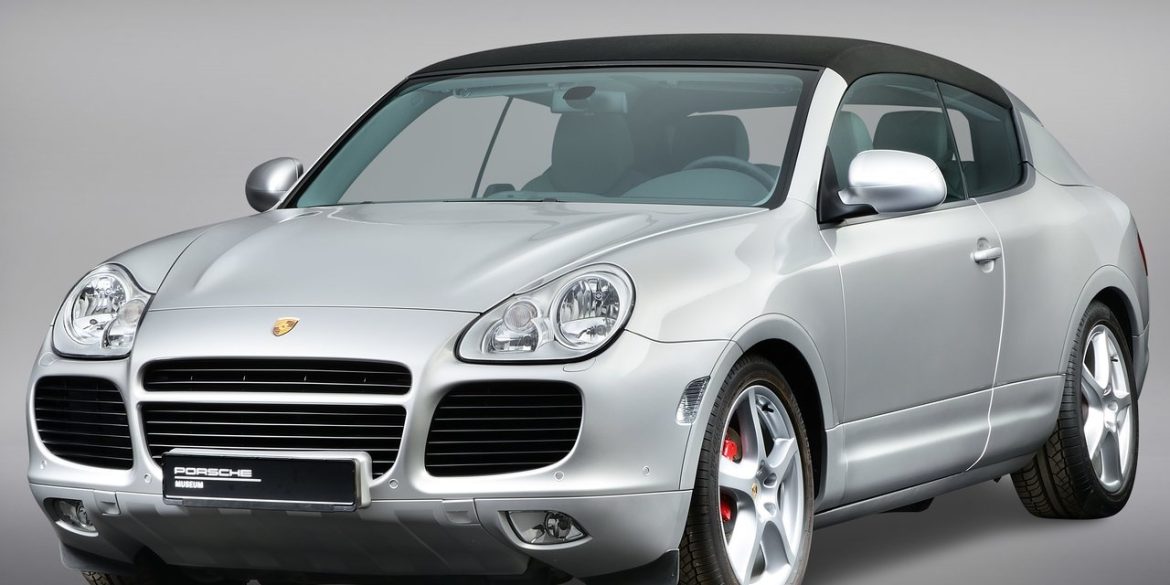
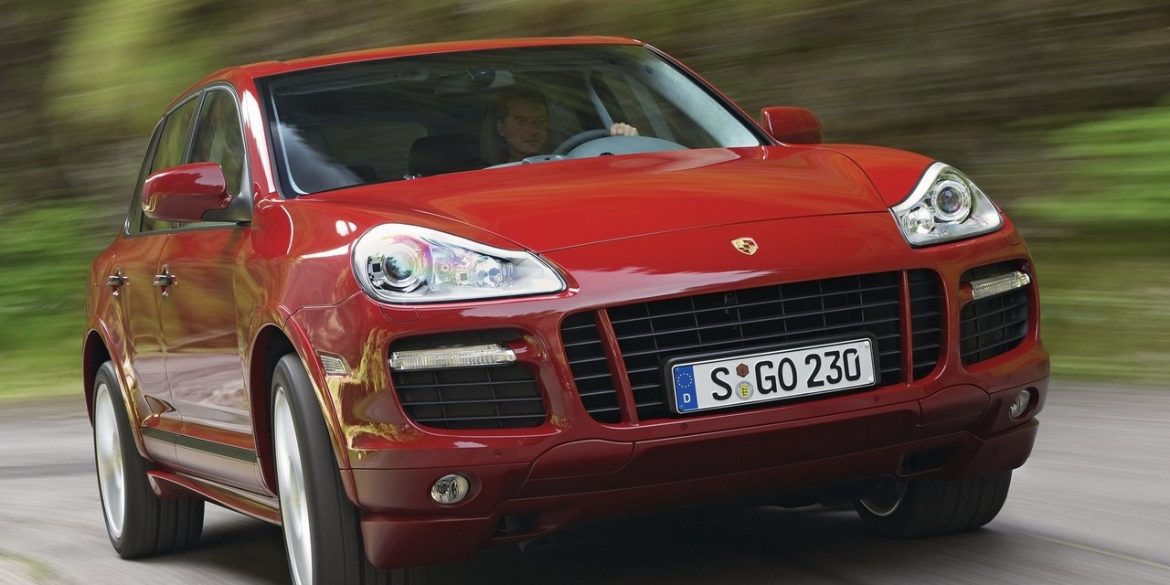
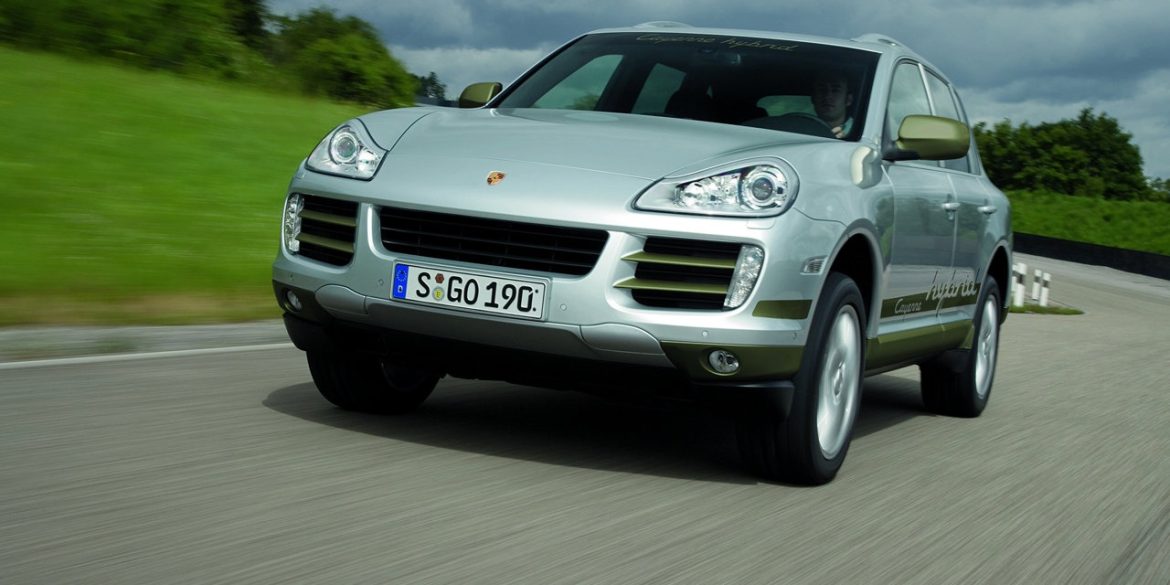
- Porsche Cayenne
- Porsche Cayenne 955/957 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman 987 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche RS Spyder (9R6)
- Porsche Boxster 986 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman 981 (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 356 Pre-A
- Porsche Boxster 987 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche Cayenne 958 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche 718 Cayman 982 (4th Gen)
- Porsche 356 A
- Porsche Boxster 981 (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 356 B
- Porsche 718 Boxster 982 (4th Gen)
- Porsche 356 C
- Porsche 968
- Porsche Panamera
- Porsche Panamera 970 (1st Gen)
- Porsche Panamera 971 (2nd Gen)
- Porsche Boxster
- Porsche Cayman
- Porsche Macan
- Porsche Taycan
- Porsche 912
- Porsche 919
- Porsche 956
- Porsche 2708 Indy
- Porsche Type 64
- Porsche 918 RSR Concept
- Porsche 918 Spyder
- Porsche 918 Concept
- Porsche 918 Spyder Prototype
- Porsche 917
- Porsche Race Cars
- 911 Carrera RS 2.7
- Porsche 550
- Porsche 718
- Porsche 901 (911)
- Porsche Concept Cars
- Porsche 904
- Porsche 906
- Porsche 907
- Porsche 908
- Porsche 910
- Porsche 911 (F-Series)
- Porsche 911 (991)
- Porsche 911 (G-Series)
- Porsche 911 (964)
- Porsche 911 (993)
- Porsche 911 GT1 Race
- Porsche 911 GT1 Street
- Porsche 911 (996)
- Porsche 911 (997)
- Porsche 916
- Porsche 919 Hybrid
- Porsche 934
- Porsche 934/5
- Porsche 935
- Porsche 936
- Porsche Mission E
- Porsche 928 S
- Porsche 928 S2
- Porsche 928 S4
- Porsche 928 GT
- 911 Speedster Concept
- Porsche 928 GTS
- Porsche 928 Specials
- Porsche 928 H50
- Porsche 928 CS/SE
- Porsche 935 Tribute
- Porsche 597
- Porsche 551
- Porsche Mission E Cross Turismo
- Porsche 911 (992)
- Porsche Concept 917
- Porsche Sport Tourer Electric
- Porsche Le Mans Living Legend
- Porsche 960 Turismo Concept
- Porsche 919 Street
- Porsche 904 Living Legend
- Porsche 906 Living Legend
- Porsche 911 Vision Safari Concept
- Porsche Bergspyder Concept
- Porsche 917 Living Legend
- Porsche Macan Vision Safari
- Porsche Vision 916
- Porsche Vision 918 RS
- Porsche Vision 920
- Porsche Vision E
- Porsche 917 16-Cylinder Prototype
- Porsche 959 Gruppe B
- Porsche Carrera GT Concept
- Porsche Tapiro Concept
- Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 Rallye
- Porsche Taycan 4S
- Porsche Taycan Turbo
- Porsche Taycan Turbo S
- Porsche Type 360
- Porsche 645 Spyder
- Porsche 550 Coupé (Prototype)
- Porsche 550 Spyder (Prototype)
- Porsche 550 Spyder
- Porsche 550 RS Spyder
- Porsche 550A RS Spyder
- Porsche 787 F1
- Porsche 804 F1
- Porsche 904 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904/6 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904/8 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 904 Bergspyder
- Porsche 906 Spyder
- Porsche 906 LH Coupé
- Porsche 965 (911)
- Porsche 906 E Carrera 6
- Porsche 942
- Porsche 906/8 Coupé
- Porsche 959 Prototype
- Porsche 906 Carrera 6
- Porsche 969
- Porsche 910 Bergspyder
- Porsche 989
- Porsche 910 Targa
- Porsche 909
- Porsche C88
- Porsche 718 RSK Spyder
- Porsche Panamericana
- Porsche 718 RS 60 Spyder
- Porsche 718 RS 61 Spyder
- Porsche 718 W-RS Spyder
- Porsche 718 GTR Coupe
- Porsche 718/2 F2
- Porsche 718 RS 61 LM Coupé
- Porsche 718 RSK Mittellenker
- Porsche 907 K
- Porsche 907 LH
- Porsche 908/01 LH Coupé
- Porsche 908/01 K Coupé
- Porsche 908/02 K Spyder
- Porsche 908 K Flunder Spyder
- Porsche 908 LH Flunder Spyder
- Porsche 908/03 Spyder
- Porsche 908/03 Spyder Turbo
- Porsche 919 Hybrid Evo
- Porsche 984
- Porsche LMP2000
- Porsche LMP1-98
- Porsche 917 LH-69
- Porsche 961
- Porsche WSC-95
- Porsche 917 K-69
- Porsche 917 ‘Interserie Spyder’
- Porsche 917 K-70
- Porsche 917 K-71
- Porsche 917 LH-70
- Porsche 917 LH-71
- Porsche 917/20
- Porsche 917/10-71
- Porsche 917/10-72
- Porsche 917/10 Turbo
- Porsche 917/20 Turbo
- Porsche 917/30
- Porsche 914/4 (1.7 L)
- Porsche 914/4 (2.0 L)
- Porsche 914/6 (2.0 L)
- Porsche 914 LE
- Porsche 914/4 (1.8 L)
- Porsche 914/8
- Porsche 914-6 GT
- Porsche 924 (Base)
- Porsche 924 Turbo
- Porsche 924 Carrera GT
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTR
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTS
- Porsche 924S
- Porsche 924 Rallye Turbo
- Porsche 924 Carrera GTP
- Porsche 924 SCCA
- Porsche 944 Coupe
- Porsche 944 S Coupe
- Porsche 944 S2 Coupe
- Porsche 944 S2 Cabriolet
- Porsche 944 Turbo Coupe
- Porsche 944 Turbo S Coupe
- Porsche 944 Turbo Cup
- Porsche 944 Turbo Cabriolet
- Porsche 944 GTP
- Porsche 944 Swiss Special
- Porsche 944 French Special
- Porsche 944 Celebration
- Porsche 944 S2SE
- Porsche 968 Coupe
- Porsche 968 Cabriolet
- Porsche 968 CS Coupe
- Porsche 968 Turbo S
- Porsche 968 Turbo RS
- Porsche 968 Sport
- Porsche 959 Rally
- Porsche 959 Komfort
- Porsche Cayenne 9YA/9YB/9YC (3rd Gen)
- Porsche 959 Sport
- Porsche Boxster (Base)
- Porsche Boxster S
- Porsche Boxster S Special Edition
- Porsche Boxster Spyder
- Porsche Boxster RS 60 Spyder
- Porsche Boxster GTS
- Porsche Boxster T
- Porsche Cayman (Base)
- Porsche Cayman S
- Porsche Cayman GTS
- Porsche Cayman GT4
- Porsche Cayman R
- Porsche Macan 95B (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayman S Black Edition
- Porsche Macan (Base)
- Porsche Cayman S Sport
- Porsche Macan S
- Porsche Cayman S Design Edition 1
- Porsche Macan GTS
- Porsche Cayman T
- Porsche Macan Turbo
- Porsche Cayman GT4 Clubsport
- Porsche Taycan (Base)
- Porsche 718 Boxster 25
- Porsche Taycan 4
- 964 Carrera
- Porsche Formula E
- 964 Carrera 4
- ’30 Jahre’ Anniversary
- 964 Speedster
- 964 Turbo
- 964 Carrera RS
- 964 Carrera Cup
- 964 RSR
- 993 Carrera
- Porsche Cayman GT4 RS
- 992 Edition 50
- 993 Carrera 4
- 993 Carrera 4S
- 911 2.0 Bertone Roadster
- Porsche Macan T
- 993 Carrera S
- Porsche Mission R Electric
- 992 Sport Classic
- 993 Targa
- Porsche Vision Gran Turismo
- 993 Turbo
- 993 Carrera RS
- 996 Carrera
- 992 America Edition 911
- 993 GT2
- 996 Carrera 4
- 993 Carrera Cup
- 996 Targa
- 996 Carrera 4S
- 996 Turbo
- Porsche 963
- 996 Turbo S
- Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 ePerformance
- 996 GT3
- 996 GT3 RS
- 996 GT2
- 996 GT3 Cup
- 996 GT3 R
- 996 GT3 RSR
- 996 GT3 RS Race
- 997 Carrera
- 997 Carrera S
- 997 Carrera 4
- 997 Carrera 4S
- 997 Targa
- 997 Targa 4S
- 911 Carrera 3.0 Coupe (G-Series)
- 997 Turbo
- 997 Turbo S
- 992 Carrera T
- 997 GT2
- 997 GT2 RS
- 997 Speedster
- 992 Dakar
- 997 Carrera GTS
- 997 Carrera 4 GTS
- 997 GT3 Cup
- 997 GT3 R
- 997 GT3 RSR
- 997 GT3
- 997 GT3 RS
- 991 Carrera
- 997 GT3 R Hybrid
- 991 Carrera 4
- 991 Carrera S
- 991 Carrera 4S
- Porsche 981
- 991 Targa 4
- Porsche Vision 357
- 991 Targa 4S
- 991 Turbo
- 991 Turbo S
- 991 Carrera GTS
- 991 Carrera 4 GTS
- 991 Targa 4 GTS
- 991 911 R
- 991 GT3
- 991 GT3 RS
- 991 GT2 RS
- 991 Speedster
- 991 GT3 R
- 991 GT3 Cup
- 991 RSR
- 991 Carrera T
- 992 Carrera
- 992 Carrera 4
- Porsche Type 540 America Roadster
- 992 Carrera S
- Porsche 718 Spyder RS
- 992 Carrera 4S
- 992 RSR
- 992 Targa 4
- 992 Targa 4S
- Porsche Mission X
- 992 Carrera GTS
- 992 Carrera 4 GTS
- 992 Targa 4 GTS
- 992 Turbo
- Porsche RS60 Spyder
- 992 GT3 R
- 992 Turbo S
- 992 GT3
- 992 911 S/T
- 992 GT3 Touring
- 992 GT3 RS
- 911 (G-Series)
- 992 GT2 RS
- 992 GT3 Cup
- 911 Carrera 3.0 (G-Series)
- Porsche Taycan GTS
- Porsche 356 SC
- 911 S (G-Series)
- 992 GT3 R Rennsport
- 911 Carrera RSR 2.8
- 911 SC (G-Series)
- 911 S/T
- 911 (Base Model)
- 911 Carrera 3.2 (G-Series)
- 911 L
- 911 SC Safari
- 911 Turbo (930)
- 911 T
- 911 Carrera RSR Turbo 2.1
- 911 E
- 911 Carrera RSR 3.0
- 911 S
- 911 SC San Remo
- Porsche 356
- Pre-A Speedster
- 911 R
- 911 Carrera 3.2 Clubsport
- Porsche 953
- 911 T/R
- 911 Carrera 25th Anniversary
- 911 Carrera RS 3.0
- 911 SC RS
- 911 Turbo LE
- Beutler Coupe
- 911 3.2 Speedster
- 911 Carrera 2.7 (G-Series)
- 911 Carrera Commemorative
- 911 Turbo 2.7
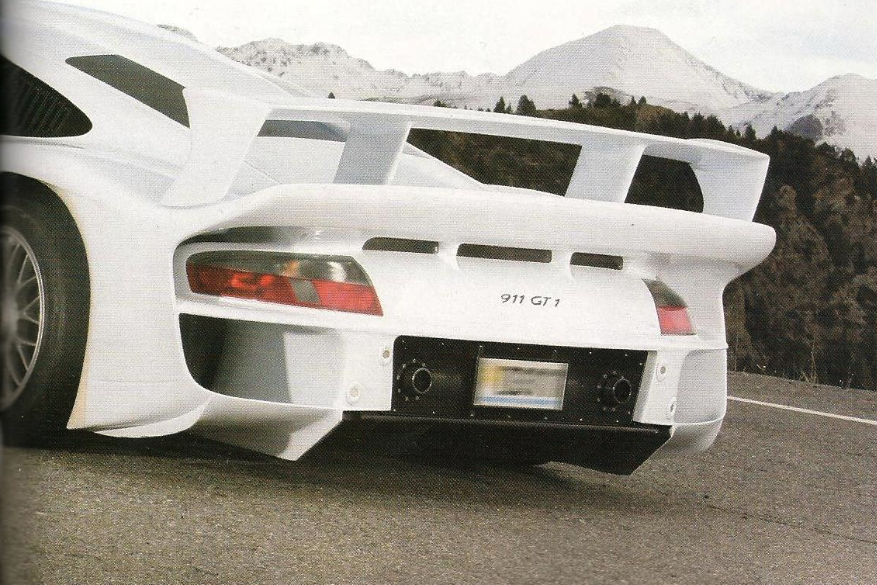
- Porsche 911 GT1
- Porsche 99X Electric
- 964 Turbo S
- Porsche Taycan Turbo GT
- Porsche Panamera 976 (3rd gen)
- Porsche Macan Electric (2nd Gen)
- Porsche 954
- Porsche Taycan Y1A/Y1B (1st Gen)
- Porsche Cayenne (4th Gen)
- Porsche Macan Turbo Electric
- Porsche Macan 4S Electric
- Porsche Macan 4 Electric
- Lohner-Porsche
- Porsche Macan Electric (Base)
- Porsche Taycan 9J1 (1st Gen)
- 992 “Turbo 50”
- Porsche Macan GTS Electric
- Porsche Type 940
- 992 Transfăgărășan Tribute
- Porsche 963 RSP
- 992 Carrera T Club Coupe
- 997 Sport Classic
- 992 GT3 90 F. A. Porsche
- Porsche Type 542
- Porsche Type 166
- Vision Renndienst Concept
- 991 50th Anniversary
- 997 Black Edition
- Porsche Cayenne Electric
- 993 Turbo S
- 992 Spirit 70
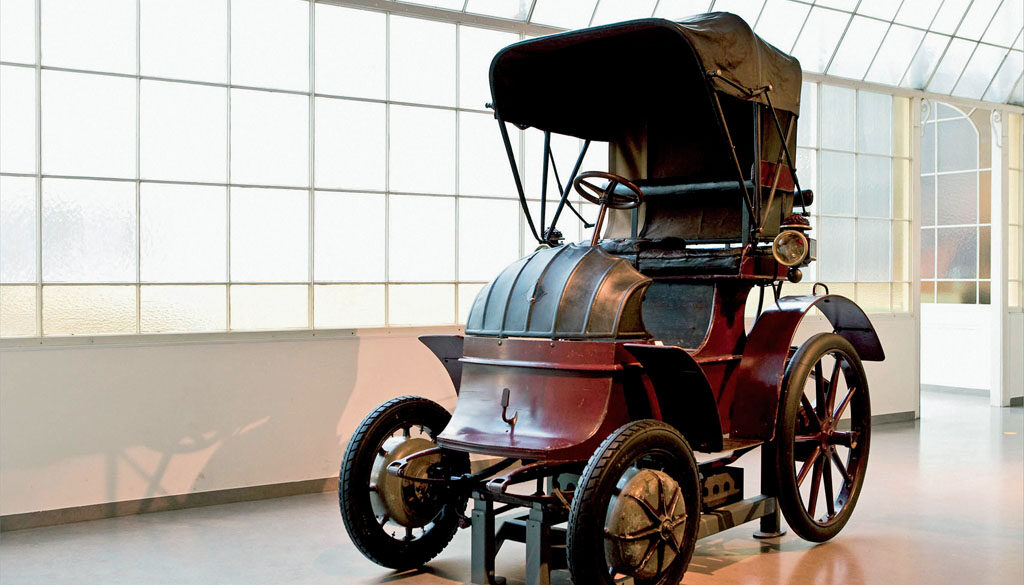
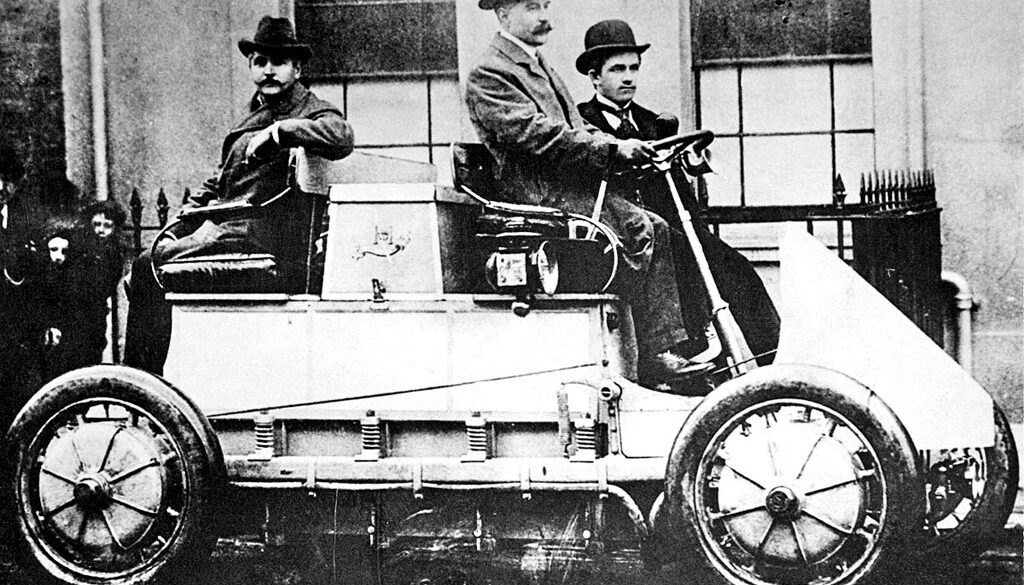
1900 Lohner-Porsche Hybrid With its future-oriented electric motors in the wheel hubs, the Lohner-Porsche was acknowledged as the absolute sensation at the Paris World Fair in 1900. On loan from the Technical Museum in Vienna, Austria, this outstanding achievement in technology protected today as a universal monument will be seen...
1901 Lohner-Porsche Phaeton Ferdinand Porsche landed his first technical job working for Jacob Lohner in 1900. Thier first car, the System Lohner-Porsche, used wheel mounted electric motors. Later cars used Daimler derived motors to power the electric engines. These systems were very elegant solutions as they did not use drive...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
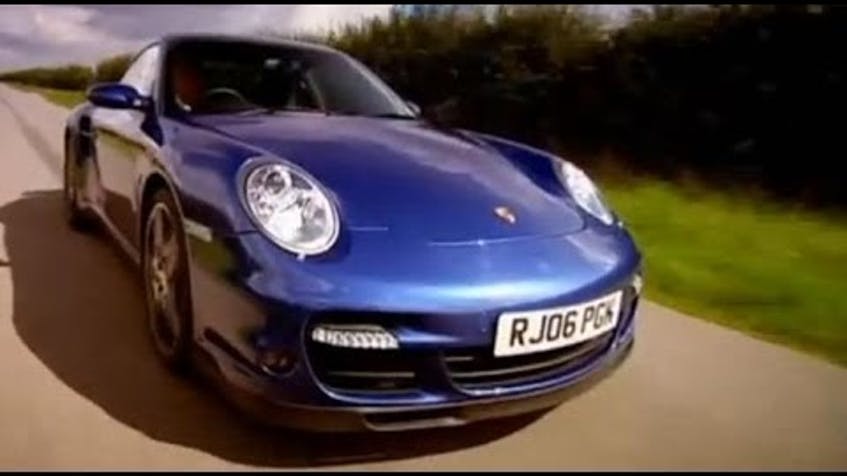
Jeremy Clarkson – Ferrari F430 vs Porsche 911 Turbo It may be hard to believe, but Jeremy finally changes his opinion about the benefits of the new Porsche 911 over his favourite brand Ferrari....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
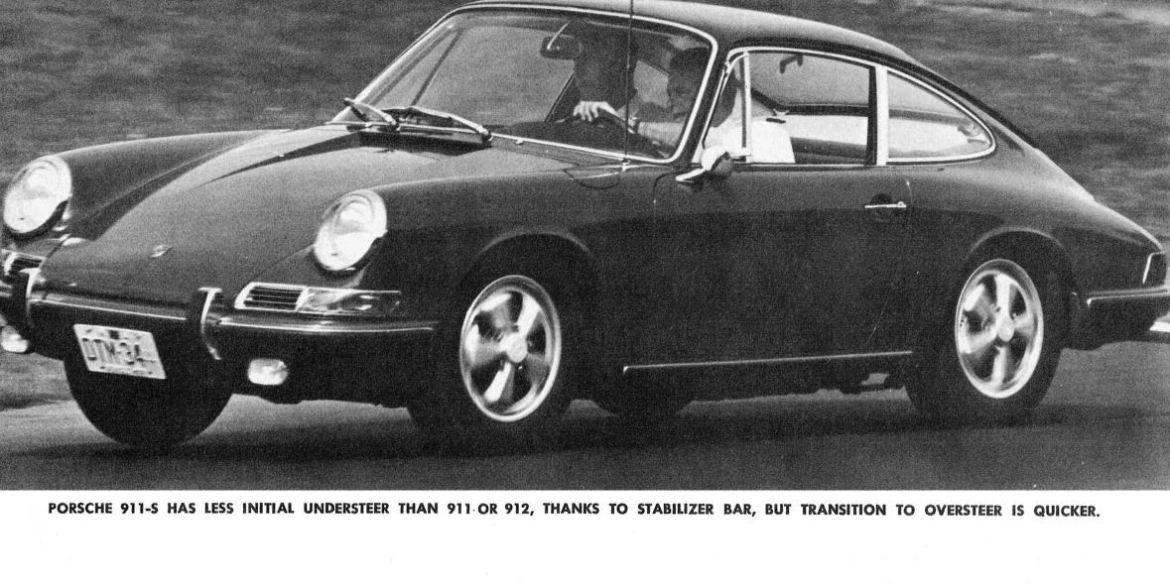
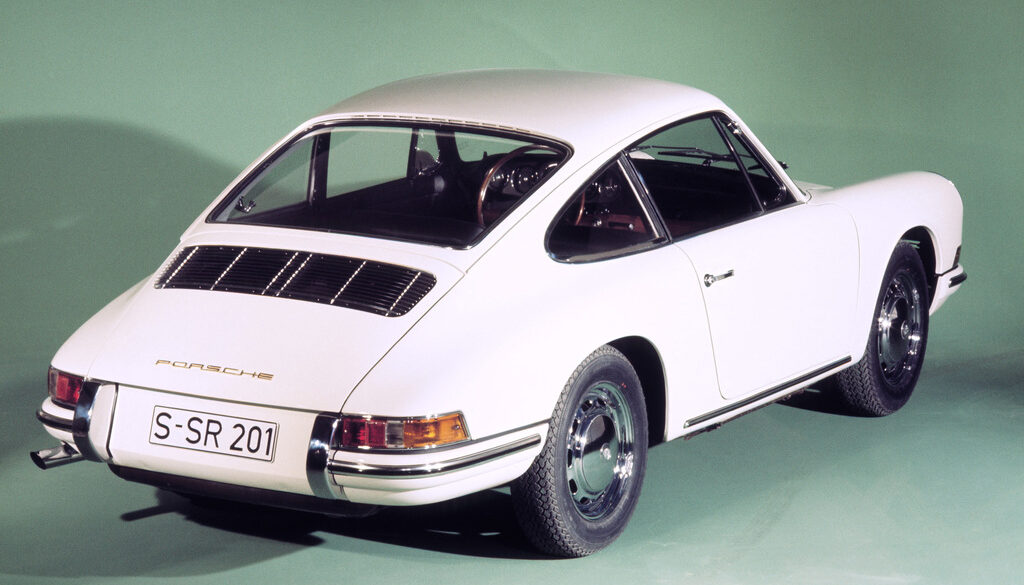
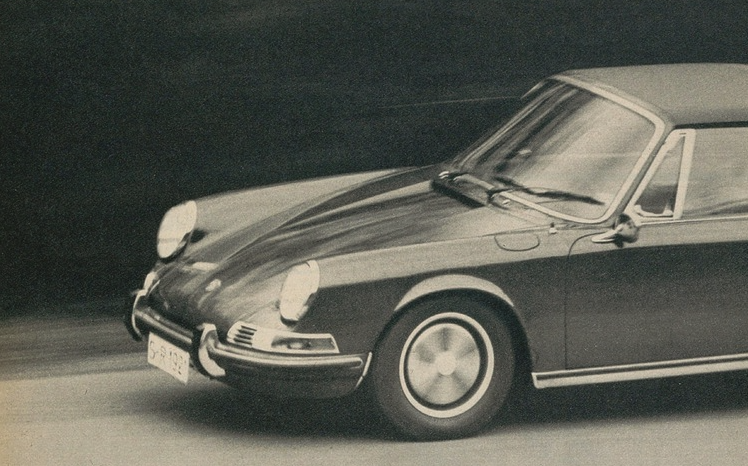
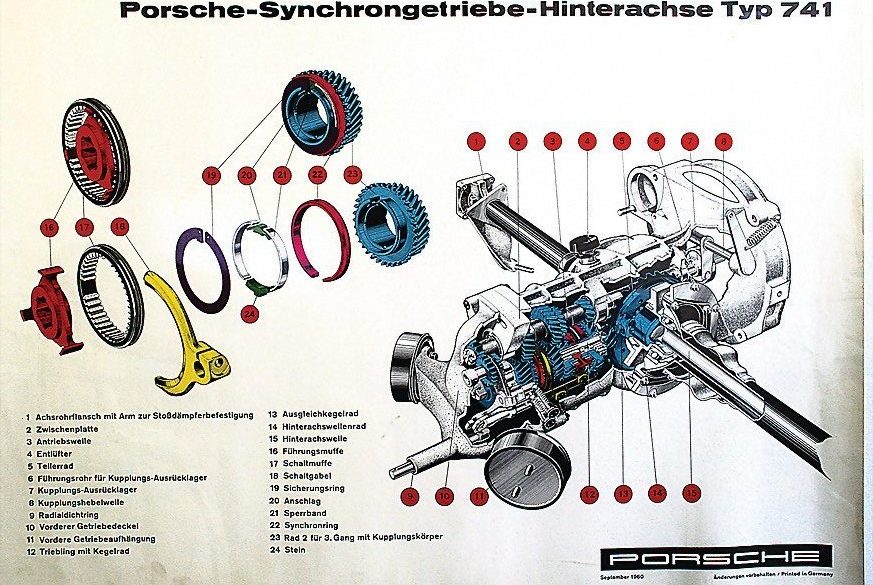
In 1963 Porsche introduced their seminal 901 at the 911 at the Frankfurt Motor Show which would be renamed 911 for the 1964 model year. The new car was sold alongside the 356C as an alternative with more power and room for a rear seat. At the 1963 Frankfurt show the public saw Porsches new direction. Compared to the 356 it had a longer wheelbase, a more compact suspension setup and much more power from the flat-6 engine.
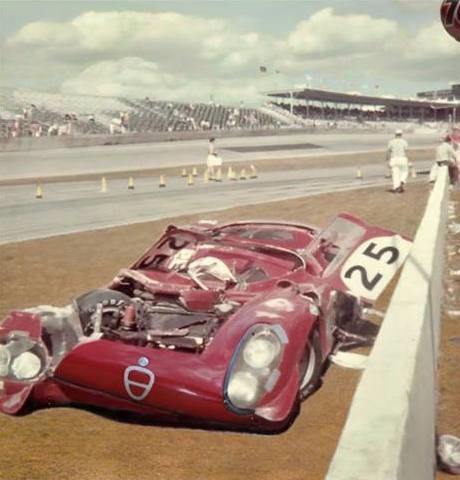
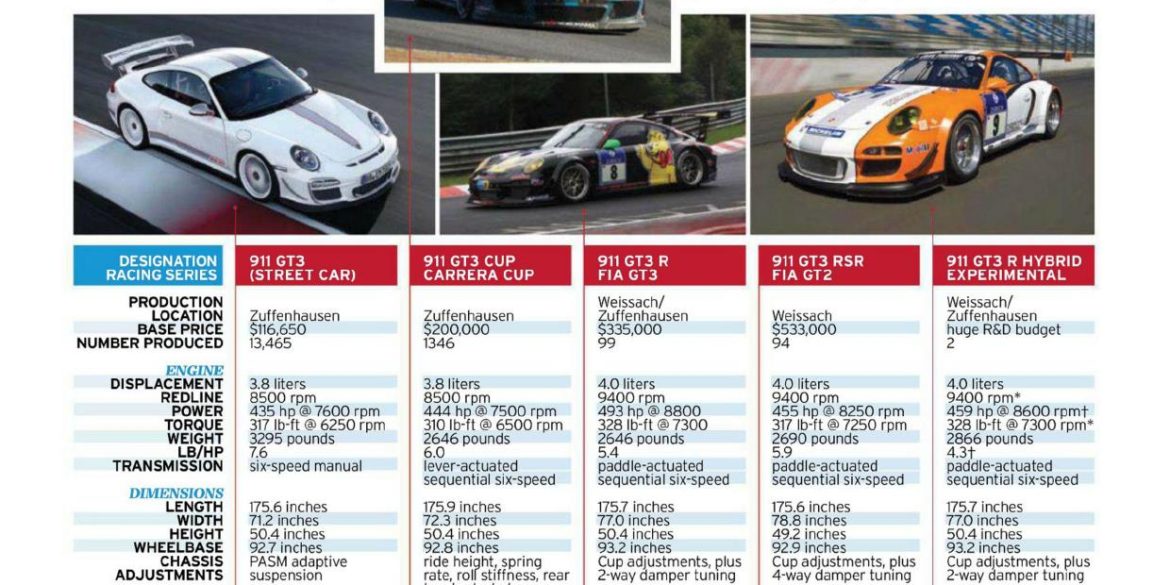
Porsche 917 Turns 40 Porsche launched the 917 40 years ago and it’s still their most important racecar to date. This dangerous, yet successful machine gave Porsche victory at Le Mans and all the other international races of its time. Porsche started their long 917 race program in 1969 with a...
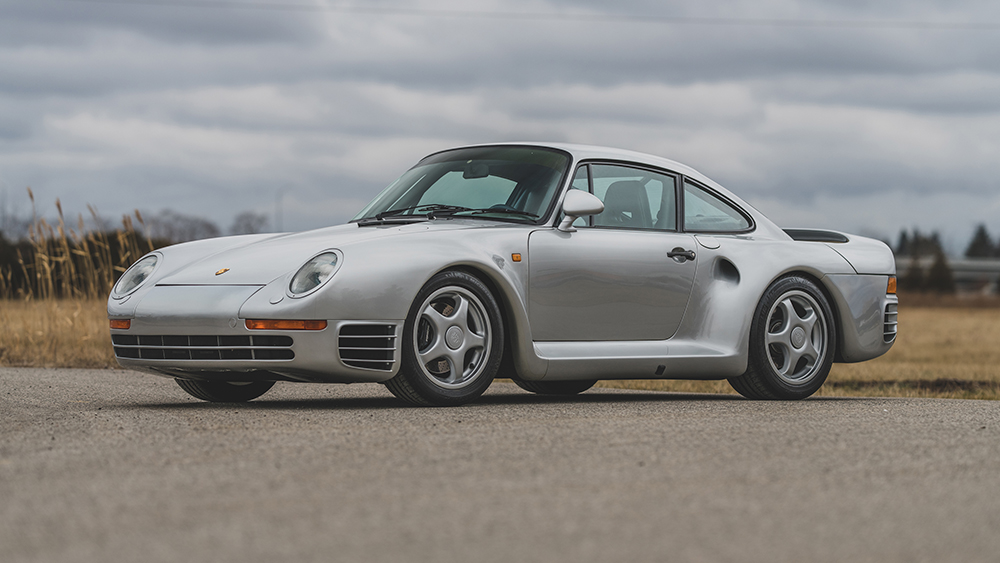
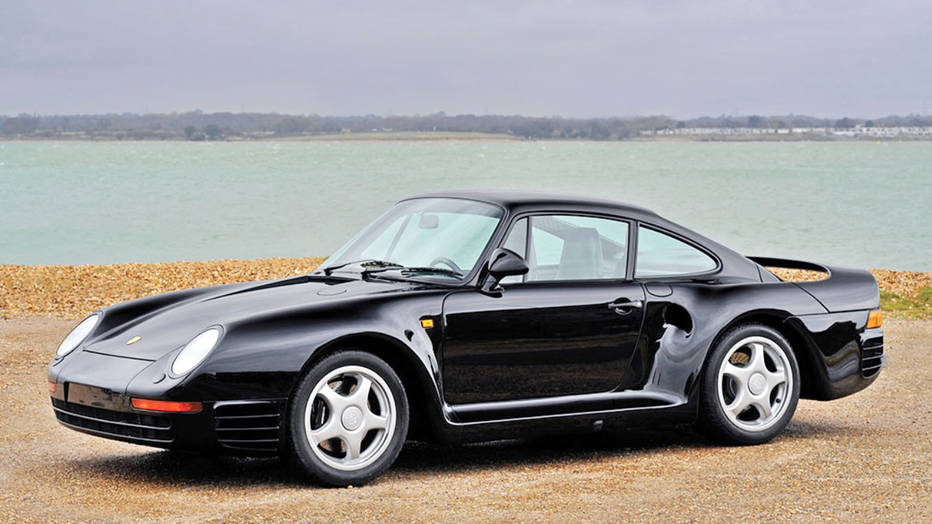
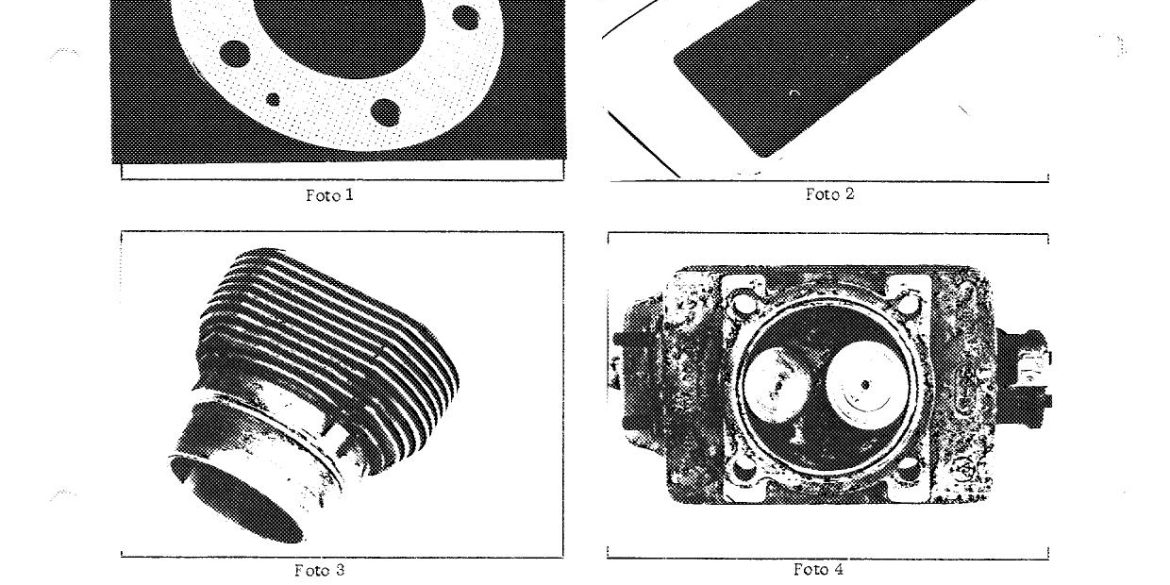
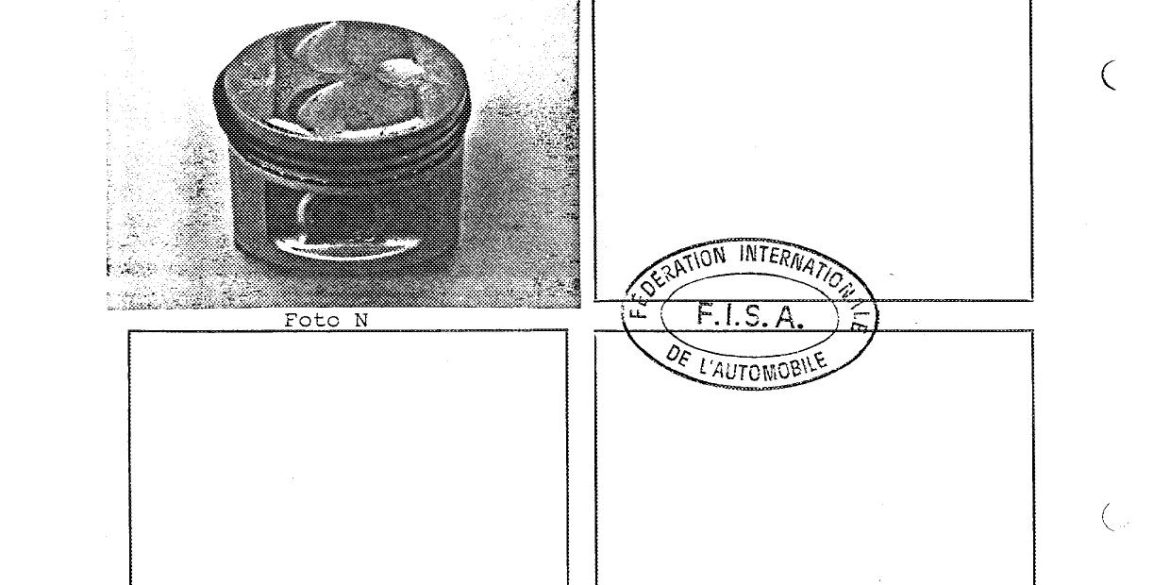
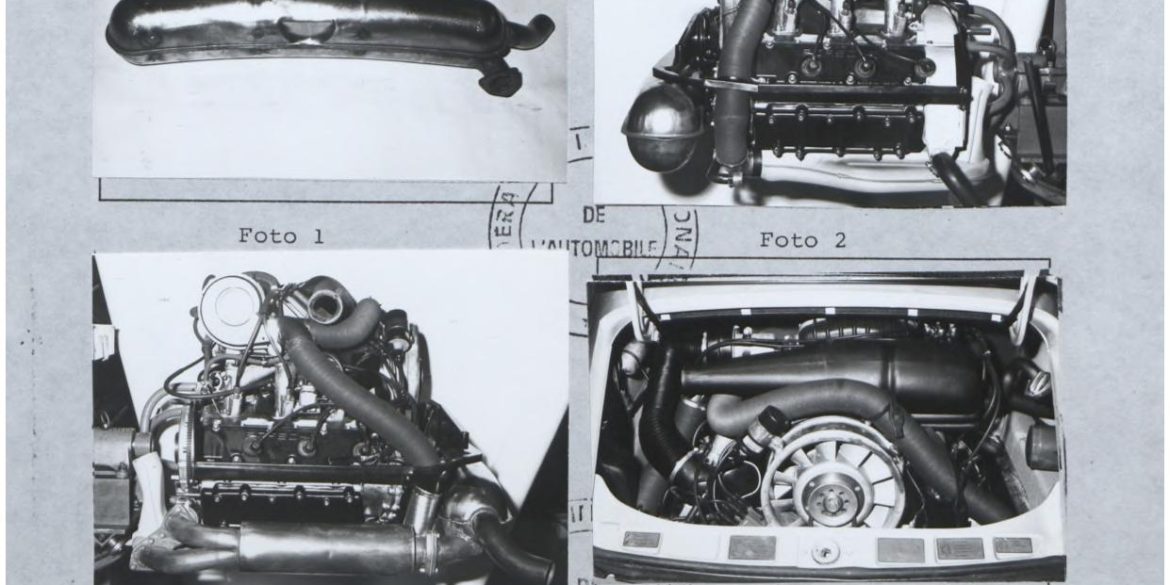
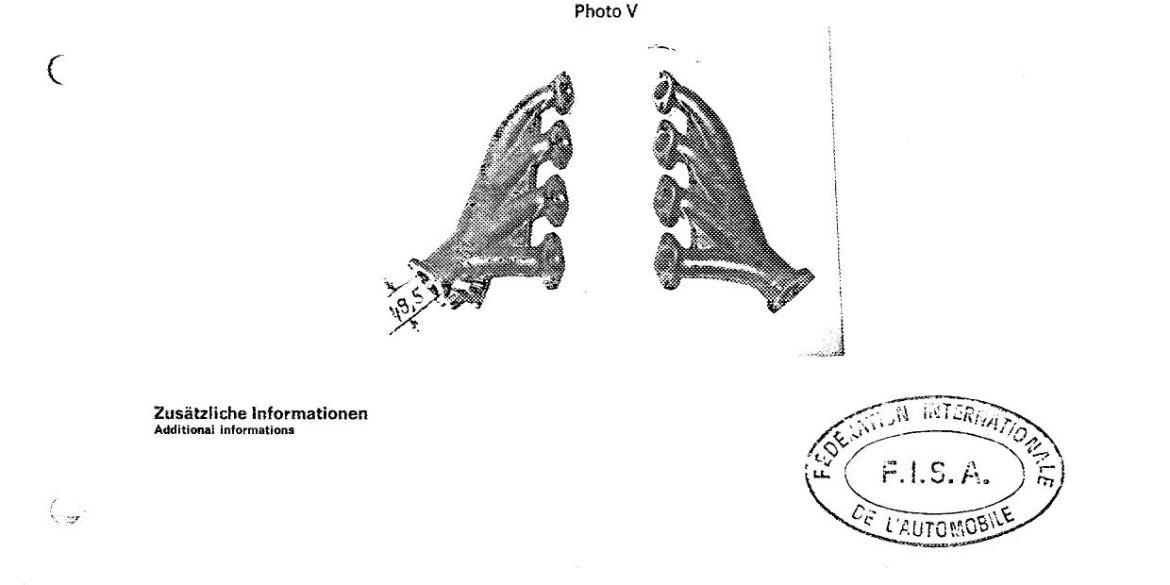
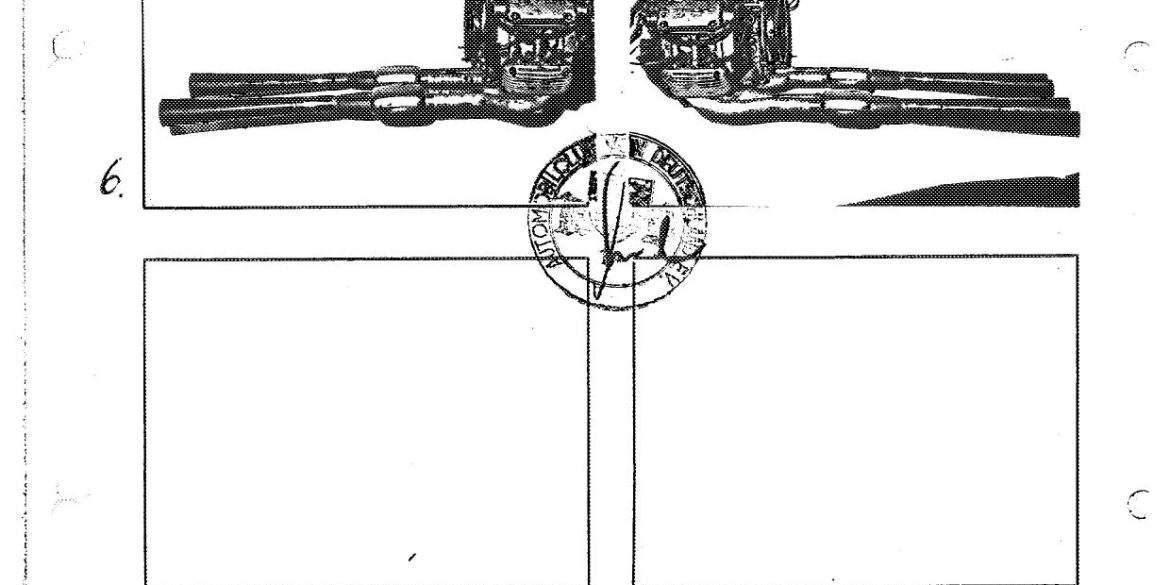
Porsche Option Codes – Porsche 959 Looking to decode your Porsche 959 option codes? Want to know what those codes are in your Porsche 959 service manual? Then this is the post for you. We painstakingly researched all the Porsche option and equipment codes. The Porsche options list is really...
Porsche 959 Spare Parts Catalogs (1987 – 1988 Model Year) These official Porsche PET Diagrams and codes for the 1987 to 1988 Porsche 959 models are free for your to download and view. Whether you’re working on your own Porsche 959 and need the total parts guide or are trying...
Porsche 959 Sales Brochure This is the original 1988 sales brochure for the 959. The 959 was produced in 1988 as a homologation for Rally racing. Tech specs included AWD, 2.6L twin-turbo engine producing 450 hp, and traction setting for dry/wet/snow. 0-60 mph 3.7 secs, top speed 197 mph. Only...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....