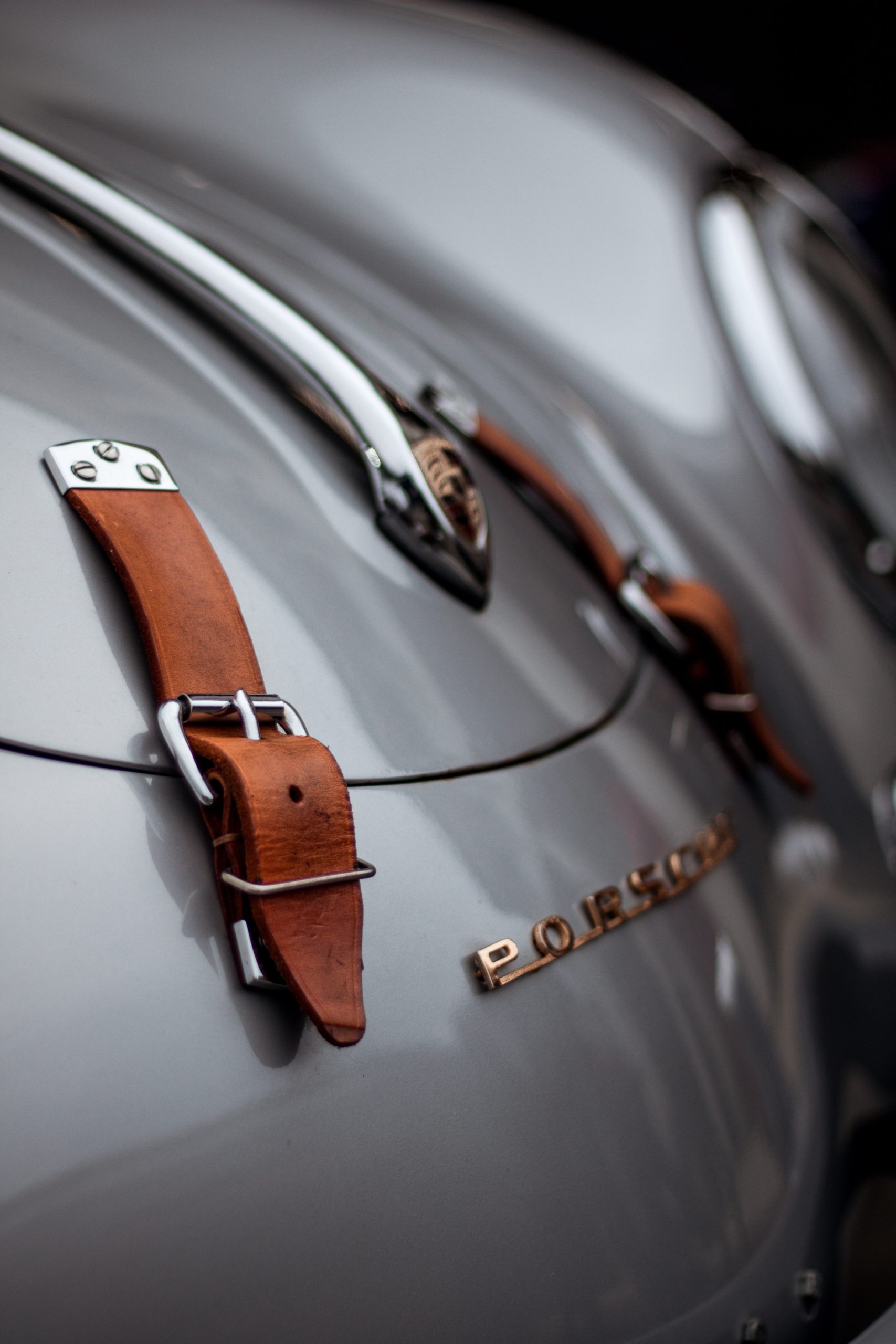
The 993 Carrera 4, sold between 1995 and 1998, uses the same powerplant as the standard 993 Carrera, but puts power down to all four wheels through a 6-speed manual transmission. A “Carrera 4” badge on the tail, along with silver-painted brake calipers and clear front and side turn signals, help distinguish the all-wheel drive C4 from the C2 sibling. Approximately 4,700 coupes and 2,500 cabriolets were made. It was replaced by the Porsche 911 Carrera 4 (996 generation) in 1999.
176 results for
911 research hub
Introduced in 1994 the Porsche 911 Cabriolet was more of a Grand Tourismo vehicle than a sports car. The 911 Cabrio featured the same cues as its coupe version, but with a few differences apart from the lack of a fixed roof, of course. The 3.6-liter engine was offered in two versions, with 275 hp and 285 hp. The latter featured the VarioCam system. Both versions were mated to either a 6-speed manual or a 4-speed automatic.
Introduced in late 1994 the standard 911 Carrera of the 993 generation was fitted with a development of the M64 3.6-liter flat six that had been found in the prior 964 generation. With a redesigned exhaust system and new hydraulic lifters, the engine produced 272 horsepower. For the 1996 model year, a Targa variant was introduced, and a variable intake runner system (called VarioRam) was added to the entire Carrera lineup, bumping horsepower to 285. Approximately 23,000 coupes were built, 15,500 cabriolets, and 4,500 Targa's, in both manual and automatic (Tiptronic) transmission. Overlapping with the last year of production, it was replaced by the 911 Carrera of the 996 generation for model year 1998.
The flat six in the Carrera 996 was a newly-developed flat-six engine that offered 300 hp. It was mated as standard with a six-speed manual. A 5-speed automatic (Tiptronic) with manual override to shift gears was on the options list. As always, the Carrera 2 was rear-wheel-drive. Designed as a grand tourer, the Porsche Carrera Cabriolet was the base version for the open-top 911 range in 1998. The retractable roof was able to be stowed away in 20 seconds at speeds of up to 50 kph (31 mph), like the rest of the 911 convertible range. With the roof up, the car was tested in the wind tunnel at speeds of up to 338 kph (210 mph).
The 996 series was a monumental update to the 911 story. The Type 996 introduced water-cooled engines and it also ushered in a new body design. The roof line with a windscreen which is around five degrees flatter gives the side view a more fluid look. Gone was the "classic" 911 design, the entire main body now much sleeker. The flat six in the Carrera 996 was a newly-developed flat-six engine that offered 300 hp. It was mated as standard with a six-speed manual. A 5-speed automatic (Tiptronic) with manual override to shift gears was on the options list. As always, the Carrera 2 was rear-wheel-drive.
In spite of its 911 moniker, the car actually had very little in common with the 911 of the time, only sharing the front and rear headlamps with the production sports car. Designed and developed to compete in the GT1 class of sportscar racing, which also required a street-legal version for homologation purposes. It was powered by a twin-turbo flat 6 that was good for 600 bhp. The 1996 911 GT1 clocked at a top speed of exactly 330 km/h (205 mph) on the legendary Mulsanne Straight.
For the 1974 racing season 911 Carrera RSR 3.0 (246 kW) and RSR Turbo 2.1 (338+ kW) were created - the 3.0L for the customer teams and the 2.1 turbo for Porsche’s own team. The Carrera RSR 3.0 was made in small numbers for racing. The 3.0 RSR would go on to become the most successful Group 4 racing car of its time thanks to its combination of low weight, immense Porsche 917 brakes, impeccable handling, and a 330+hp naturally aspirated flat-6.
Introduced in 1973, the RSR was a factory-built racing car based on the 911 chassis. The Porsche 911 Carrera RSR 2.8 was the first 911 to ever wear the RSR badge. Homologated for racing by the iconic 1973 Porsche 911 Carrera RS, the RSR’s racing career got off to the perfect start thanks to Brumos Racing’s overall triumph in the 1973 24 Hours of Daytona, while a factory car won the latest ever Targa Florio road race. For the privateer in the mid-1970s who wanted to go sports car racing this was the chosen weapon.
Porsche, for lack of a better term, is on a roll. They are one of the few companies that make...
A rare gem has surfaced on Bring A Trailer – a 1994 RUF RCT, possibly the only one ever built...
While many have modified the 911 over time, Gunther Werks stands apart, envisioning a scenario where Porsche continued refining the...
Before the Porsche Taycan was released, if you wanted a fast EV, you weren’t exactly spoiled for choice. When 2019...
The 981 Cayman, introduced in 2013, marked a significant leap forward in Porsche’s lineage of sports cars, drawing ever closer...
At the start of 2023, after a few years of teasing and testing, the Porsche Type 963 LMDh Hypercar was...
By the time the mid-1960s arrived, Ferdinand Piëch had got his hooks well and truly into Porsche’s motorsport programme. With...
Setting the Scene The 1960s represented for Porsche, the busiest decade in the company’s history to date, with ten new...
The 964 generation has become highly popular, primarily due to its iconic styling and air-cooled design. Among the 964 models,...
Kalmar Automotive, enhancer and restorer of bespoke sports cars and special purpose-built adventure vehicles, has revealed its first water-cooled ‘Adventure...
“To hell with the timing. This is more important,” Wilfried Reinhardt says to himself. He hesitates for just a moment,...
While originating from the East Coast, 5001 Workshop founder Marlon Goldberg gravitates towards building Porsches for their experience, not their...
22,093 feet above sea level– no car has ever gone higher. On December 2, 2023, racing driver Romain Dumas set...
The Porsche 718 Cayman GT4 RS has been designed for maximum driving pleasure. It stands as the pinnacle of the 718 Cayman...
The Porsche GT3 RS from the 992-generation is an exceptional performance car that focuses on track driving. It is Porsche’s...
Porsches have consistently attracted tuners and racing teams aiming to enhance the performance of already formidable sports cars. The 356...
TECHART has unveiled a head-turning new lightweight rear spoiler for the Porsche 911 Carrera Coupe models and the GT3 Touring....
One of the limited run of 25 Porsche 911 models configured to the 400R standard by Gunther Werks is currently...
After debuting in its famed role in “Transformers: Rise of the Beasts”, the Autobot Mirage and the movie car, a...
One of the most colorful episodes in the history of Porsche was their 13th Le Mans victory in 1994 with...
The GT4 RS stands as the pinnacle of the 718 Cayman lineup, delivering a raw, loud, and brutally powerful driving...
A remarkable and low mileage example of a Porsche 911 GT2 RS Clubsport, number 98 out of a limited production...
The third example commissioned at Rauh-Welt Begriff Los Angeles, “JennaBelle,” was individually crafted according to custom specifications by RWB’s founder,...
In this video from AutoTopNL, we get to see and hear a RUF SCR 4.0 being pushed to its limits...
Edit Automotive has unveiled its vision of the Porsche 911 named the g11, an intricately crafted sports car predicated on...
Singer Vehicle Design has emerged as arguably the foremost name in the realm of customizing Porsche 911s to date. Their...
The Iconic Autobody 386 Speedster Homage pays a handsome tribute to the legendary Porsche 356 Speedster, built on the well-regarded...
The Porsche 911, the undisputed king of sports car evolution, has continued to be transformed since its 1963 debut. One...
The “Carbon Noire Commission” is a remastered version of the 911s based on the 933-generation by Gunther Werks. The car’s...
Porsche honored As the honored marque of this year’s Festival of Speed the sportscar manufacturer showed off with different actions....
Featured here is a 1995 Porsche 993 that has undergone the highly coveted RWB (Rauh-Welt Begriff) conversion package, resulting in...
Porsche Vision 357 Goodwood debut Celebrating three decades of the renowned Goodwood Festival of Speed, Porsche presents the Porsche Vision...
Porsche records a significant increase in sales Just announced by Porsche, the first six months of 2023 ended successfully with...
Commissioned for ‘Mr. Le Mans’ Tom Kristensen, the Kalmar 7-97 is an homage to the Danish driver’s inaugural Le Mans...
The Glasgow Commission, reimagined by Singer, is based on a right-hand drive 964 Targa. The car showcases carbon fiber bodywork...
It only happens once in a lifetime; your 75th birthday. This June 8th marks Porsche’s 75th anniversary so Bring-a-Trailer auction...
Live now on PCARMARKET is a Canadian-market 1992 Porsche 964 Carrera 2 Coupe that was commissioned as a one-of-a-kind backdate...
Akira Nakai, the renowned customizer behind RWB (Rauh-Welt Begriff) Porsches, is responsible for creating some of the world’s most iconic...
Around a year ago, we wrote an article about the future of Porsche powertrains, covering full electric, hybrid, and sustainable...
Gunther Werks’ latest creation, Project Tornado, is a road-legal coupe that follows the company’s tradition of building models around the...
If there is one thing that can be said about those who are enthusiastic about, or even own, a car...
Gunther Werks Dunkelgrun Commission – one of 25 remastered 993-generation 911s the custom shop will build. Photos by Gunther Werks...
Porsche, as we all know, is a name that is synonymous with clean, simple lines that highlight the peak of...
Let’s talk about Porsche GT cars—the modern production cars in particular. On the 911 spectrum, this would encompass any of...
The folks at AutoTopNL managed to get their hands on a beautiful Porsche 964 Targa restomod built by Speed Service,...
Overview The GT3s are the low volume 911s, road-going production cars homologated for what was Group 3 competition. The original...
Quarter mile drag race between the air-cooled Porsche 964 RS versus a 911 Turbo from the 997-generation....
The Gunther Werks 400R is a modern version of Porsche’s last air-cooled 911 and is the first car from the...
By Rex McAfee Best of the Best: Weathertech Raceway, Laguna Seca, CA. Returning to the iconic Monterey Peninsula, the 2022...
If there is one thing the Germans do better than almost anyone else in the world, it’s having a knack...
Let’s face it, the Porsche 914 was not the most iconic of sports cars in the storied history of the...
If there is one thing that Porsche does better than pretty much any other car manufacturer, that is providing their...
Episode One: The Porsche 356 Summary Welcome to The Audiobahn, the Stuttcars.com podcast focused on all things Porsche. In our first...
Some pretty interesting Porsches are currently being offered at Bring A Trailer at No Reserve: a 1964 Porsche 356C Coupe,...
The premise was disarmingly simple: a race bringing together the best drivers in motorsport, all competing in identical cars, in...
We stumbled on this pretty cool video of a Porsche 964 transformation and loved it. It is a sped up...
Porsche 924 / 928 / 944 / 968 The Ultimate Model Guide to Porsche’s Transaxle Models The Research Hubs / 924 Model...
In 2004, the Boxster S Special Edition, also called 550 Spyder Boxster S Special Edition was introduced with a production run of just 1,953 cars (paying homage to the 550 Spyder's year of introduction). 500 cars were made for the US Market. These were all painted in GT Silver Metallic, the same colour as the Carrera GT concept presented in 2000, and had unique cocoa-brown full-leather interior as standard with grey natural leather as a no-cost option.
Porsche Cayman (987) The Ultimate Model Guide 2nd Generation Porsche Cayman (2007 – 2012) The Story / Timeline / Model Guides / Performance & Specs / Data &...
Porsche Boxster (987) The Ultimate Model Guide 2nd Generation Porsche Boxster (2005 – 2012) The Story / Timeline / Model Guides / Performance & Specs / Data &...
Porsche 924 History & Story The Porsche 924 emerged as the result of a Volkswagen engineering order which did not...
Porsche 914 History & Story Porsche needed an entry-level car to replace the 912 and Volkswagen needed a sports car...
The Story of The Porsche Crest As Germany underwent a revolution in 1918, a German state of Kingdom of Württemberg...
ACO Museum, Le Mans 16 September 2020: As it was the 50th anniversary of Porsche’s first win at Le Mans,...
The All Time Greats – 70 Best Porsches of All Time (Ultimate List) Clearly we have been a bit of...
Searching for more muscle? The 718 Cayman S got a new 2.5L turbocharged boxer 4-cylinder. Power comes in at 345 bhp @ 6500 rpm and torque is a really strong 310 ft lbs @ 1900 rpm. For reference, the outgoing 981 Cayman S had 311 bhp and 265 ft lbs of torque. While we hate the drone of the turbo four cylinder, there is absolutely no doubt that is much more powerful and that performance numbers are much stronger. 0 – 60 mph is over in just 4.0 seconds and the quarter mile is finished in 11.9 seconds flat. Much faster than the outgoing model. But is it as engaging? No.
With the 982-generation Boxster/Cayman platform, Porsche went back in time to pull out the 718 name, a reminder that the sports car maker has been doing the small sports car thing for a long time. The 718 of course, is diminutive race car that won the Targa Florio race in 1959 and 1960. The marketing stunt was meant to evoke these past Porsche racing successes with light cars like the 718 that outmaneuvered competitors with larger and more powerful engines. The reason? Porsche got rid of the naturally aspirated flat-6 engines and instead would now have flat-4 turbocharged engines.
The Porsche 914 was first shown at the 1969 Frankfurt Auto Show was, as intended, a true conglomeration. The front suspension was largely derived from the 911 with some VW components, and the interior was a blend of both companies' parts bins. The initial engine offering was Volkswagen's 80-hp fuel-injected 1.7 liter flat four, while the 914/6 had a twin-carburetor 2.0-liter Porsche flat six tuned for 125 hp.
No More Content