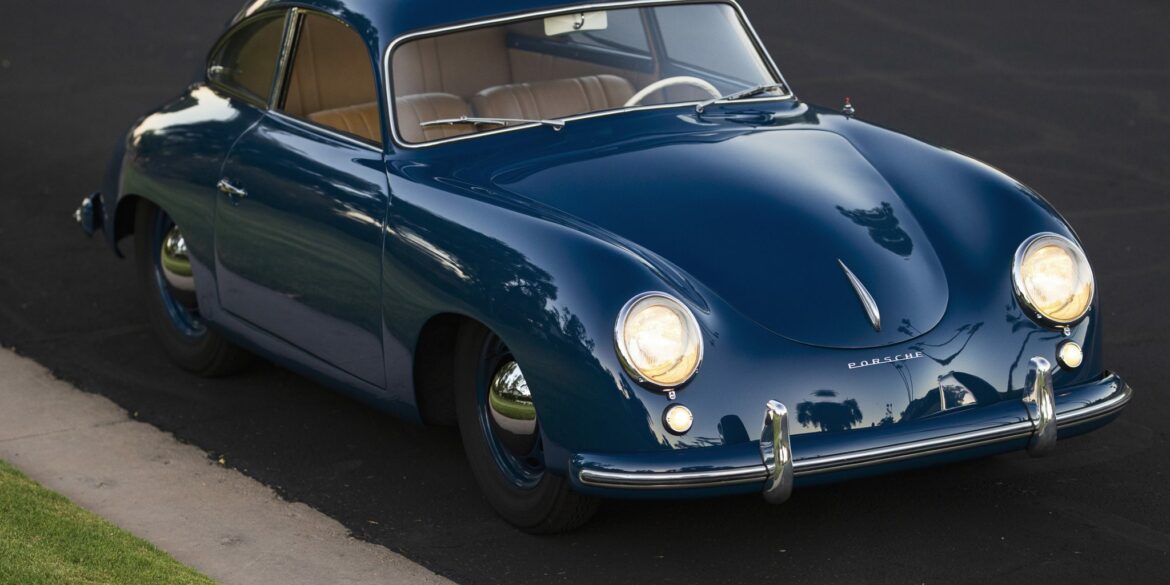
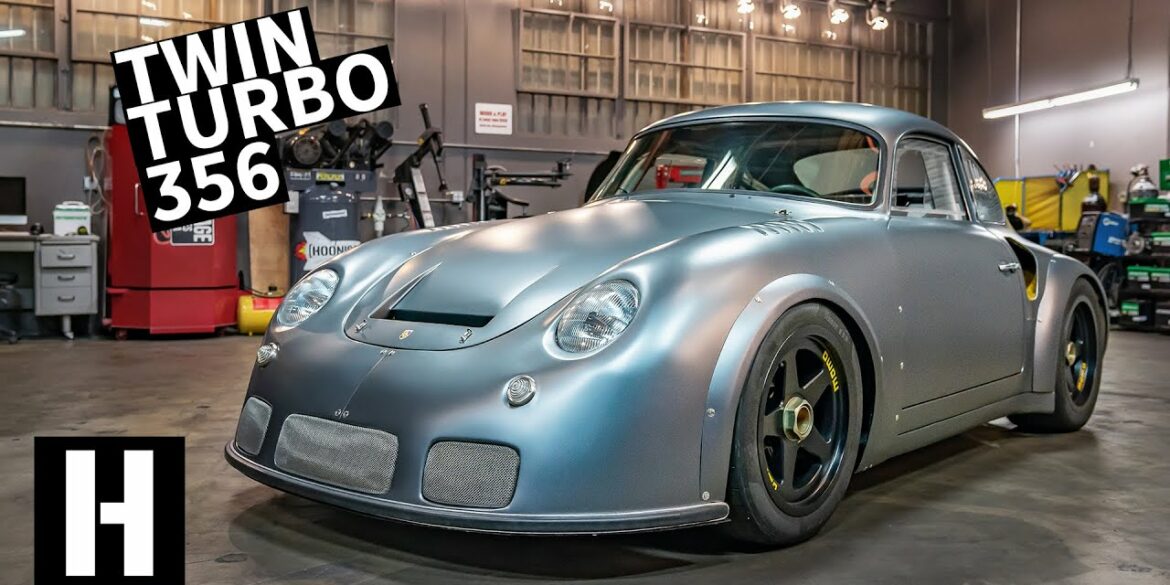
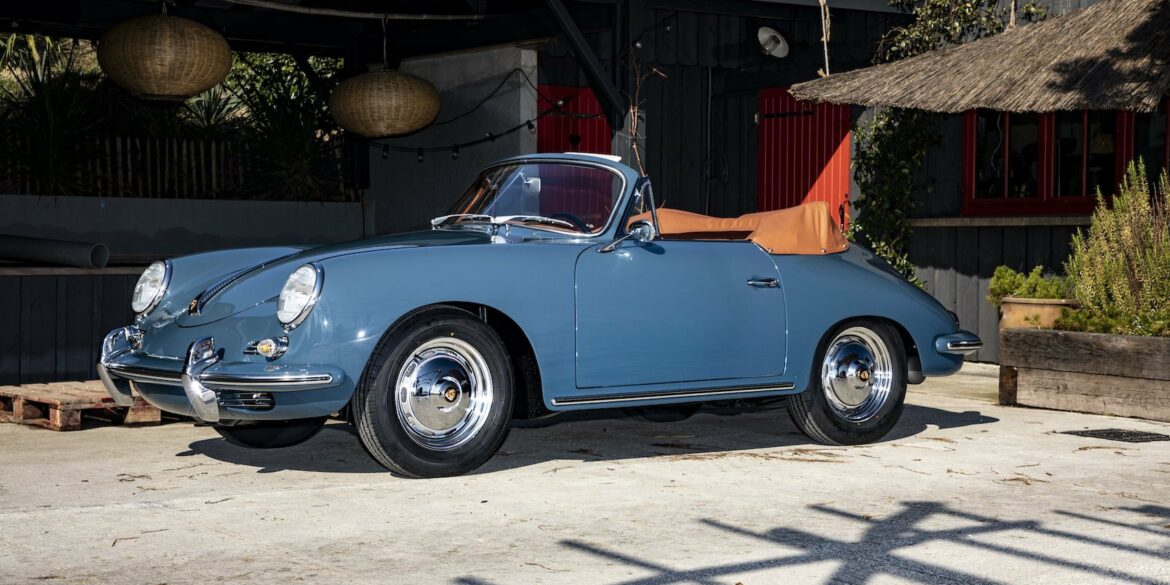
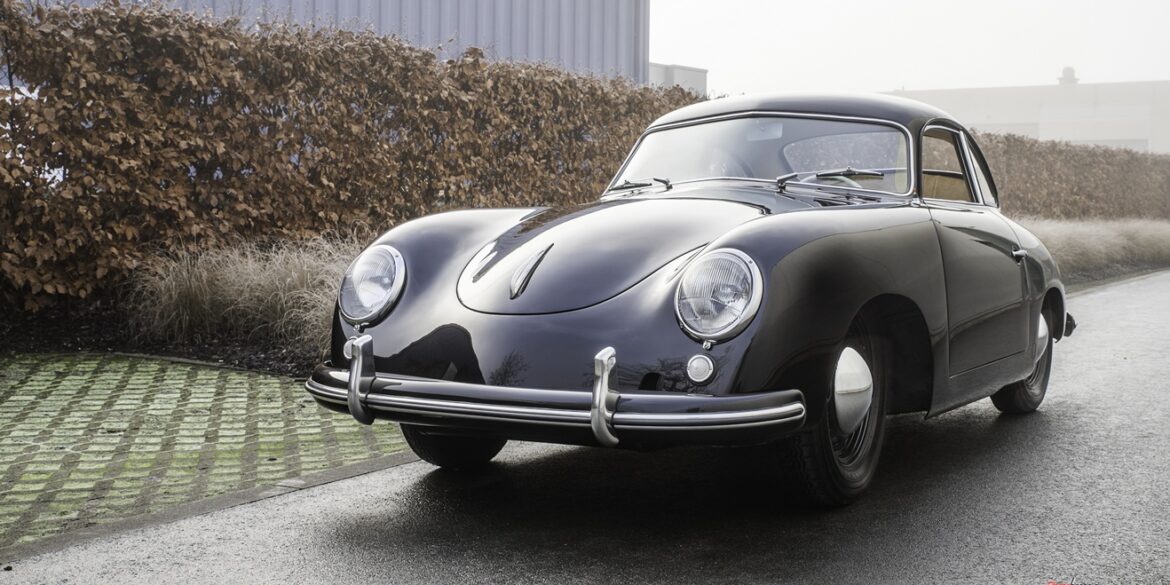
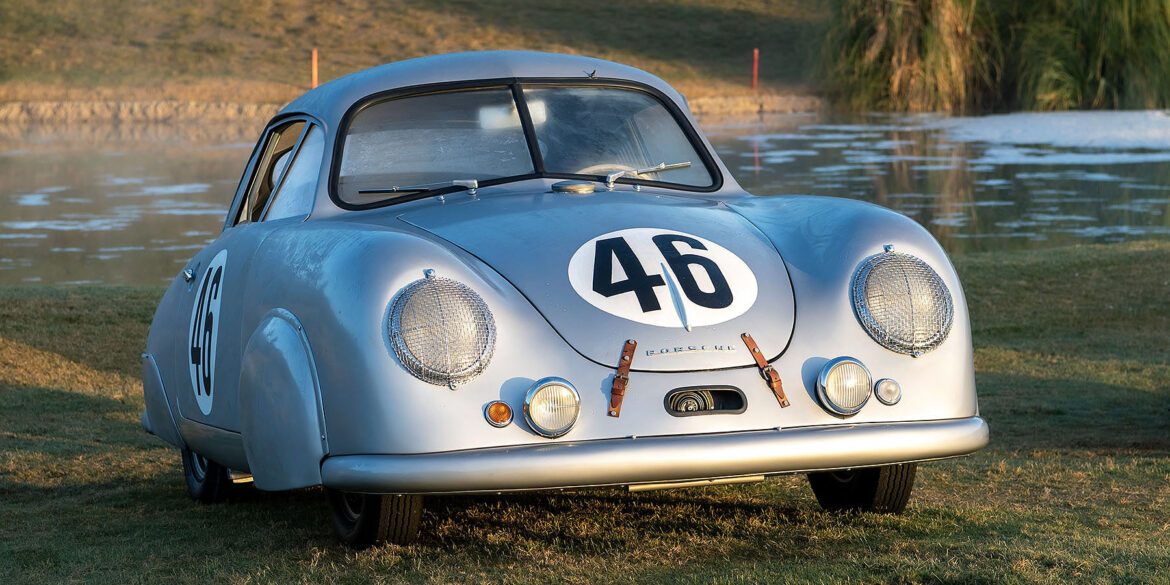
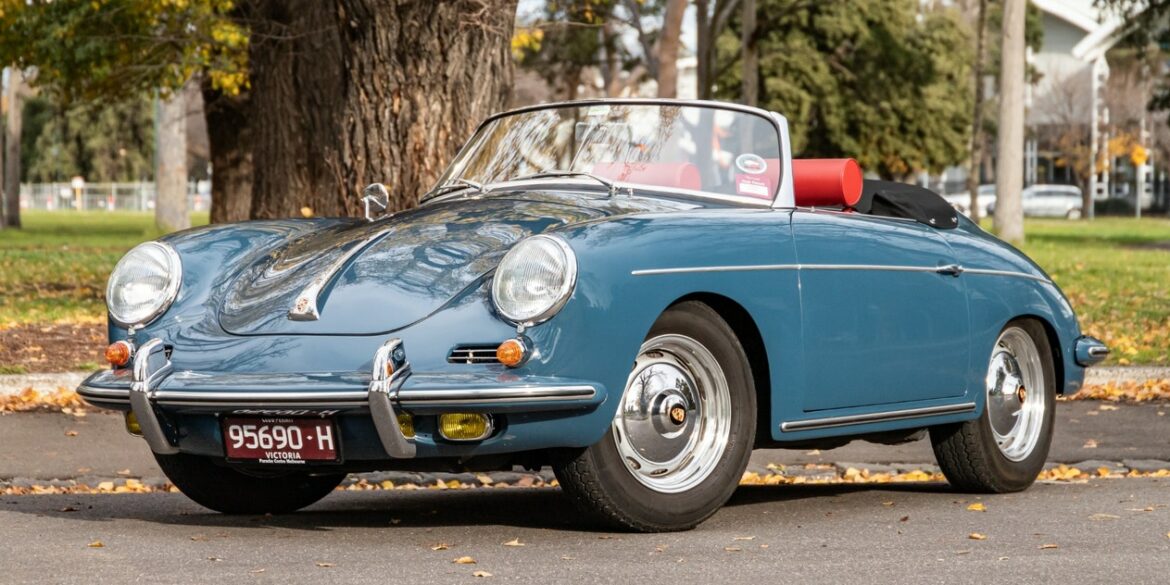
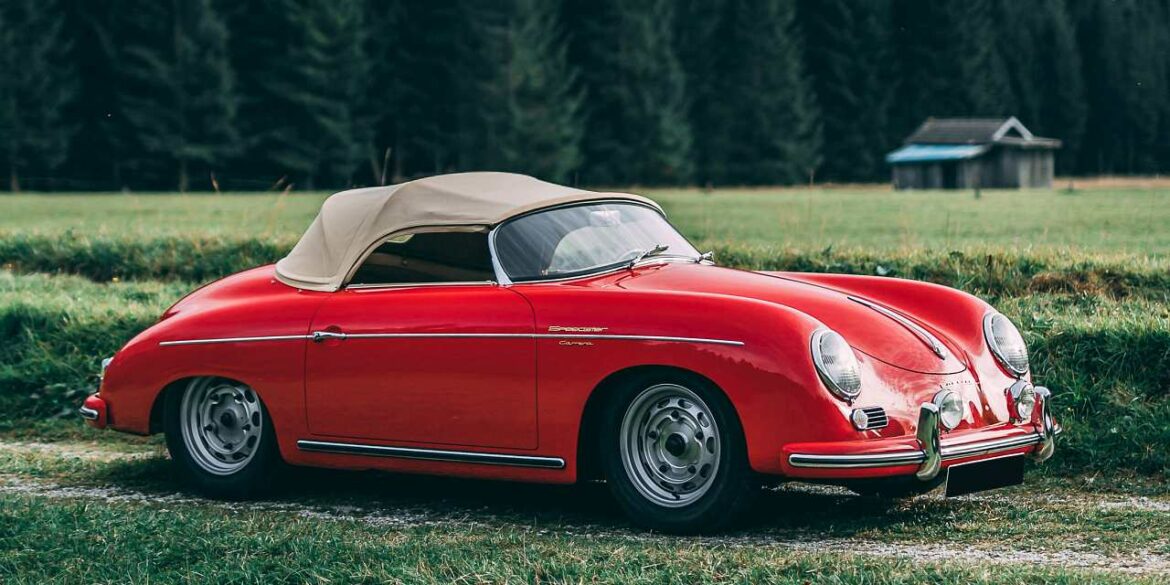
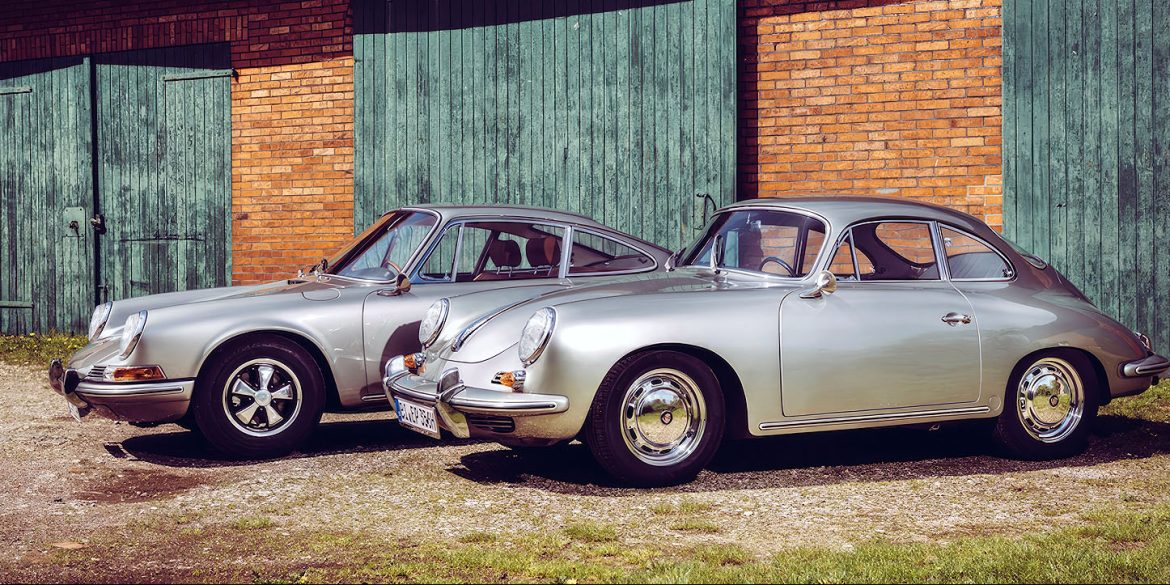
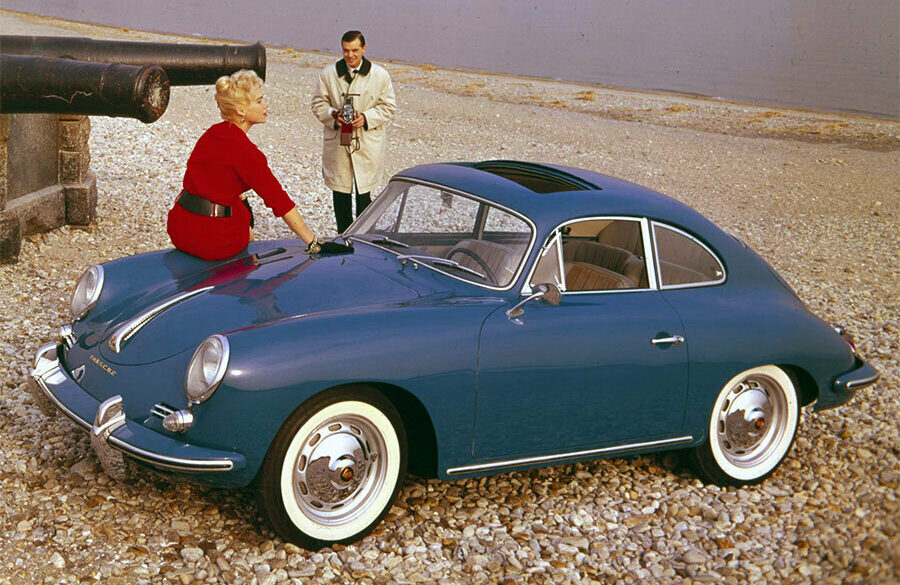
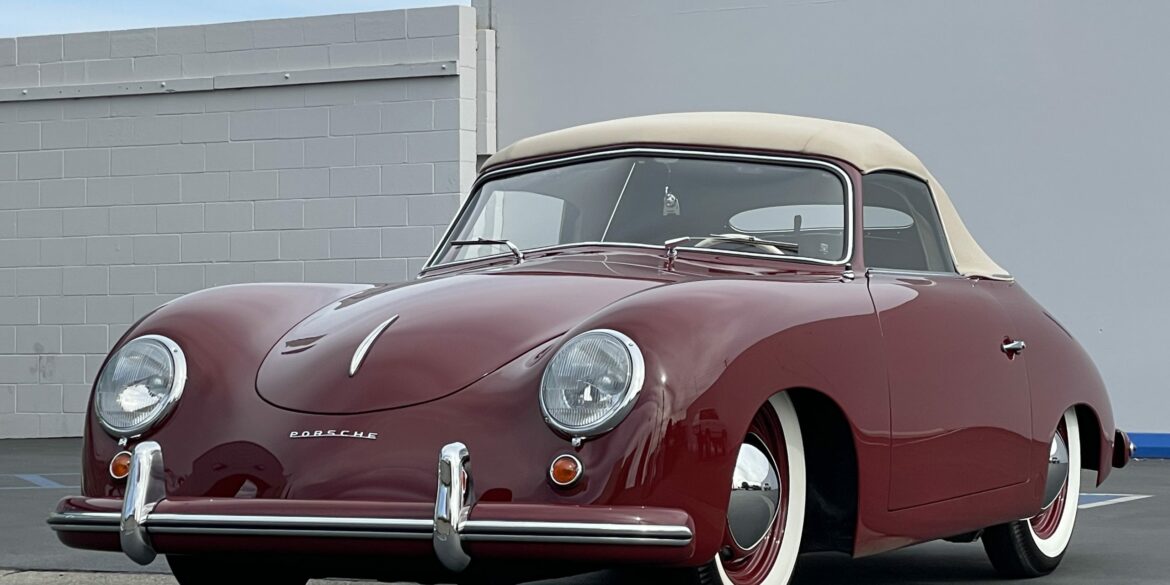
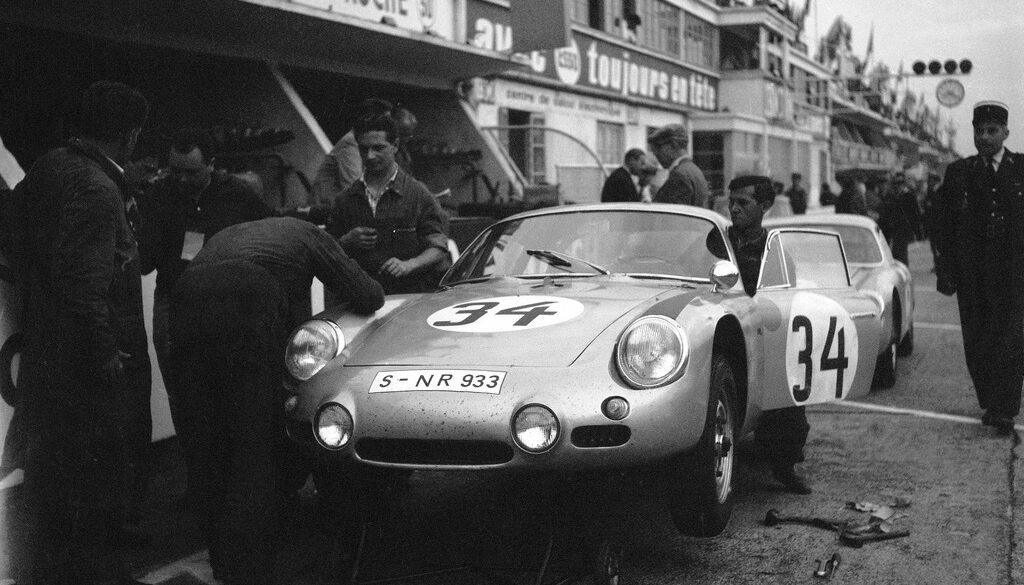
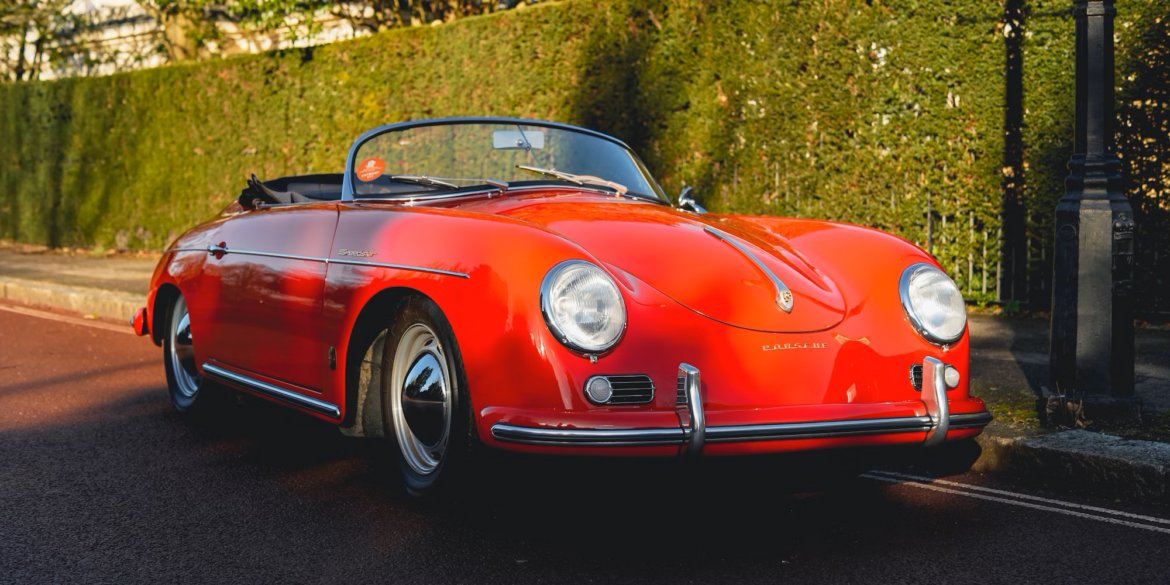
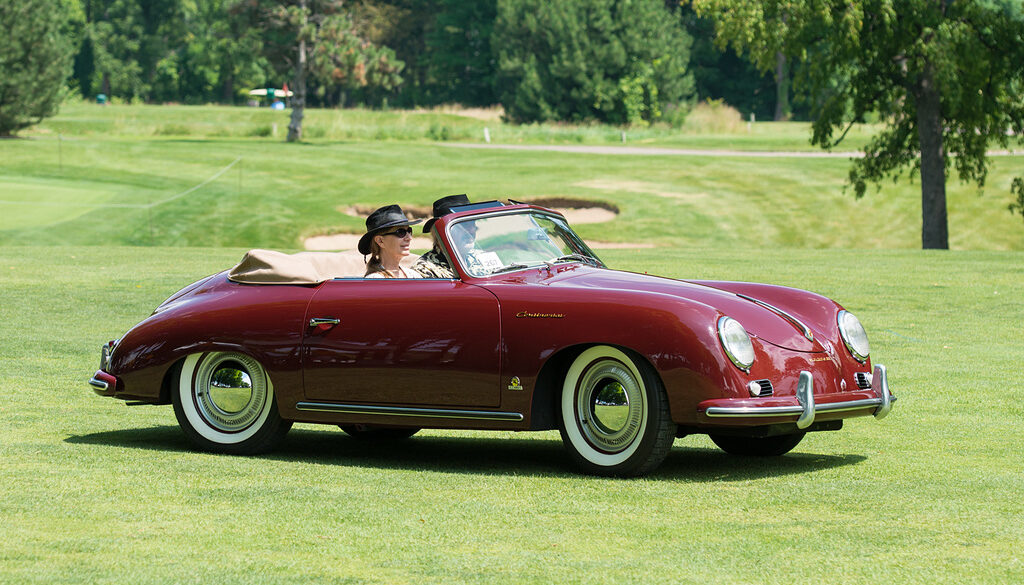
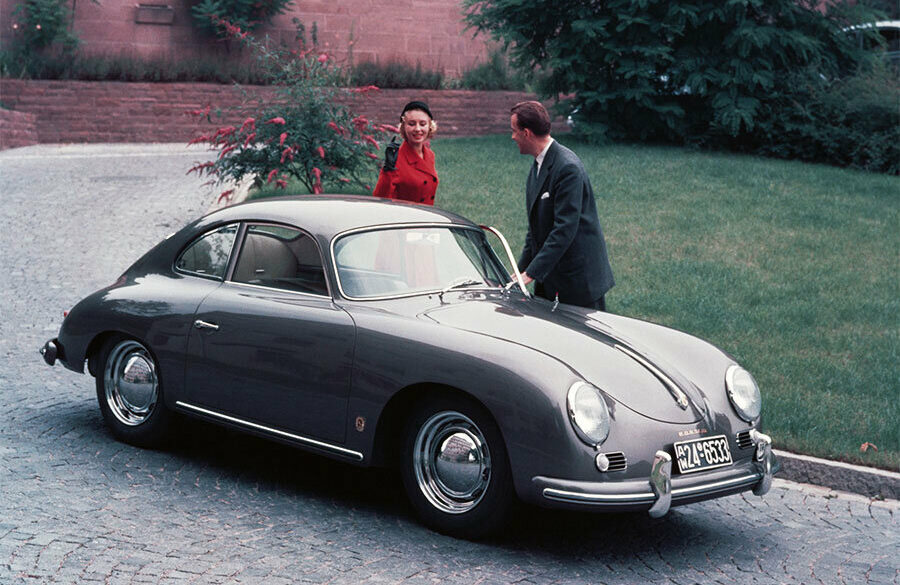
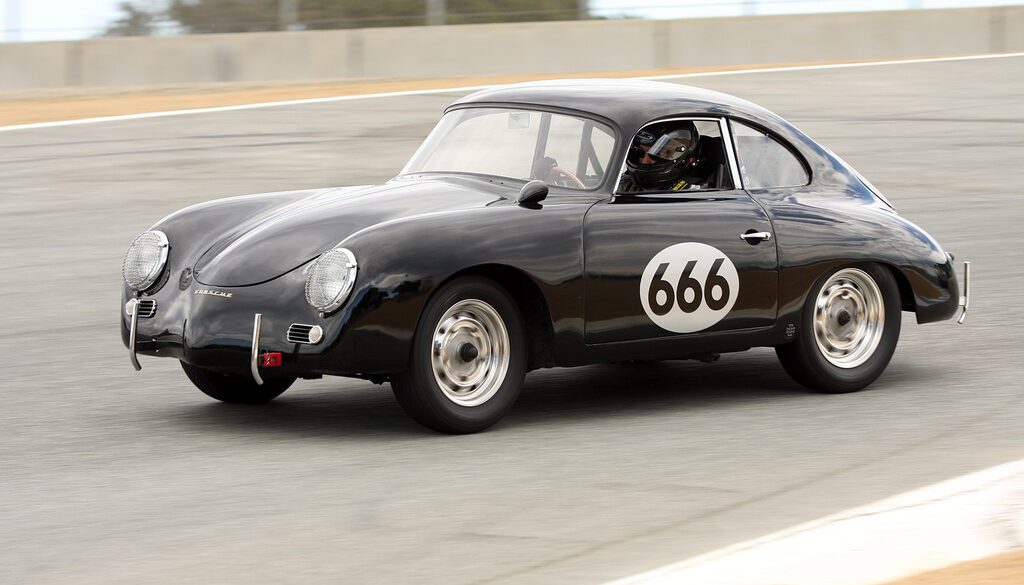
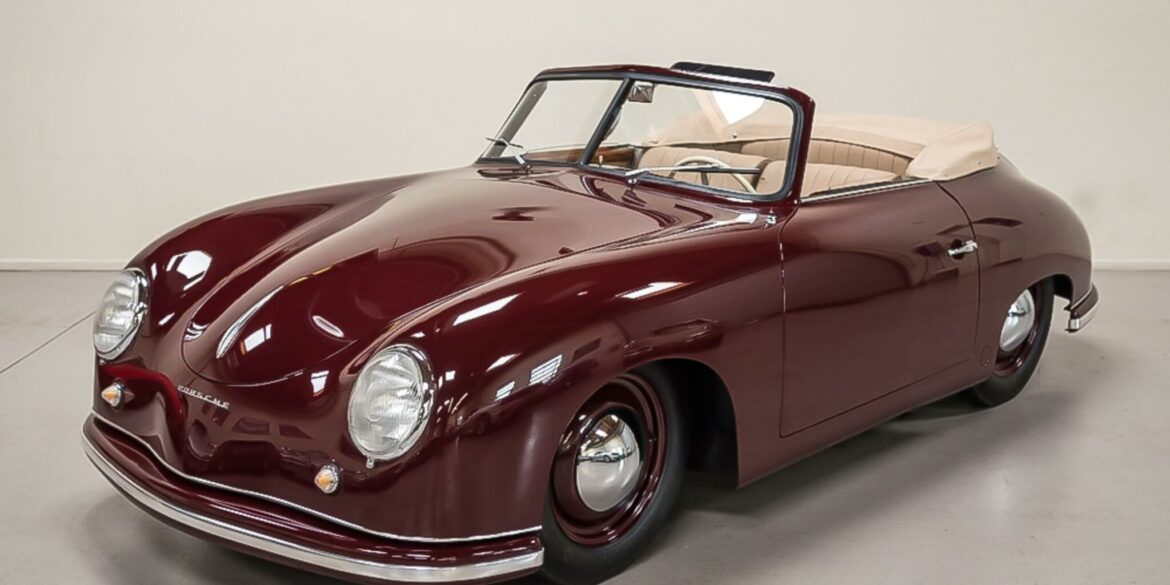
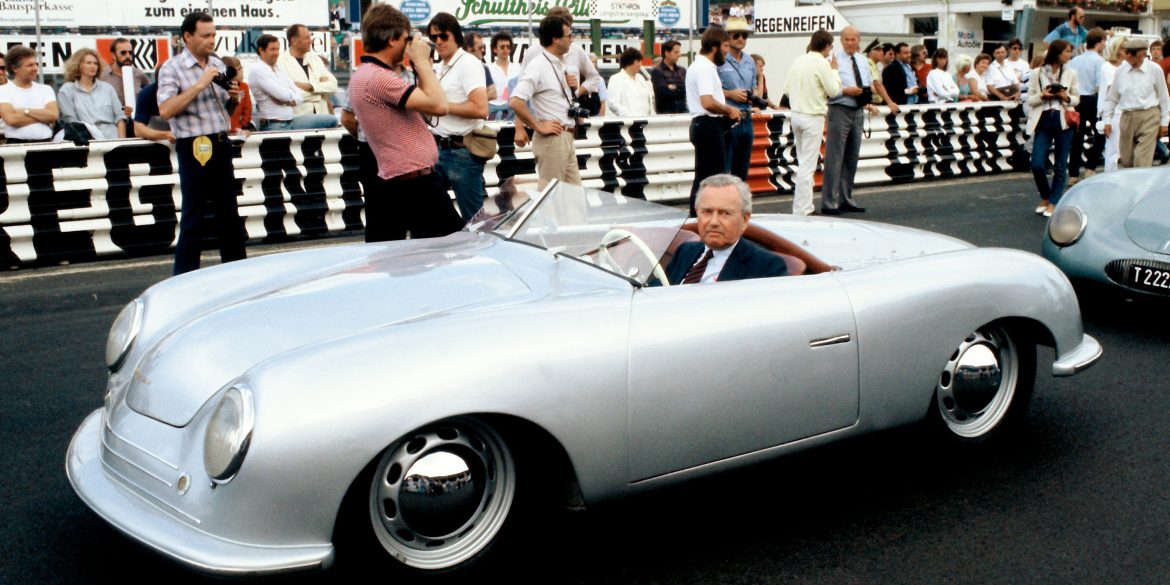
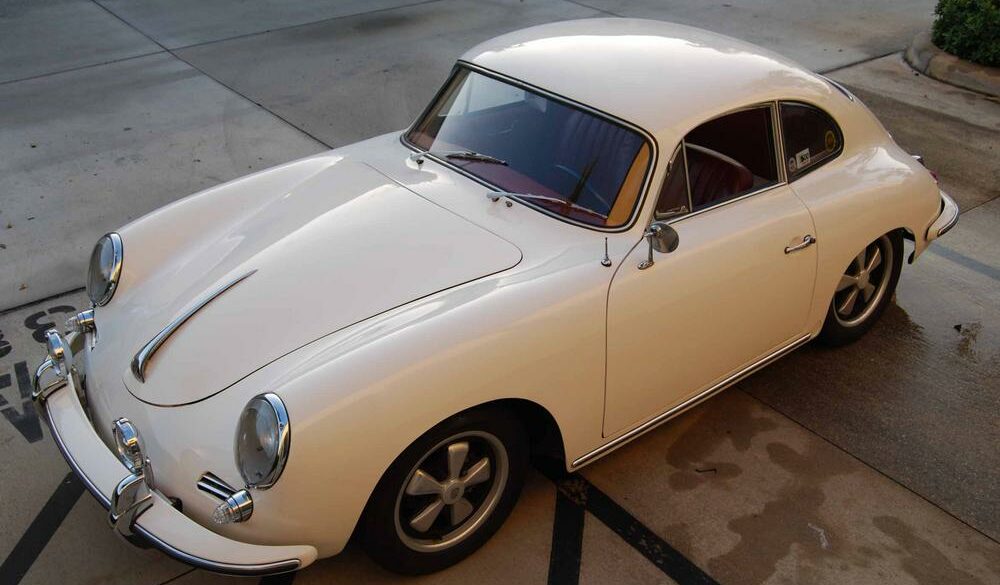
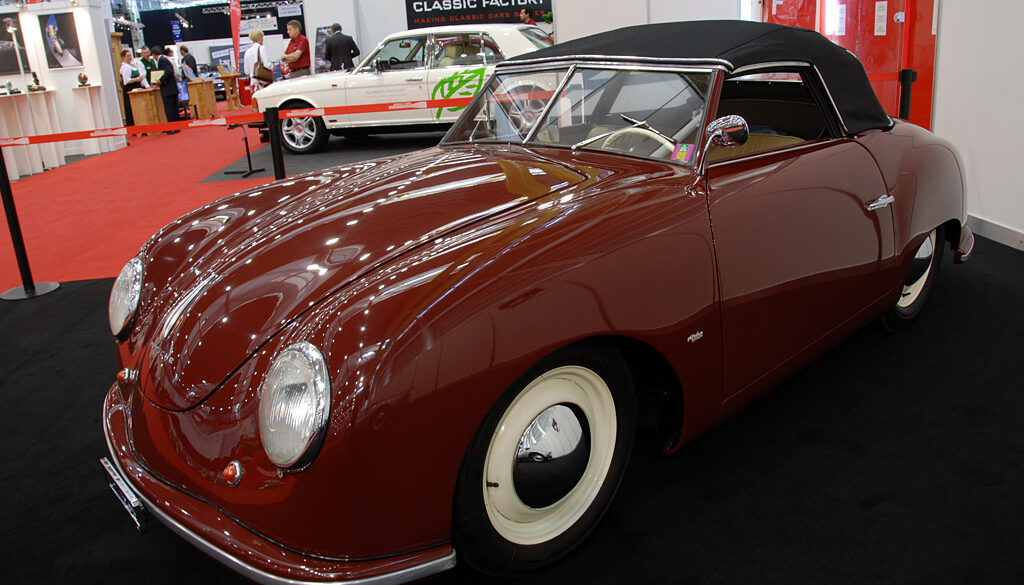
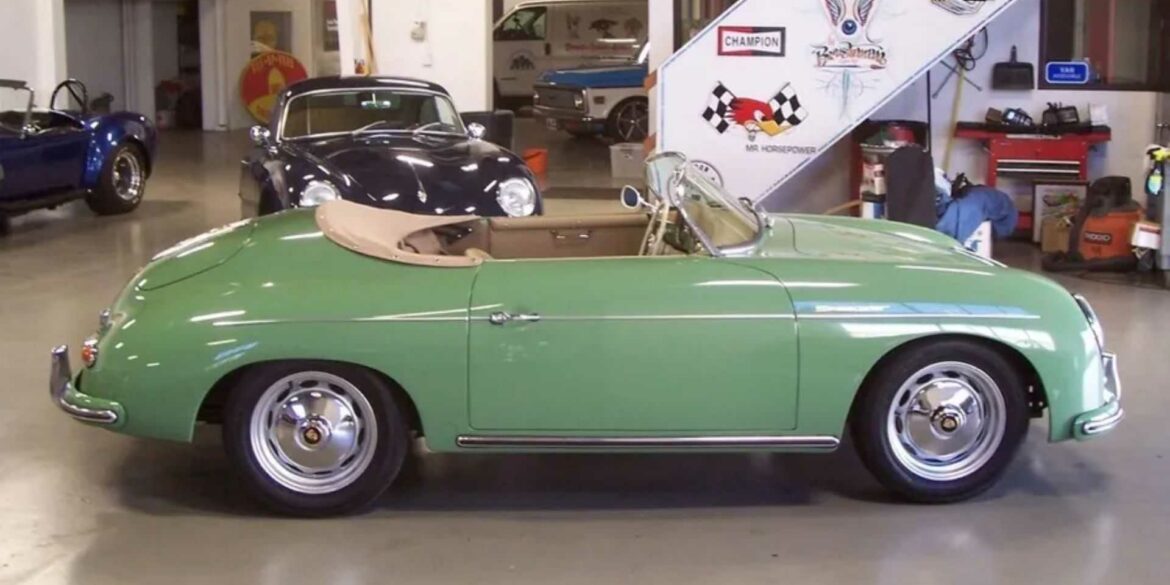
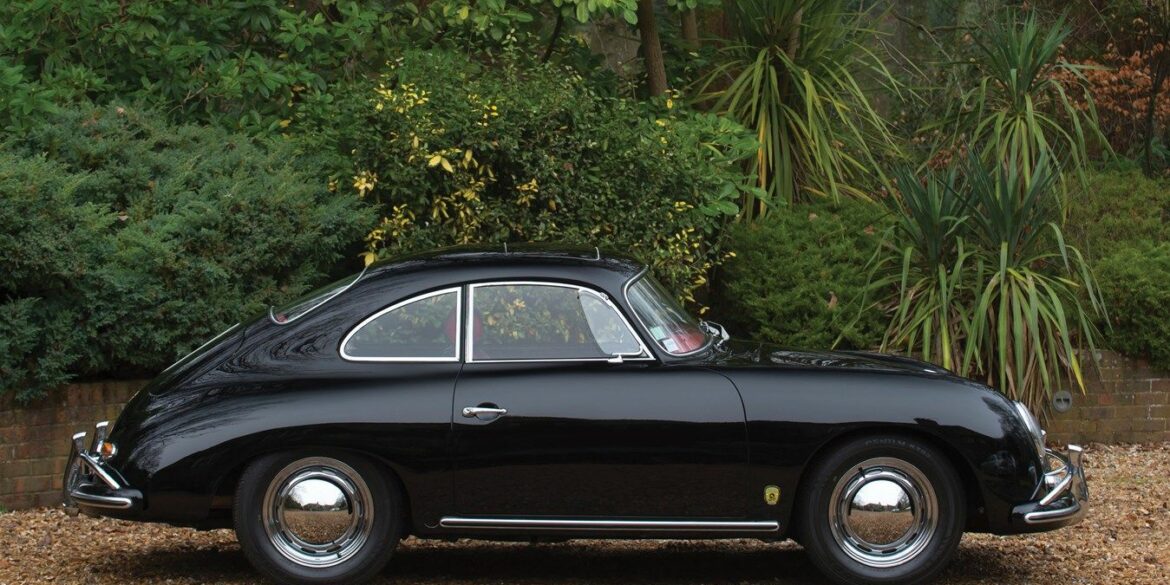
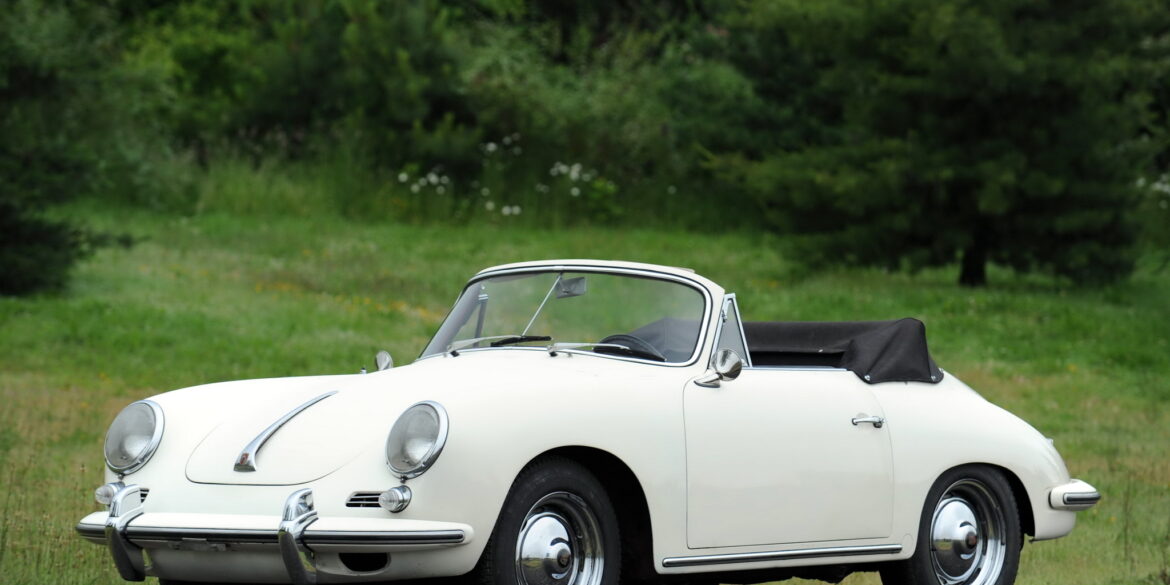
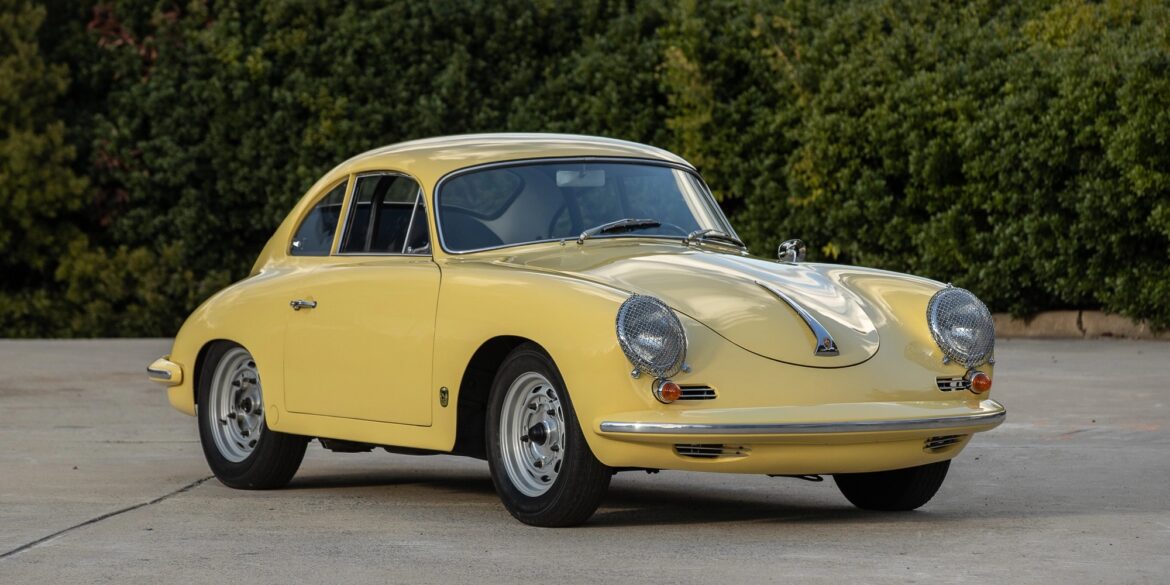
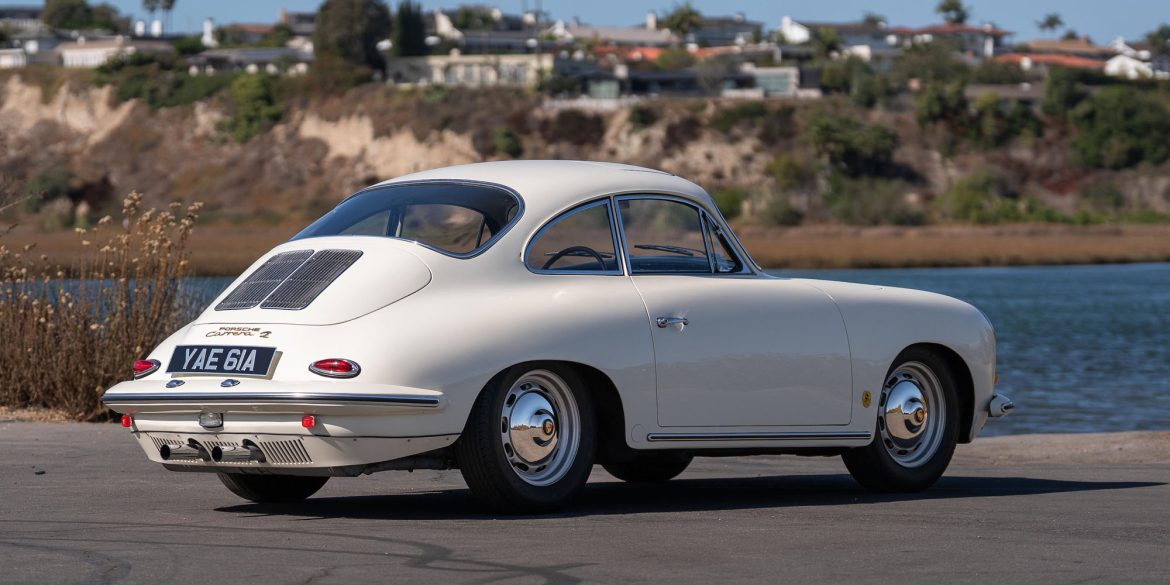
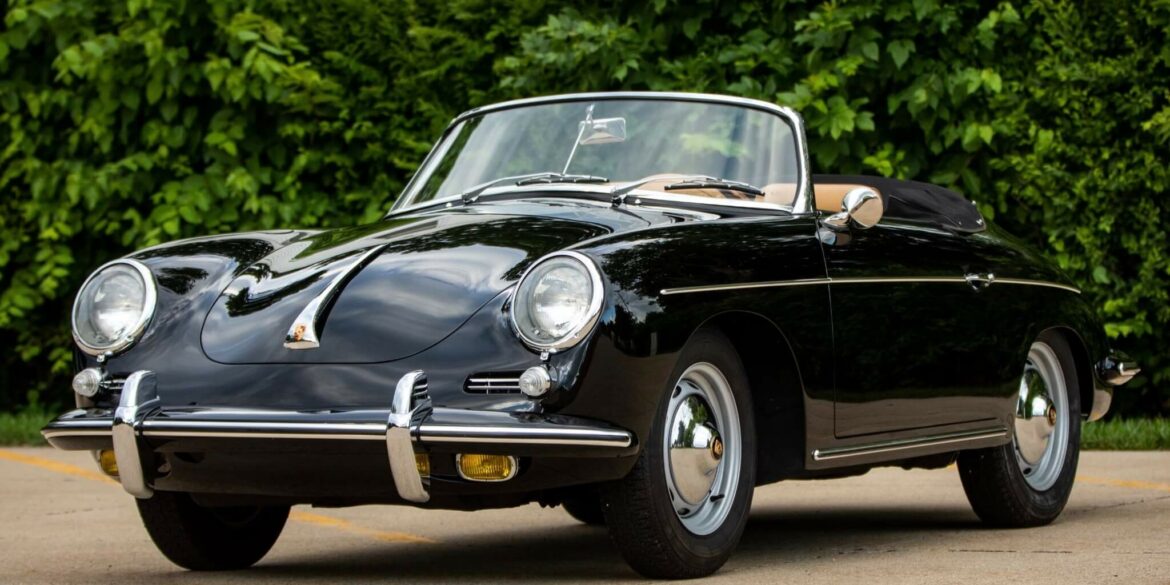
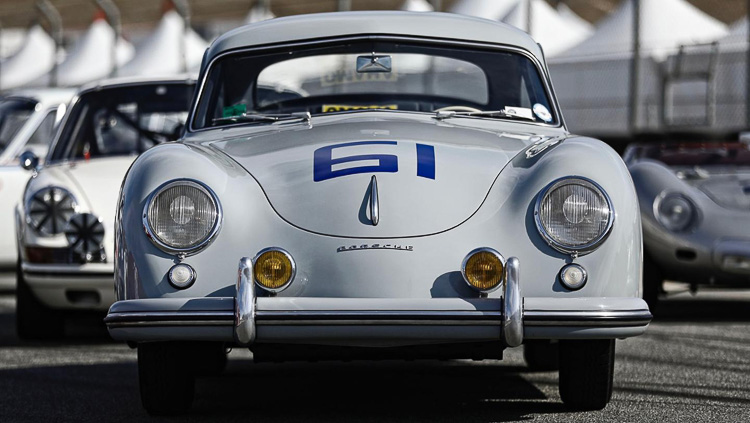
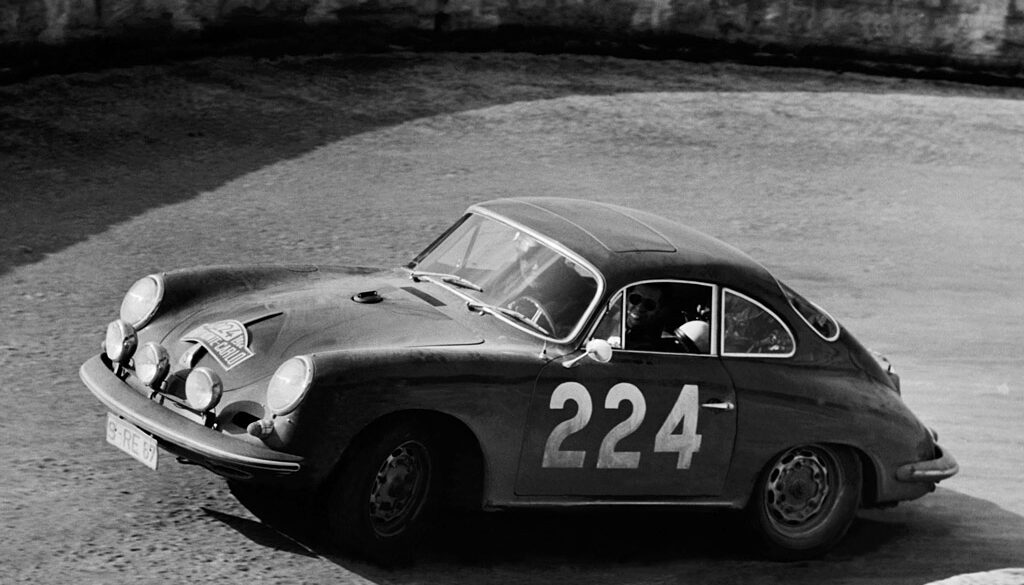
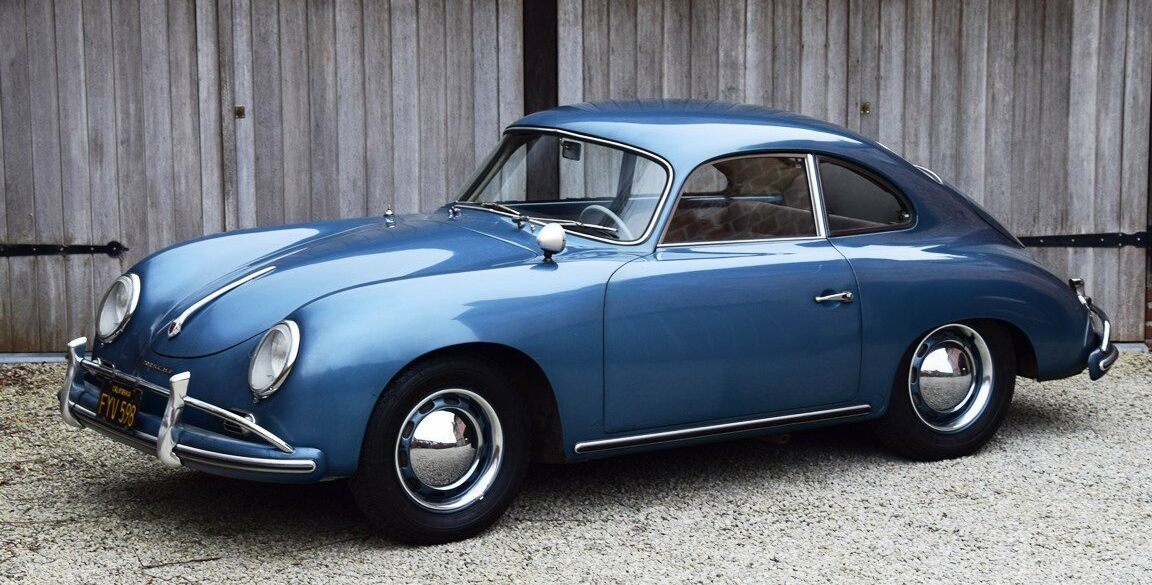
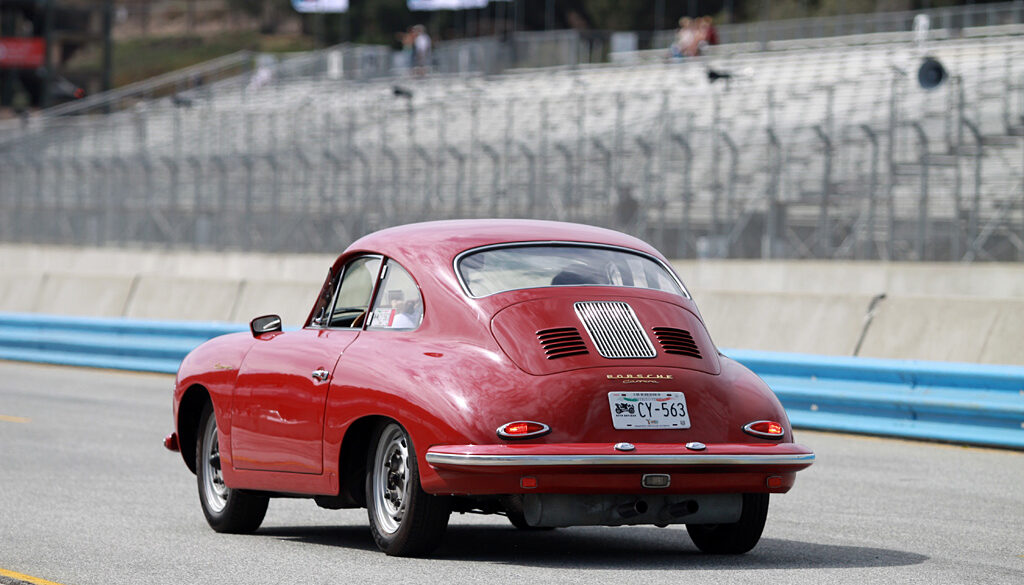
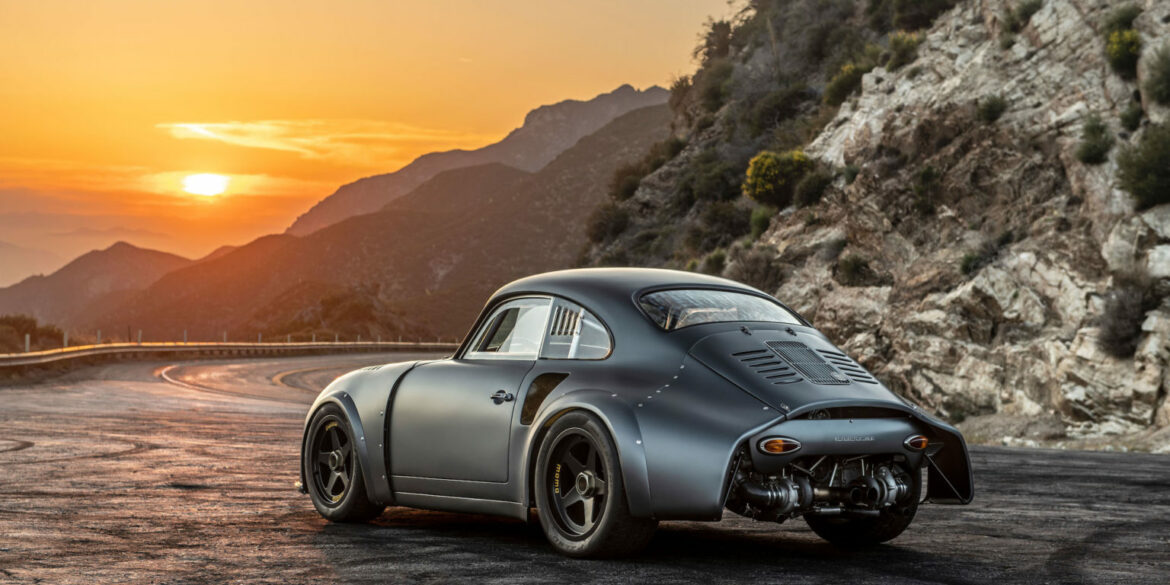
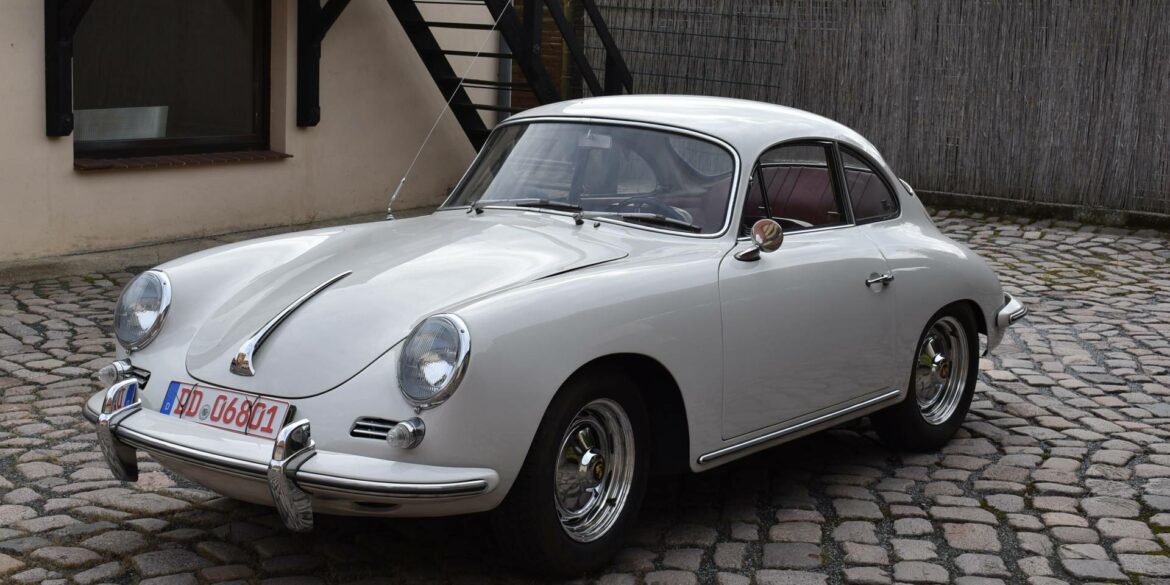
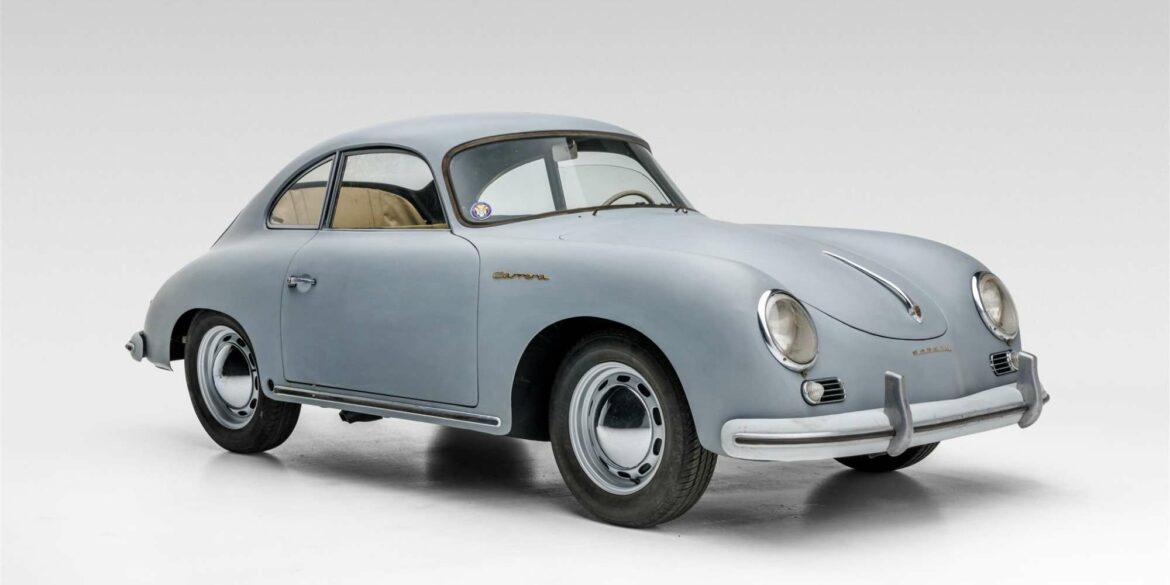
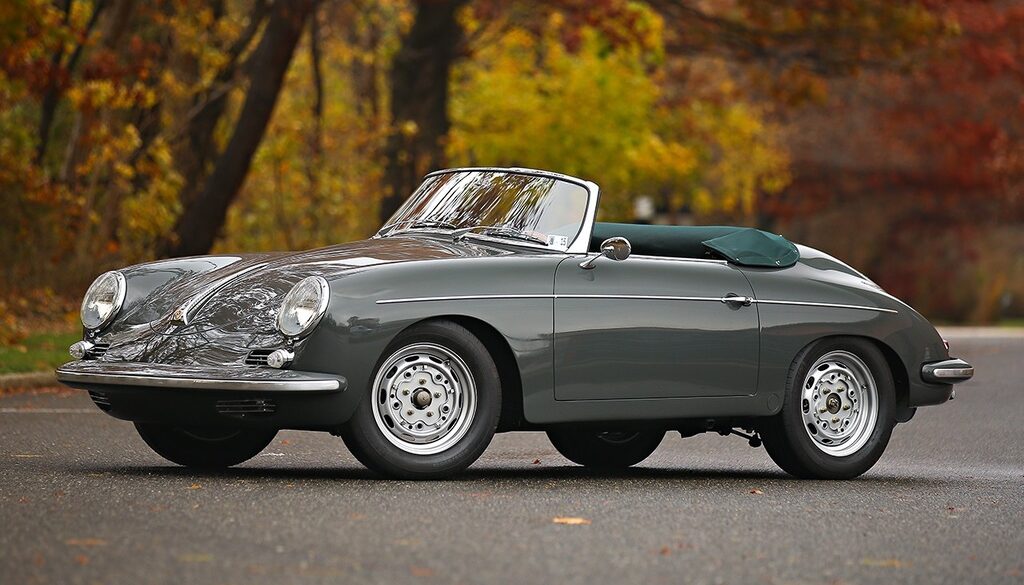
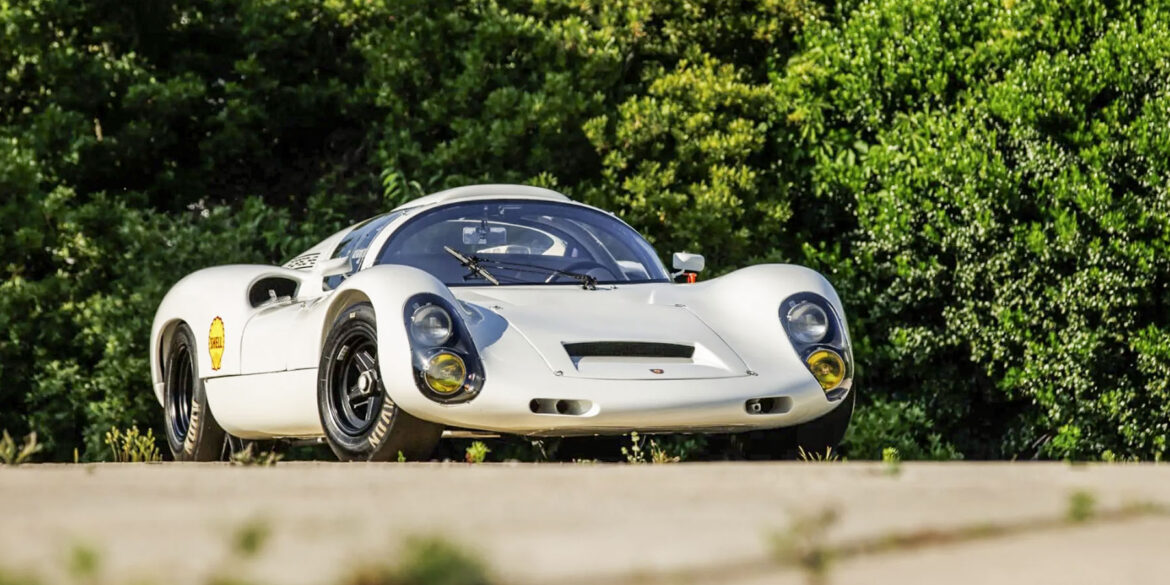
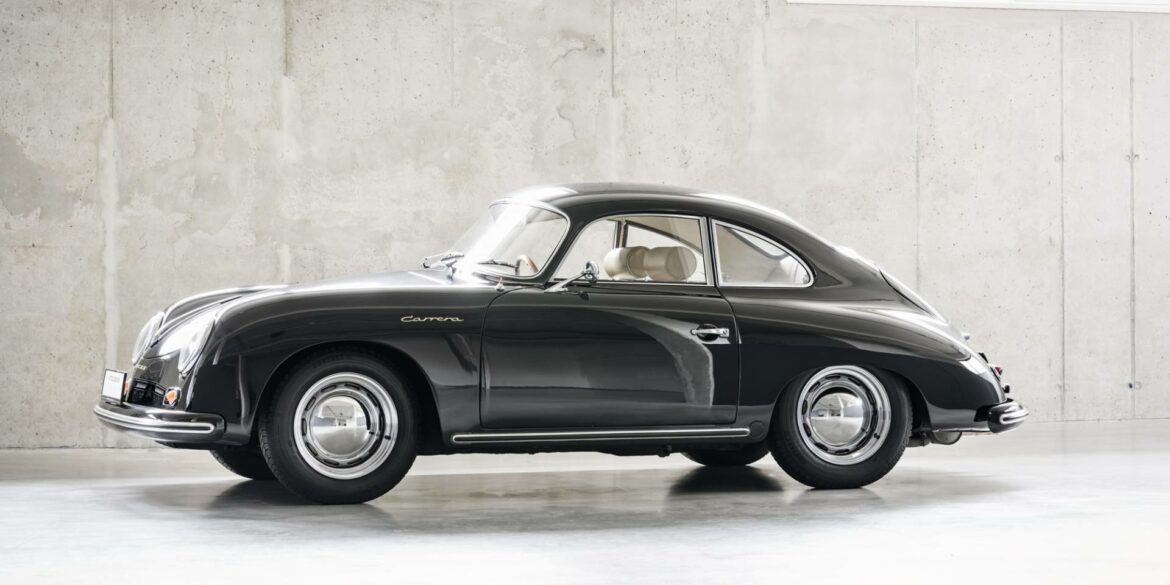
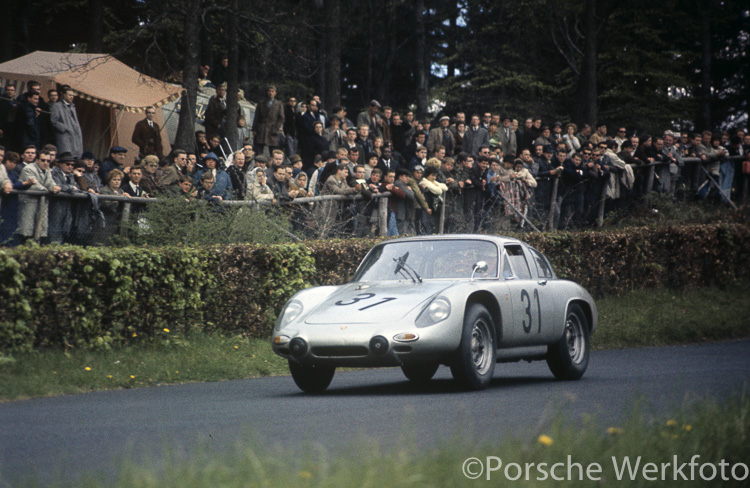
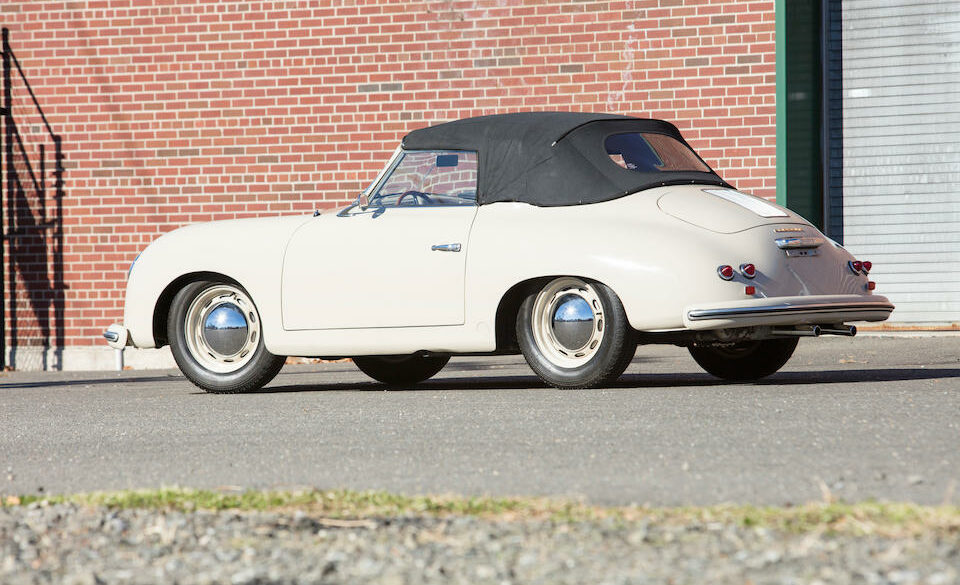
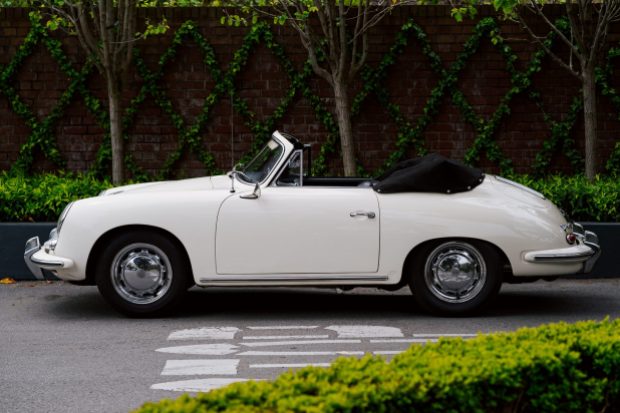
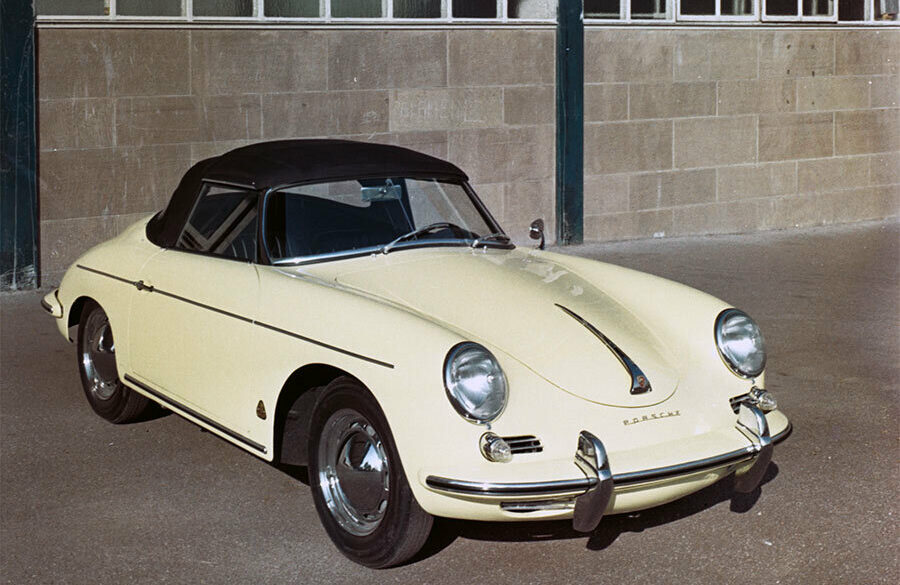
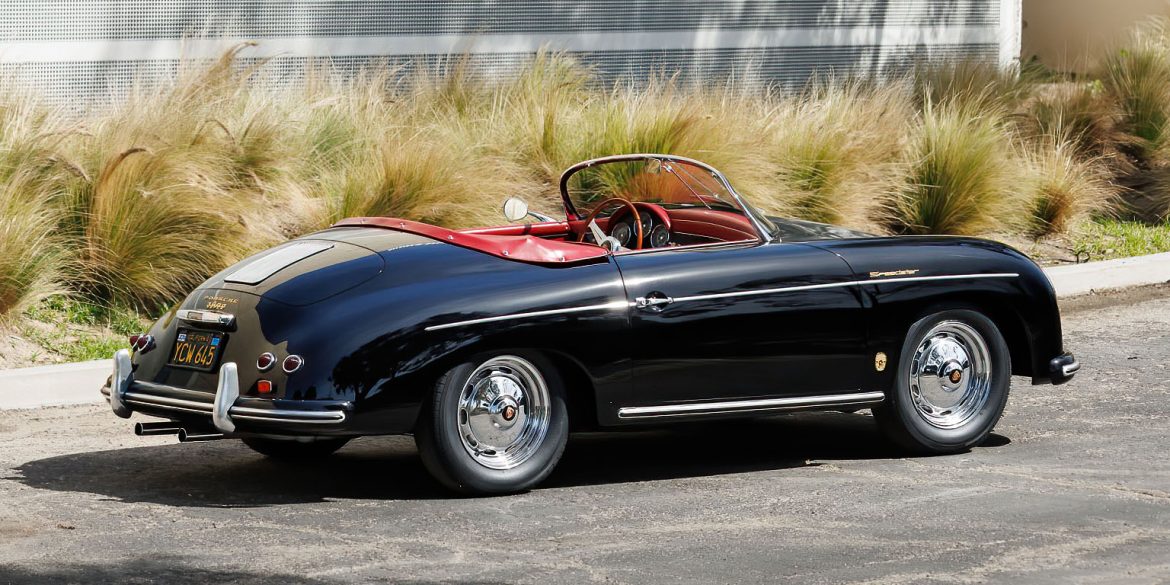
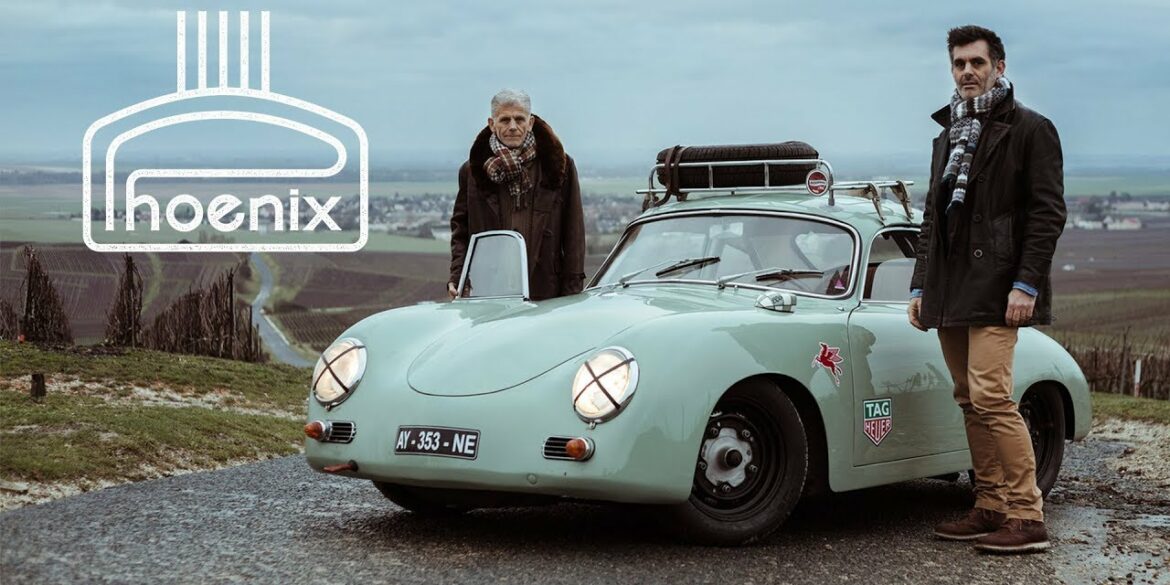
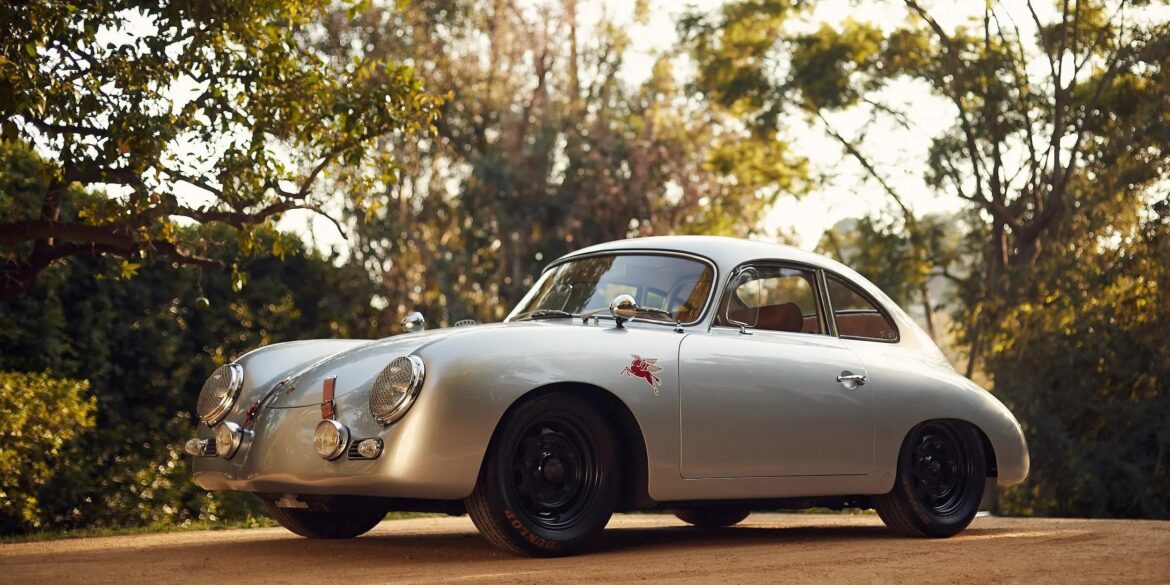
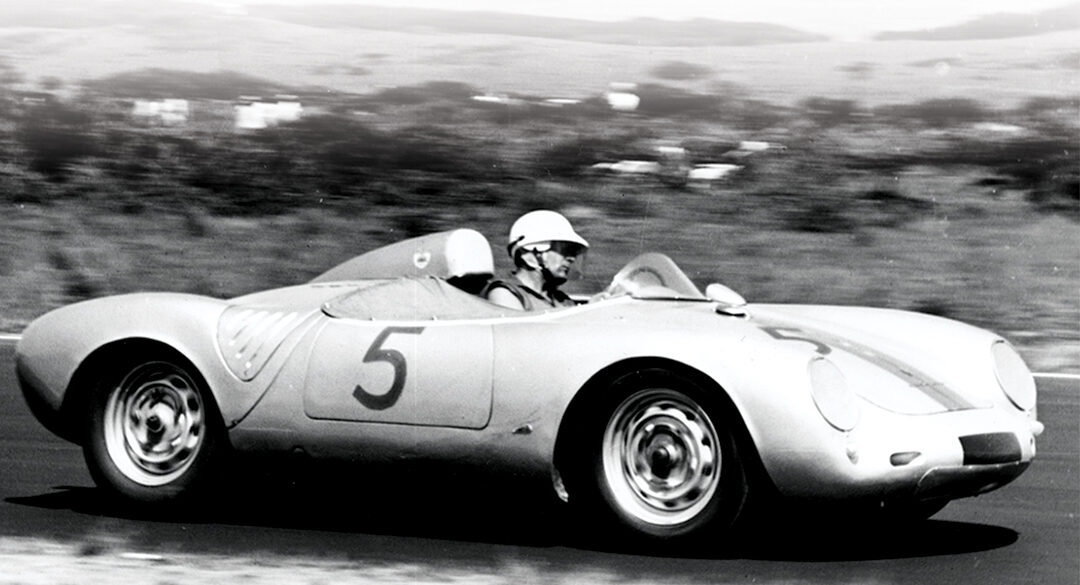
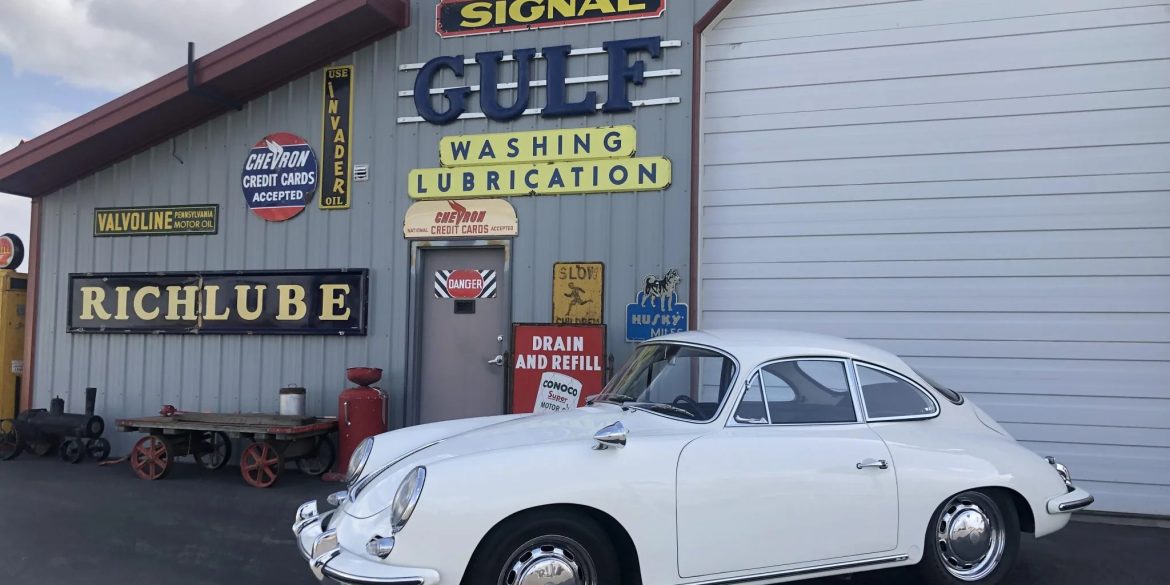
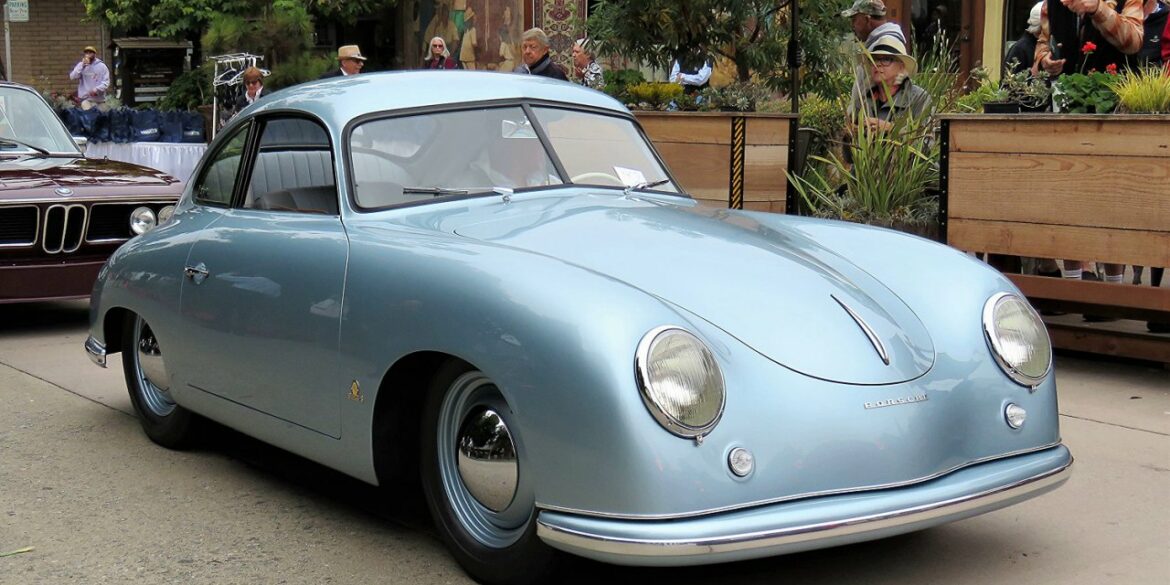
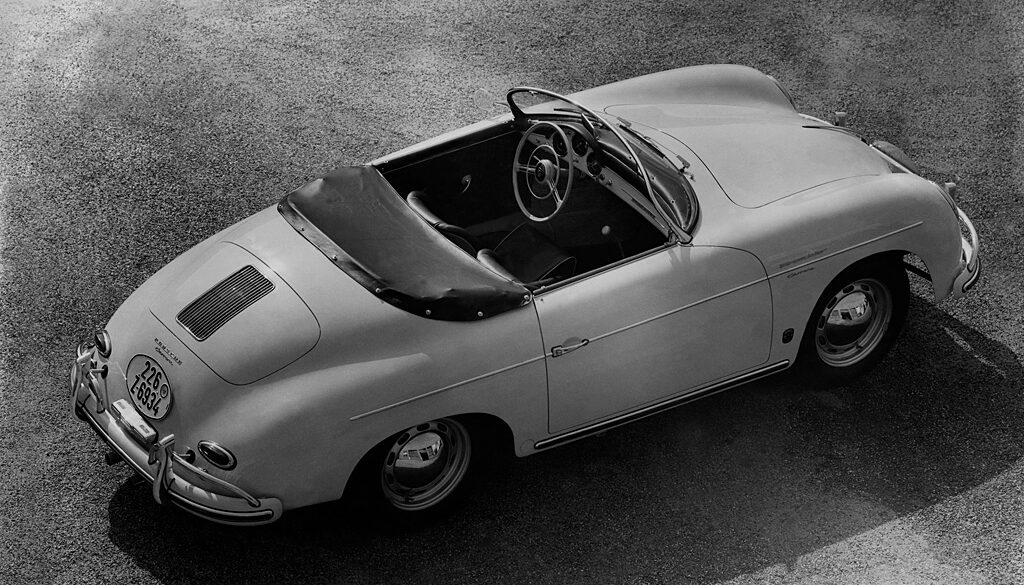
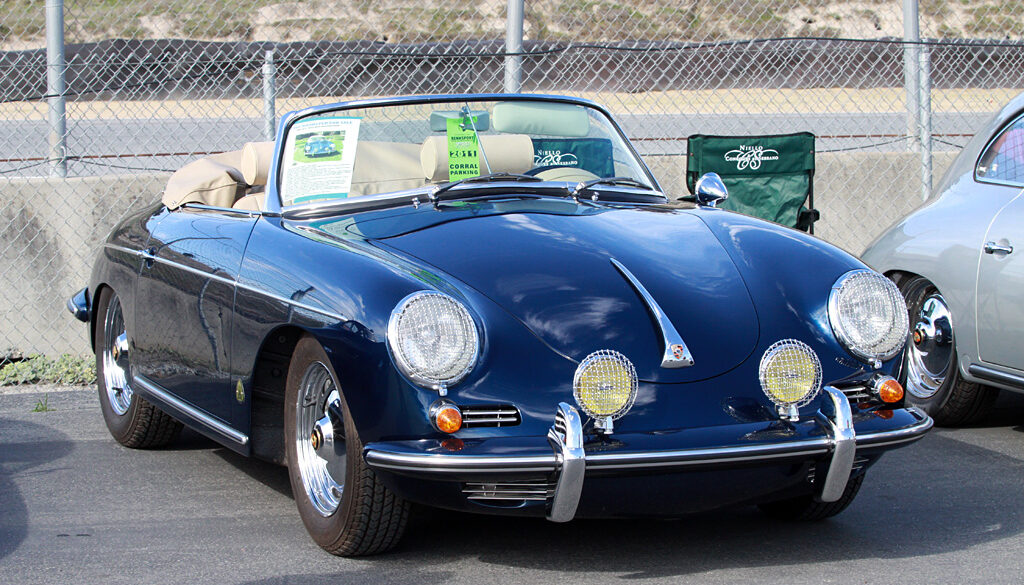
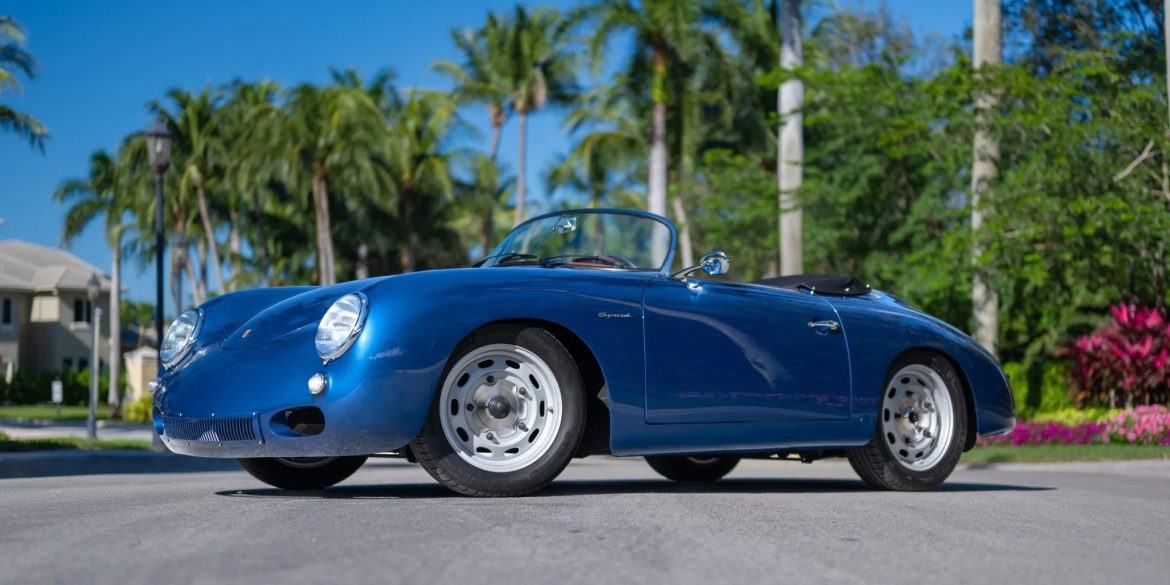
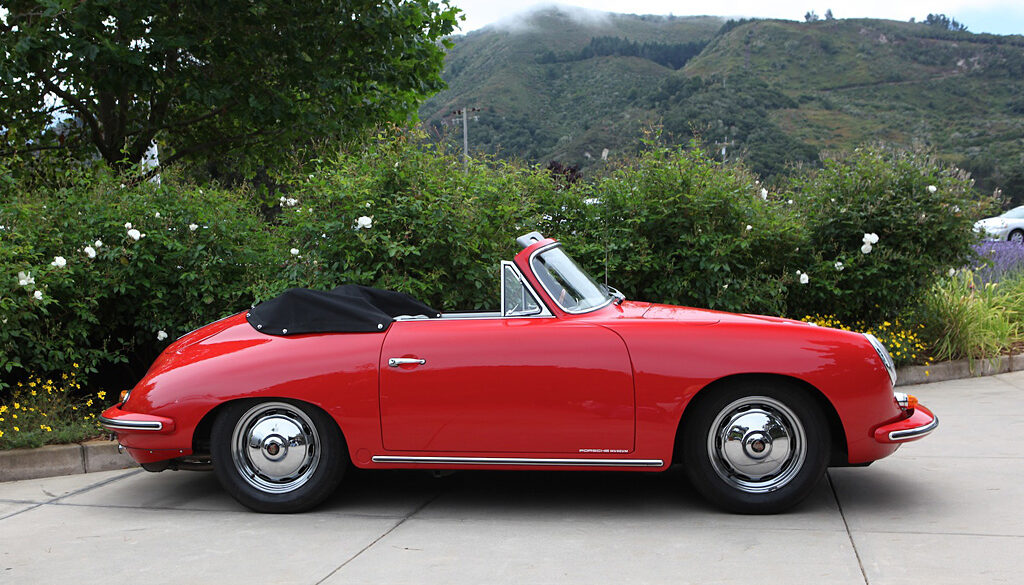
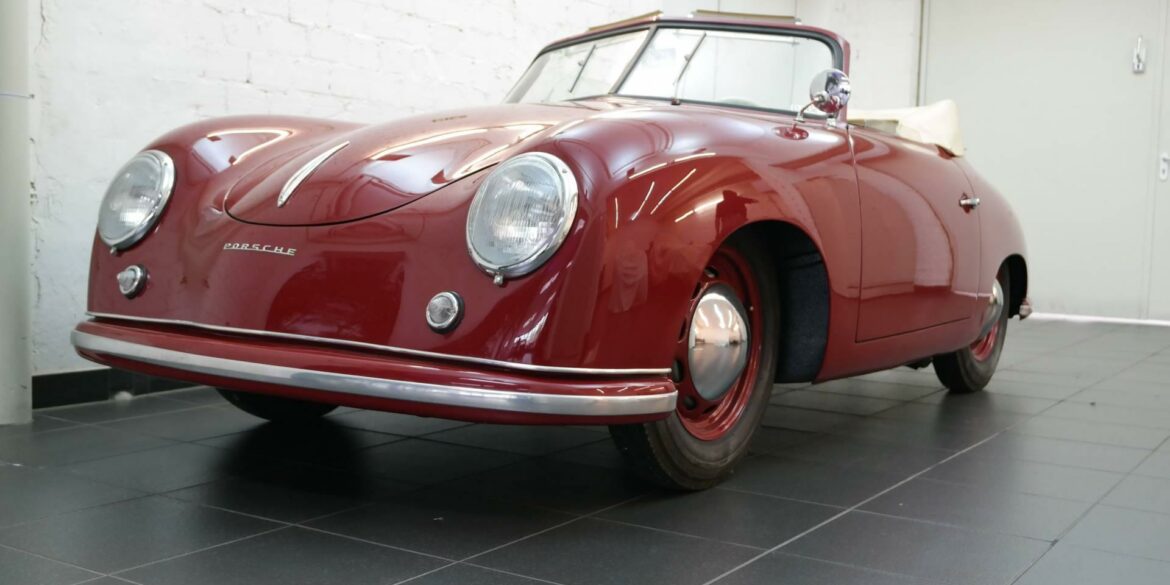
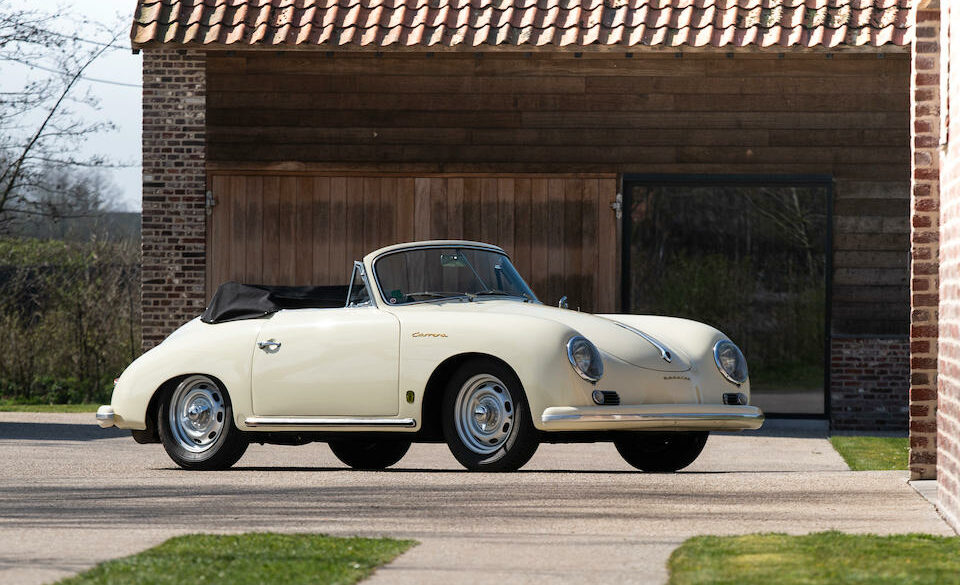
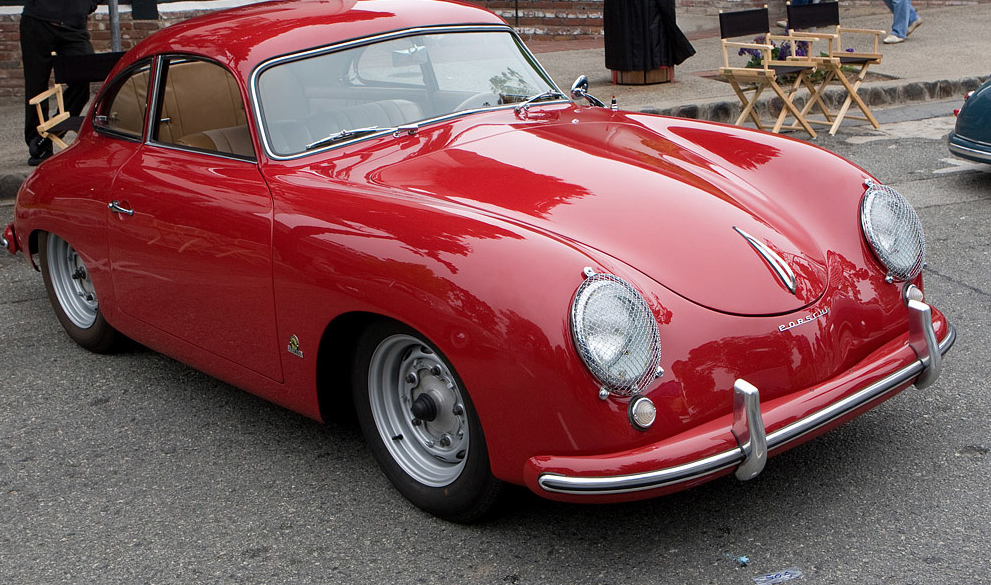
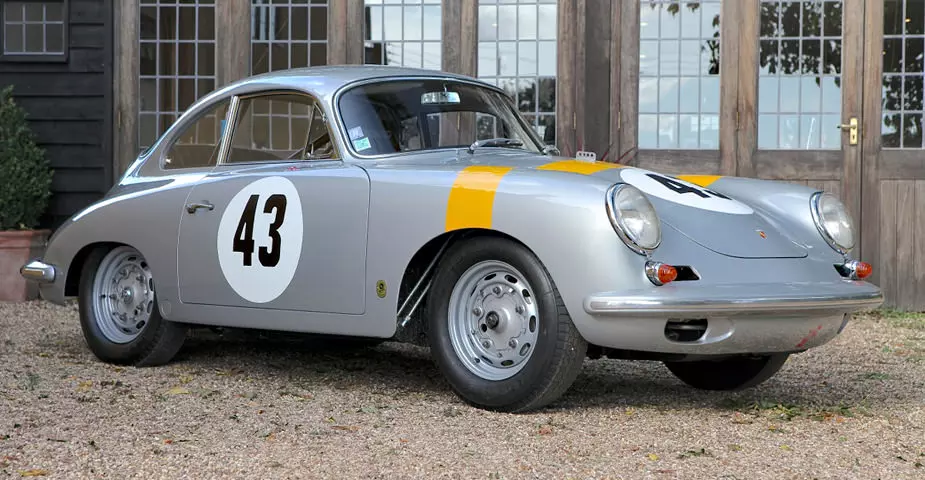
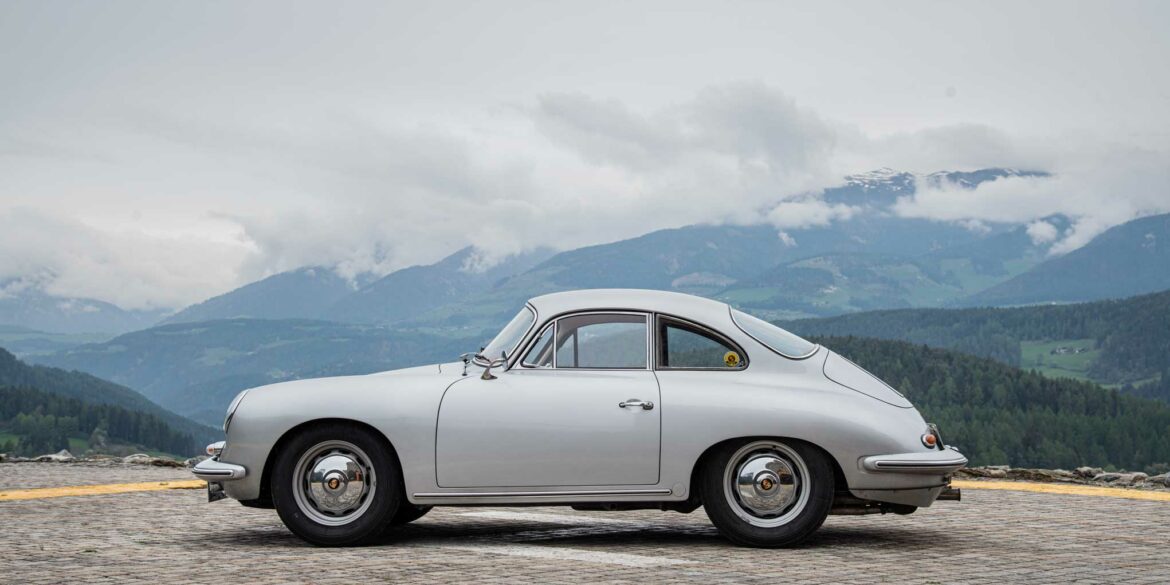
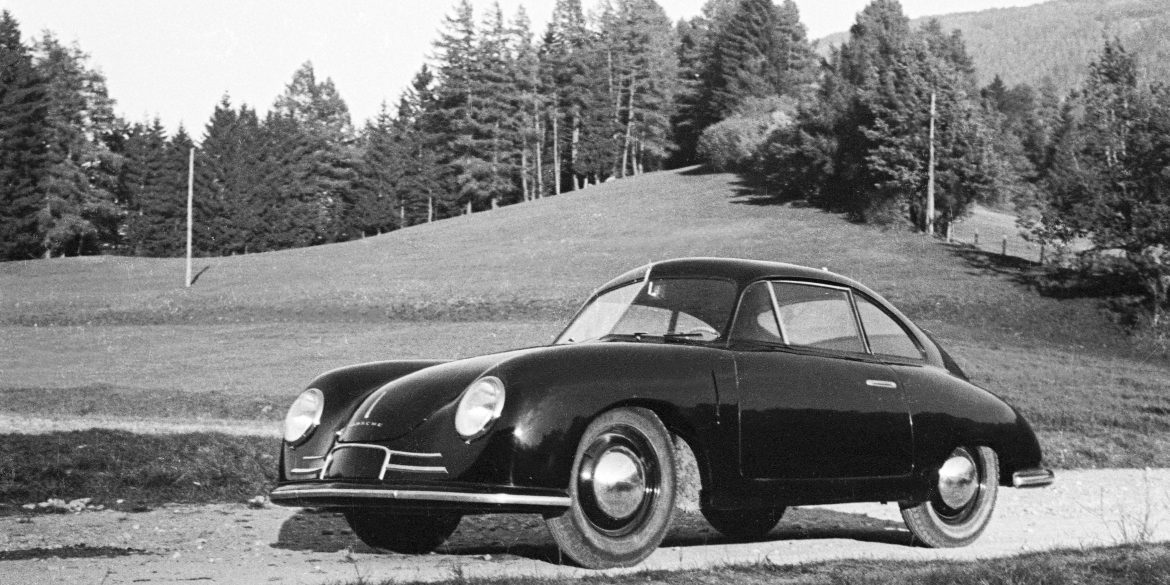
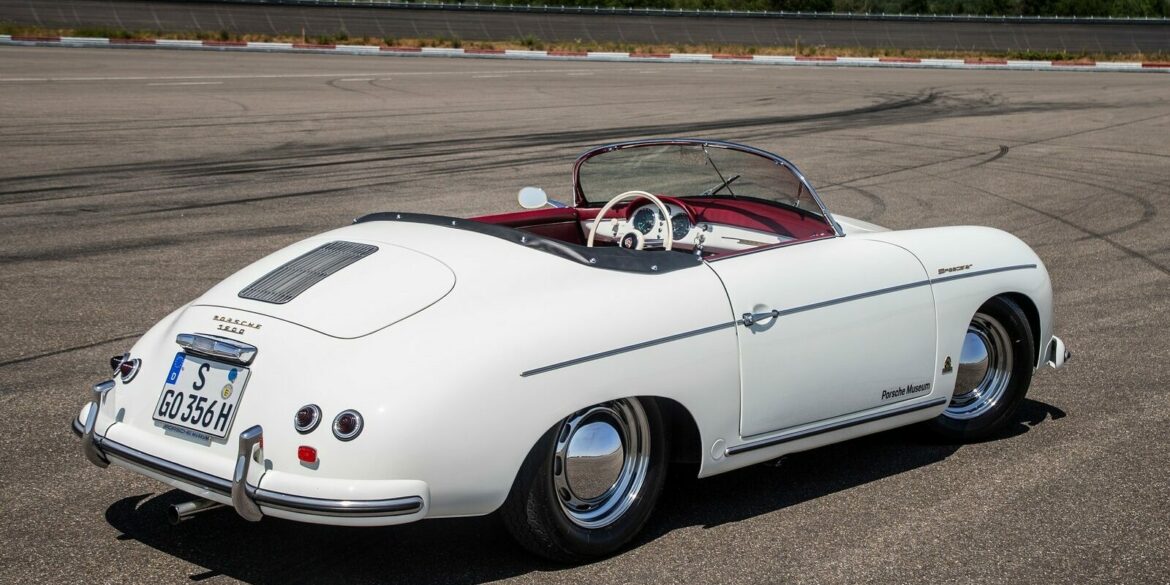
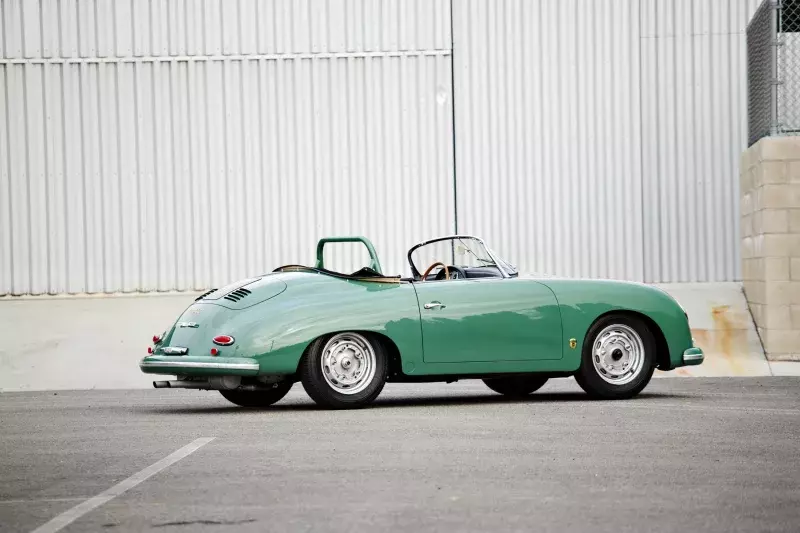
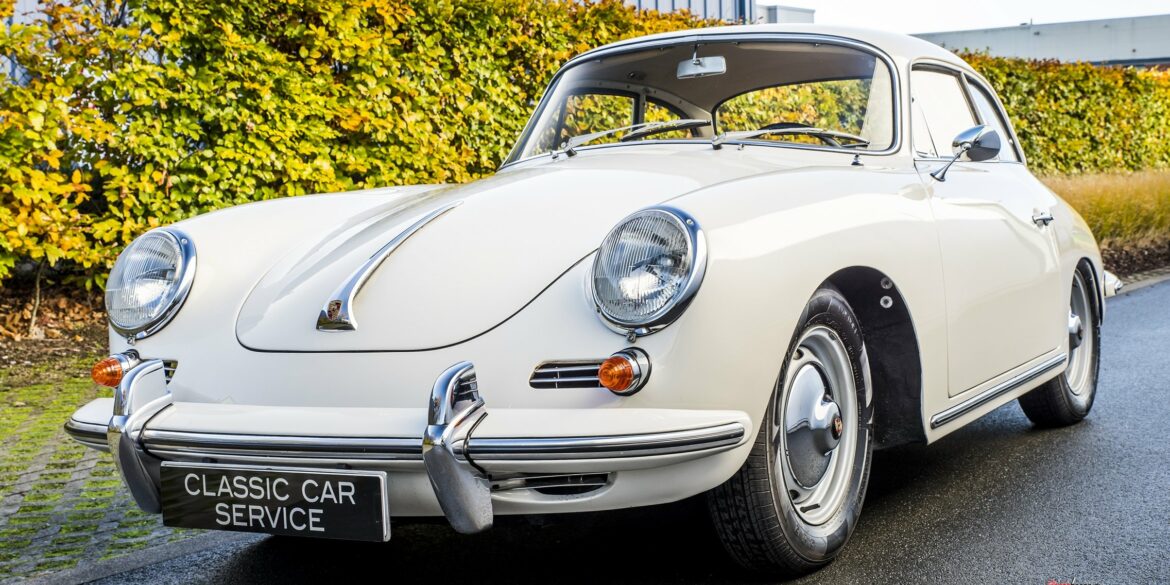
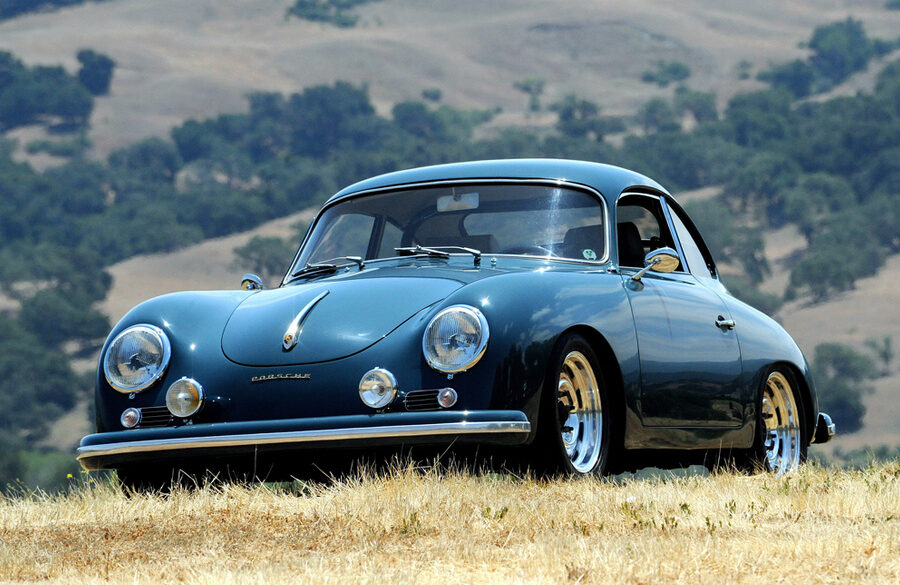
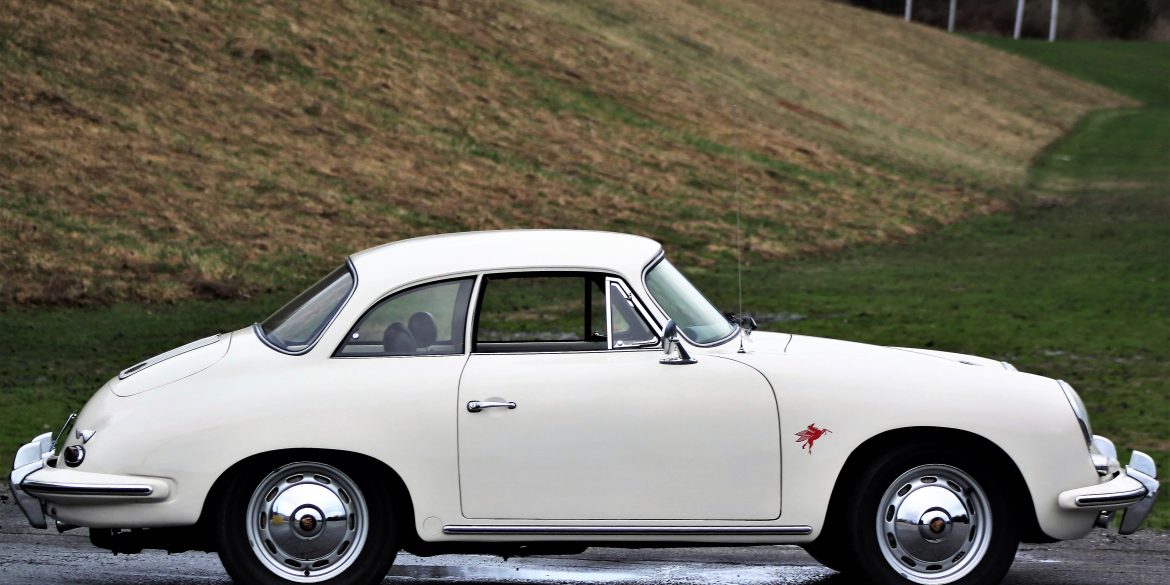
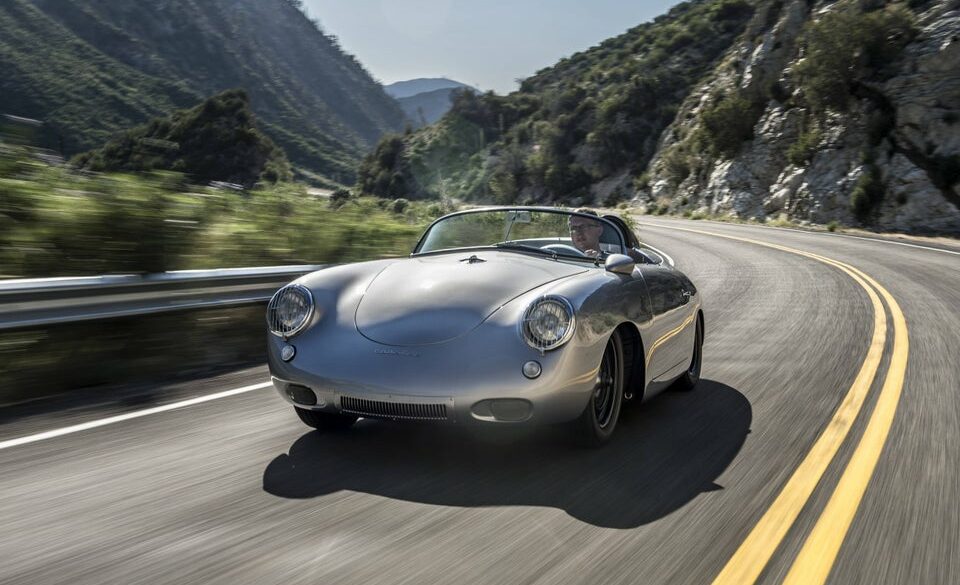
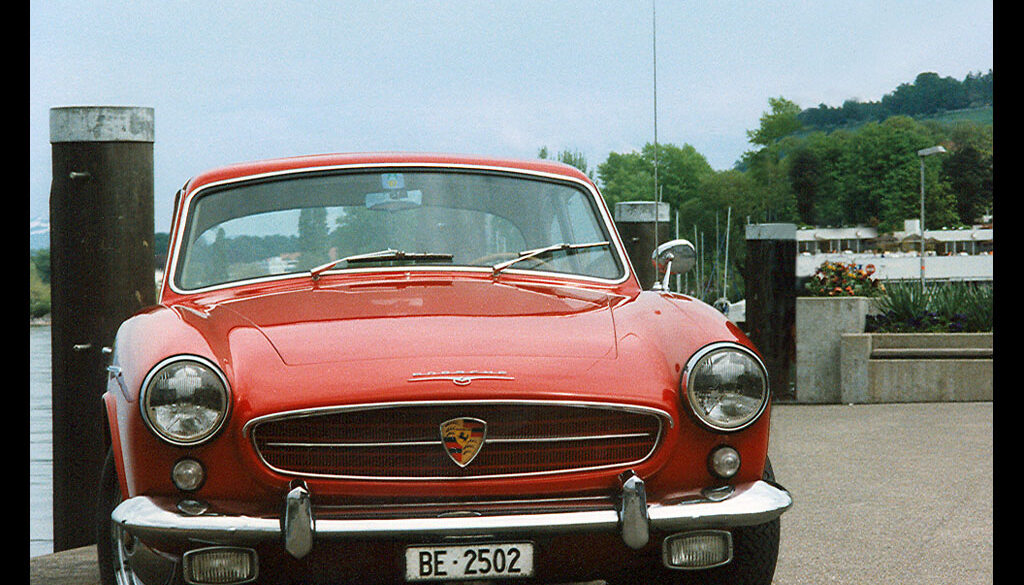
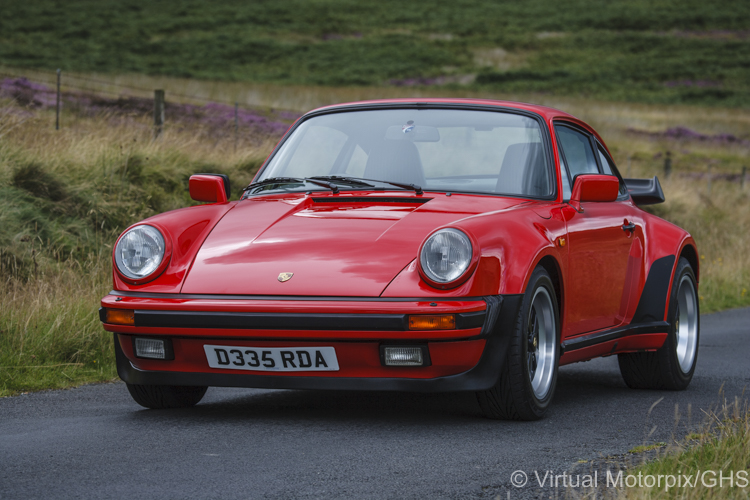
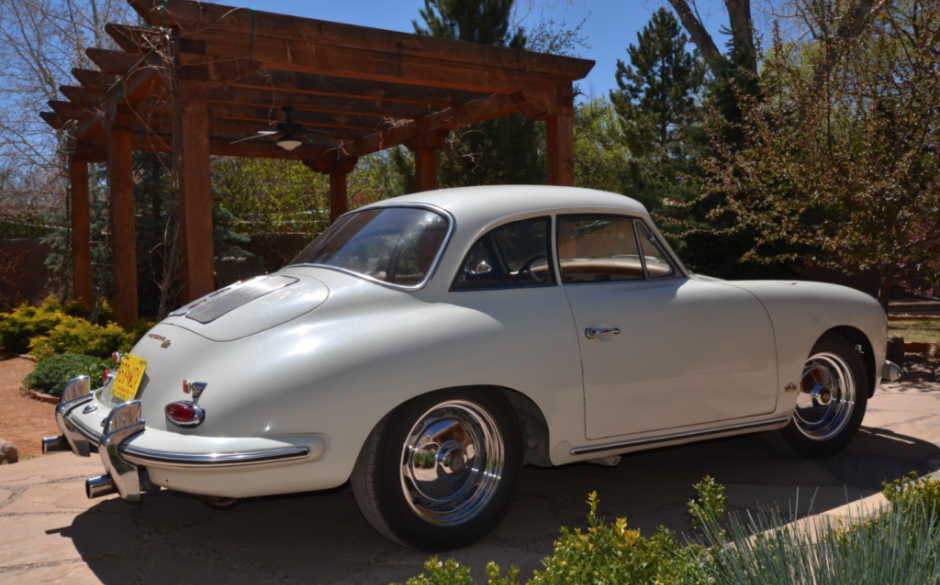
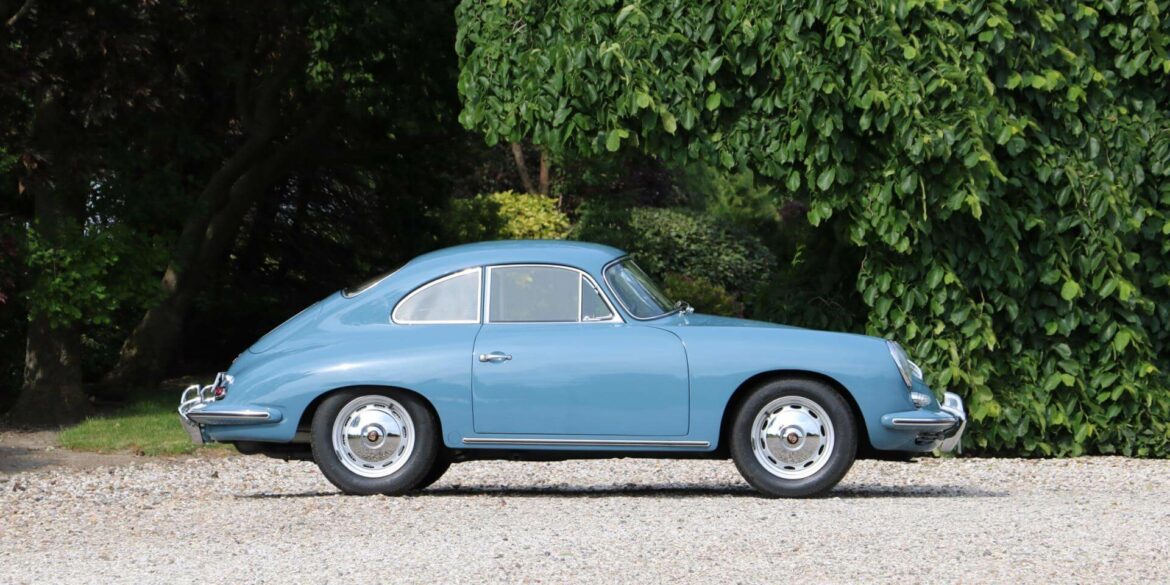
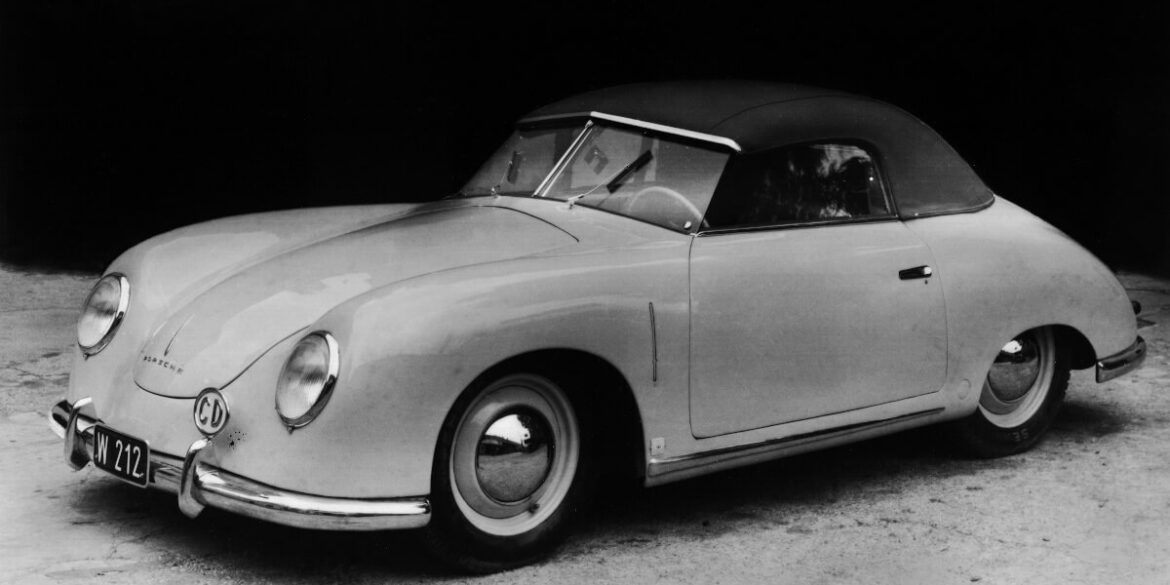
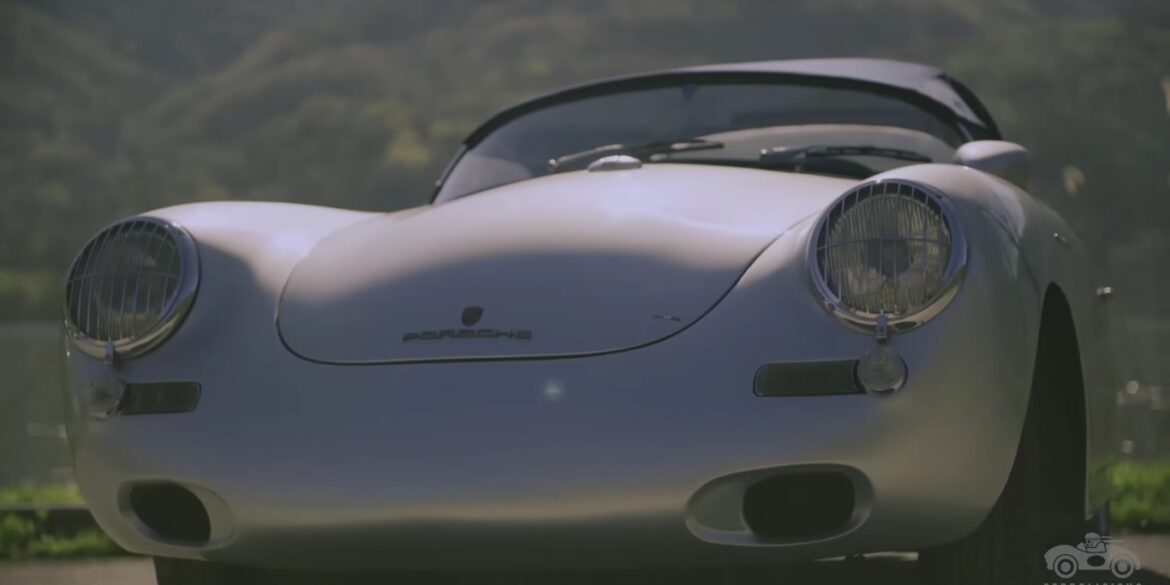
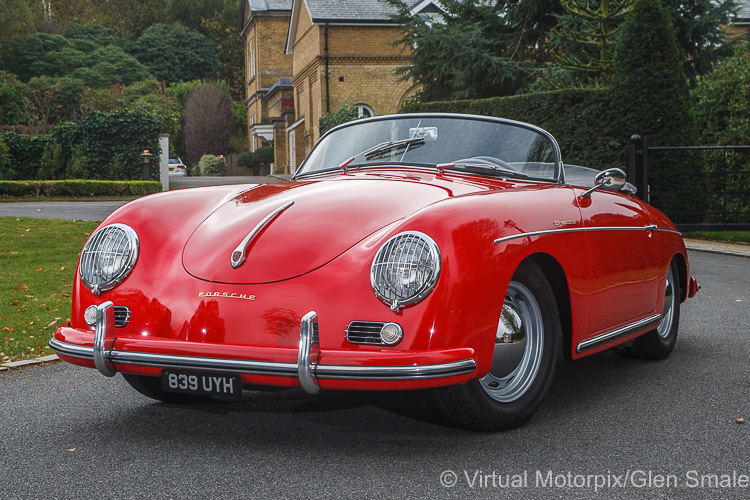
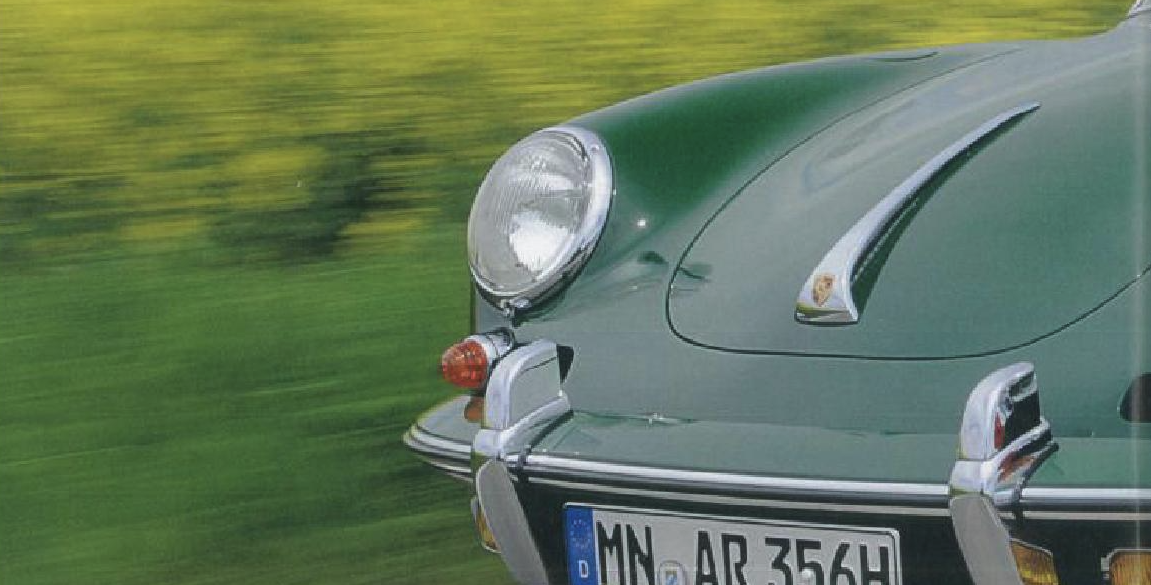
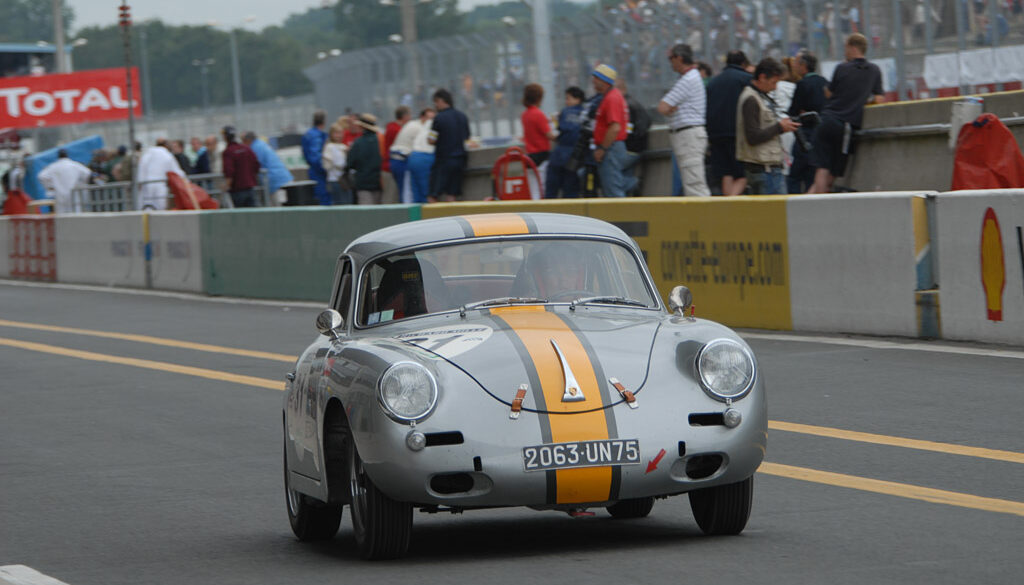
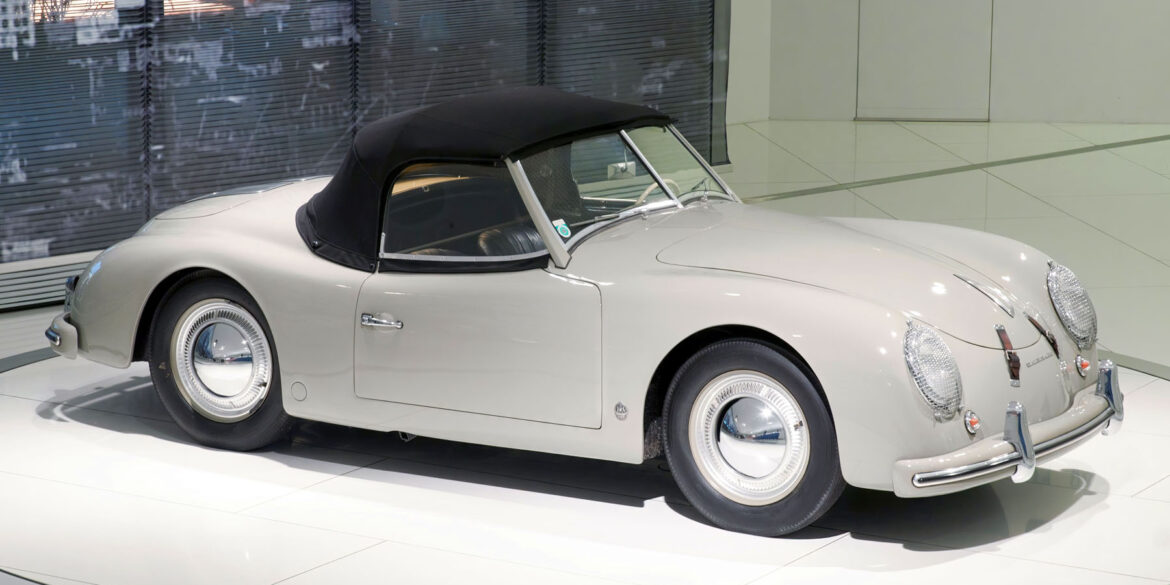
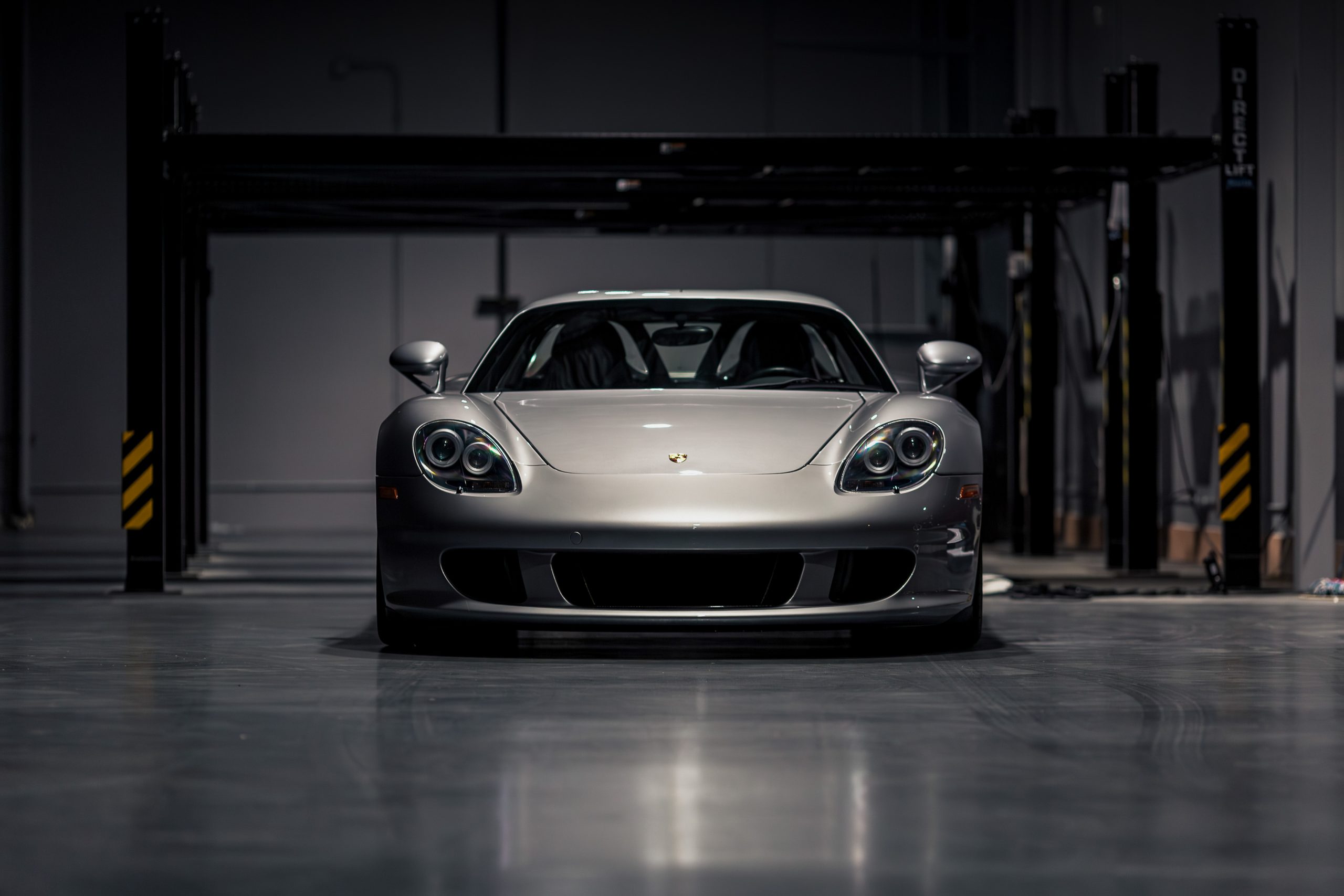
Rod Emory and his team at Emory Motorsports are experts in restoring and customizing Porsche 356 coupes and convertibles. Although this timeless model ceased production in 1956, it remains a favorite of car collectors worldwide. One of their best creations, the “Emory Special”, offers a modern twist on this classic...
Porsche 356 Engine Codes There are several important numbers to identify a 356 engine. The first, and most obvious one, is the serial number, which uniquely identifies each engine. It is on the “third piece” of the case, or timing cover, below the generator stand (or on the generator stand...
Barn Find Porsche Becomes A Twin Turbo Frankenstein Build How we made the 1959 Emory Outlaw RHD Coupe in GT SilverRod Emory is a legend in the Porsche game – so when he’s got a new build, you know it’s going to be worthy of an in-depth look. His 356...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1952 – 1954 Porsche 356/1100 Coupe (Pre-A) Pictures & Gallery...
Proven through competition Engineering, design, innovation; while the list is long for what describes the Porsche name, it can be distilled into one word; racing. Even before the days of cars that would bare his name, Dr. Ferdinand Porsche believed competition was the ultimate test for proving excellence in design...
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 Super 90 Roadster Pictures & Gallery...
Porsche – The Golden Years: Leonardo Acerbi © Virtual Motorpix/Glen Smale It is always a pleasure when a top-quality book lands on my desk, so when Porsche – The Golden Years arrived at the Porsche Road & Race offices, I was especially pleased. We had the pleasure of reviewing Ferrari...
Beginning in 1954, a new version of the Pre A 356 was introduced that is now known as the Porsche 356 Pre-A Carrera, with a powerful engine that was available in coupe, cabriolet, and Speedster variants. Highly desirable today, the Carrera name denotes the race inspired 1500 cc four cam motor that produced an astounding 110 hp. Approximately 97 of these motors were produced sometime between 1954 and early 1955. The Carrera versions would continue in the next generation 356 as the Porsche 356 A Carrera.
A Drive In An Emory Outlaw 356 Third generation SoCal gearhead Rod Emory takes Jay through his 1958 Emory Special and 1959 Emory Outlaw....
Did you know that 2023 sees the Porsche 356 C turning 60? We think it’s a birthday still worth celebrating, even in a year with so much else going on in it. This fine example has been living in a garage in Bielefeld for more than half its life and...
The 356 B T5 Coupe was the direct replacement of the Porsche 356 A Coupe. The T5 Coupe bodies were produced by German coachbuilder company Reutter. The 356 B T5 Coupe played a huge role in the growth seen by Porsche in the early 1960s. Like the Cabriolet, Roadster, and Notchback Coupe siblings, the Coupe was offered with 1600, 1600S, S90, and Carrera engine options paired to a four-speed synchromesh 741 transmission. In late 1961, Porsche introduced the T6 body and updates, which built on the success of its very popular predecessor.
Porsche 356 – Made by Reutter: by Frank Jung © Delius Klasing Verlag When the second edition of this fine publication was released back in April 2019 in German, I enquired immediately as to when the English edition would be available. I was told it would be coming onto the...
1951 – 1953 Porsche 356/1300 Split-Window Cabriolet (Pre-A) Pictures & Gallery...
In keeping with FIA regulations, Porsche created a new lightweight 356 with help from Abarth. After Porsche had considered numerous Italian companies to manufacture a lightweight 356 body, they settled on Abarth. Franco Scaglione penned the first initial drawings which attempted to reduce frontal area, overall height. Included was an adjustable scoop on the rear deck lid. Made entirely of aluminum, Abarth's body was smaller than the Reutter 356.
Collecting Cars is currently offering a 1957 Porsche 356 A Speedster that was purchased and owned for 50 years by the famous co-creator of Woodstock Music & Art Festival, Michael Lang. Michael Lang started out as an owner of a head shop that was based in Coconut Grove, Florida. After...
1955 Porsche 356/1500 Continental Cabriolet Pictures & Gallery...
In the fragile postwar years, the team behind the first Porsche was driven by two forces: stubborn ambition and harsh reality. They had the vision for a true sports car, but building one was another matter entirely. The sleek shape of the Porsche 356 came together relatively quickly, but under...
Porsche 356 Spare Parts Catalogs (1950 – 1959 Model Year) Porsche 356/356A Parts These official Porsche PET Diagrams and codes for the 1950 to 1959 Porsche 356 models are free for your to download and view. Whether you’re working on your own Porsche 356 and need the total parts guide or...
1956 – 1959 Porsche 356A/1600 Coupe Pictures & Gallery...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
The Porsche 356/1 was the first real car created by Ferdinand "Ferry" Porsche. This prototype car was a two-seater open roadster with a mid-mounted, air-cooled flat-4 engine of 1,131 cc displacement. While the body was an original design, most of the mechanicals were from the Volkswagen Beetle. Only one 356/1 was made.
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 S Coupe Pictures & Gallery...
Porsche 356/2 Gmünd Cabriolet Specifications type Series Production Car production years 1948 – 1951 built at Austria production 41 price $ $ 3,750 engine Type 369 Flat-4 position Rear, Longitudinal valvetrain Pushrod OHV fuel feed Dual Solex 26 VFJ Downdraft displacement 1086 cc / 66.27 in³ compression 6.5:1 power 29.8...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1956 – 1959 Porsche 356A/1600 Super Coupe Pictures & Gallery ...
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 Super 90 Cabriolet Pictures & Gallery ...
For decades, Porsche has established itself as a renowned car manufacturer, celebrated for its adaptability and agility. It has consistently catered to the desires of racing enthusiasts and discerning clients by creating special versions of their beloved cars. During the early 1960s, the 356s were no exception to this tradition....
Background Introduced at the 1955 Frankfurt Motor Show, the Porsche 356 Carrera marked the first appearance of this legendary performance car nameplate. Central to the Carrera’s spec sheet was the special race-bred engine developed since 1952. Dr. Ernst Fuhrmann was tasked with reworking the classic Porsche flat-four into a world-class...
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 S Roadster Pictures & Gallery...
Kim Copperthite watches the Porsche 919 Hybrid Evo during its record run at the Porsche Rennsport Reunion VI, Laguna Seca, 2018 (© Mike Copperthite) It is interesting how, sometimes when you trace an old classic car or historic racer back to its roots, you end up not far from the...
Amongst Porsche 356 enthusiasts, perhaps no model is more coveted than a C-Series Carrera 2. The Carrera 2 represents the culmination of Porsche’s racing technology fitted into a road car package and the ultimate performance-first sports car in the 356 model lineup. The 1,966-cubic centimeter, mechanically complex four-cam Type 587/1 engine was the most powerful unit that Porsche had ever created for a production car, developing 130 brake horsepower at 6,200 rpm.
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1962 – 1963 Porsche 356B/2000GS Carrera GT Pictures & Gallery ...
Want to Join the Outlaw Gang? Rod Emory makes some of the most insane modified Porsches out there. This Porsche MOMO 356 RSR Outlaw built by Rod Emory is currently for sale and it’s an absolutely beautiful car unlike any other on the road. This car debuted in 2019 at...
Porsche 356C Driven In today’s video, we don’t learn much – but we do get to see me go rather gooey over a 1964 Porsche 356C....
Episode Two: The Porsche 901/912 Summary Welcome to The Audiobahn, the Stuttcars.com podcast focused on all things Porsche. In our first series, we’re exploring the history of venerable 911: its history, origins, achievements, and future. Audiobahn Episode Two is all about the Porsche 901/912, the car unveiled in 1963 at the...
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 Super 90 Coupe Pictures & Gallery ...
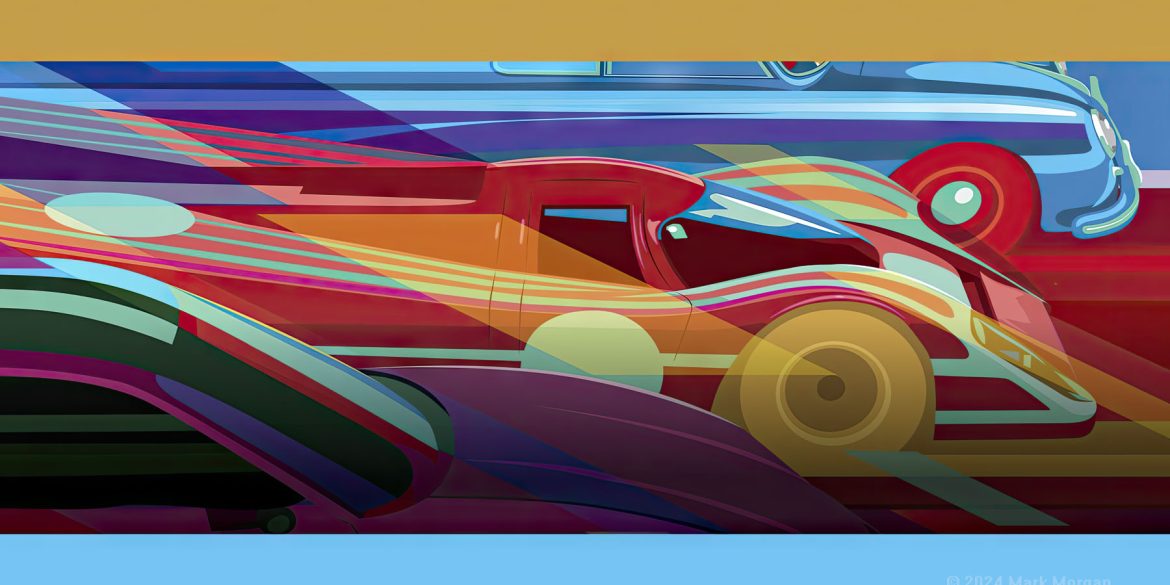
If you were lucky enough to visit Rennsport Reunion 7 in Monterey, California, then chances are you gazed at one of Mark Morgan’s illustrations without even realizing it. An illustrator based in the U.K., Mark has mixed his passion for Porsche and his artistic talents to yield some truly exciting...
Episode One: The Porsche 356 Summary Welcome to The Audiobahn, the Stuttcars.com podcast focused on all things Porsche. In our first series, we’re exploring the history of venerable 911: its history, origins, achievements, and future. In our first-ever Audiobahn episode, we’re starting with where the 911 began: the Porsche 356. Read...
We Love This 1964 Porsche 356 Why does Catherine Sutton drive? Because looking after her car is a choice, not a chore. She presides over her 1964 Porsche 356 with its wrinkles and patina as if it were a loved one, carefully operating the clockwork of its clutch and accelerator,...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
Despite looking outwardly similar to the preceding models, Porsche thoroughly updated their 356 line in 1956 and called their new model the 356A. At the core, this included a larger 1600 cc engine, but also a curved-glass windshield and a thoroughly revised suspension. At the 1955 Frankfurt Motor Show in September of 1955, Porsche released the 356A/1600 to the world with cabriolet, coupe and speedster bodies from Reutter. The 356A/1600 was a great performer, good for a sprint to 60 mph in 13.5 seconds and hit a top speed of 109 mph.
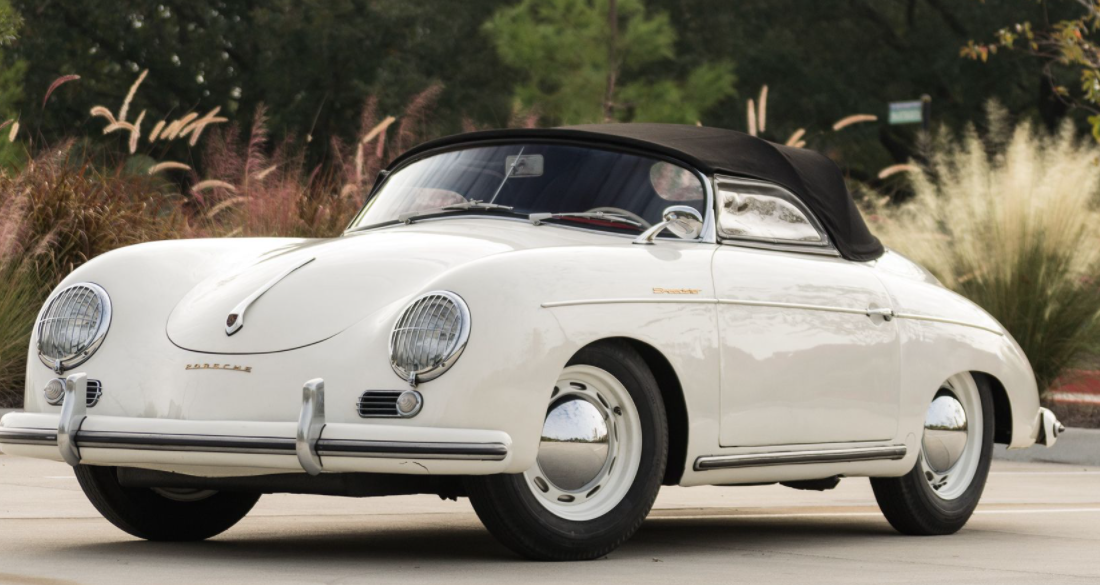
An export hit, built in response to customer demand: the American importer Max Hoffman requested a Porsche costing less than 3,000 dollars for his market. The 356 Speedster was the answer, naturally with a spartan equipment specification. But the lightweight car was a big hit in the USA. It was used mainly for motor racing and soon became a regular feature of the motor sport scene.
8 minutes of Porsche 356 goodness British Touring Car runner-up Sam Tordoff had quite the time in the Fordwater Trophy at Goodwood Revival 2018. After grabbing a pole from Darren Turner’s Aston Martin DB2, Tordoff’s Porsche 356 stalled when the flag dropped. The ensuing drive was absolutely scintillating: enjoy eight...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
It only happens once in a lifetime; your 75th birthday. This June 8th marks Porsche’s 75th anniversary so Bring-a-Trailer auction juggernaut decided to give Porsche enthusiasts a special treat; Gruppe P. A collection of 7 truly impressive Porsches whose auctions collectively end on June 8th, Gruppe P is likely to...
Available in all body styles, the Porsche 356 A Carrera featured the race car-derived 1500 cc four-cam engine (type 547) developed for the Porsche 550 Spyder. Rated up to 110 hp, it was the top performance 356 A model available. Variants included the Carrera 1500GS and Carrera 1500GT, differentiated by their horsepower. In 1958, Porsche updated the Carrera engines (now type 692), increasing the displacement up to 1600 cc and output increased to 105 and 110 hp respectively. In 1959 horsepower for the GT increased again to 115.
One of the most confused of all Porsche is this DKS or Dreikantschaber. It might appear like a mid-engine RS61 Coupe, but it is a rebodied 356B with a rear-mounted engine. Unlike the earlier 356s, this one featured fared-in driving lights and cut-off greenhouse reminiscent of of the RS61 coupe. Porsche didn't give this new a car a name since it was homologated and considered a Carrera 2 by the FIA. It was nicknamed Dreikantschaber.
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
The Ultimate Book of the Porsche 356 by Brian Long © Veloce Publishing Limited Brian Long’s original book on the Porsche 356 was published in 1996, and this was later printed in softback form. A few years later a revised version of this book was published which included more colour...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
While the staff here at Stuttcars can never get enough of Porsche’s latest GT3s and 963 prototypes, there’s true reverence for the sports car that founded the company, the 356. It’s true beauty in its simplicity, the 356 has earned a spot in collections the world over with a reputation...
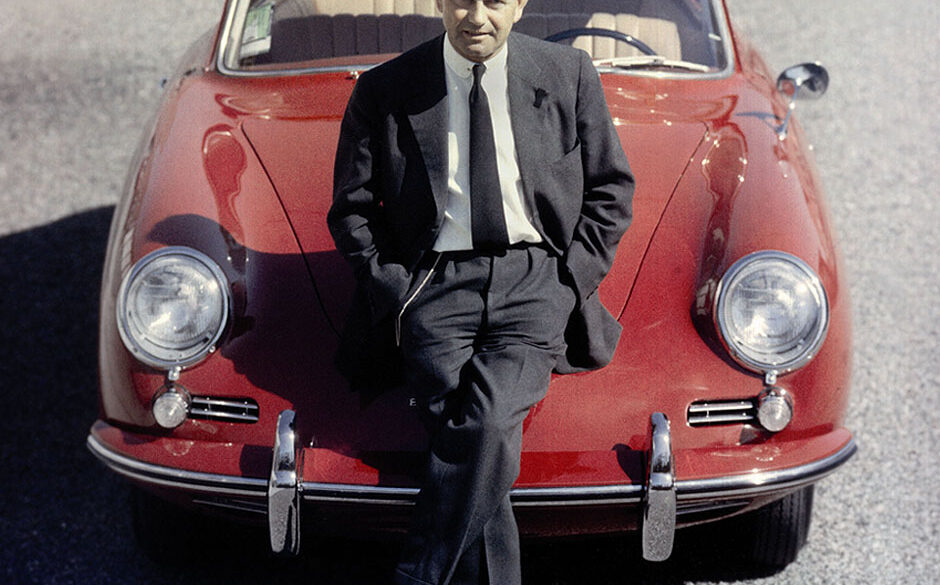
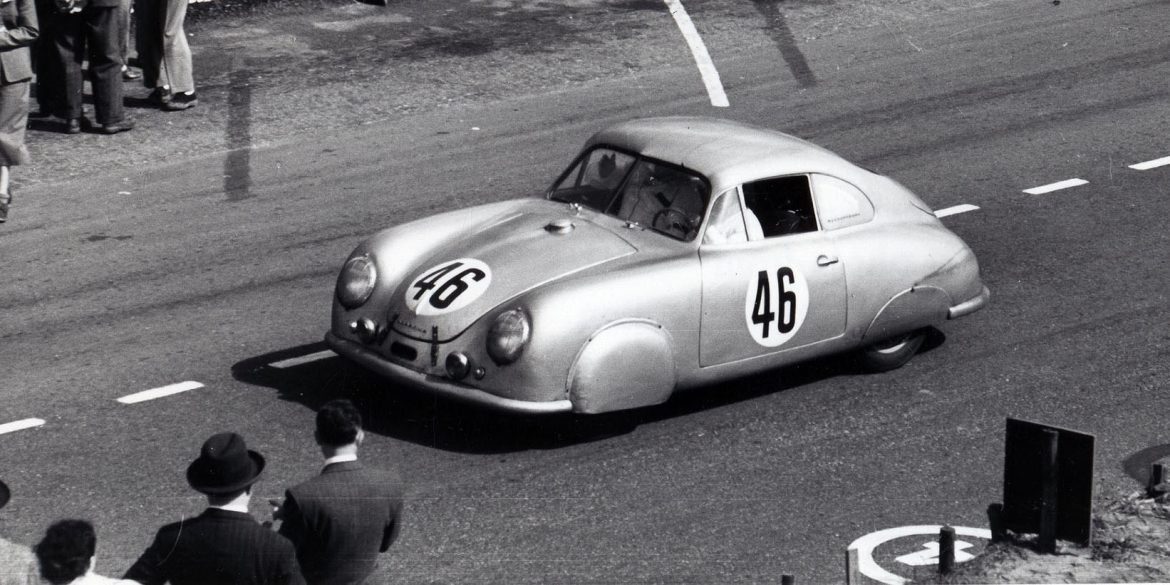
The Porsche 356 Story Porsche engineering company had designed cars for other companies for a long time, but it was finally in 1948 that a first “Porsche” was made under the leadership of Ferdinand Anton Ernst “Ferry” Porsche, the son of Ferdinand Porsche. At that time Porsche company was located...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
The Auratium Green 356 A Type 2 Please turn on Closed Captions to enjoy this film in English. This is the story of following a trail of gas into the a tractor barn. It is a story of a family legacy of mechanical inclination and a desire to learn from...
Emory Motorsports is a company that makes the best Porsche “Outlaw” cars. The attention to detail is stunning and there are few more beautiful machines to exist. This particular model based on a 1959 Porsche 356A is no exception to Emory Motorsports’ reputation. It’s immaculate and absolutely gorgeous. The car...
Invitation to race from Charles Faroux Charles Faroux was a car enthusiast, a racing official, a leading French motor-publication editor at La Vie Automobile and a charmer. Europe’s major automobile manufacturers entrusted their engineering secrets and newest models to him in hopes of a favorable review. Everyone respected his opinions....
Generally speaking the early models or so called ‘Pre A 356′ models are more desirable than the later models. At the top of the pyramid and the most exclusive is the Carrera version which carries the legendary 4 cam ‘Fuhrman’ engine. But just below that comes the ‘Super’ speedster. The ‘super’ version had more horsepower (75 vs the standard 60) and the powerful ‘type 528 engine’ for the 1500 Super version.
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
For some, motor racing is an inevitability. It is a passion that they are born with and it is just a matter of time before they slip behind the wheel of a racing car. For these chosen few, this inborn factor elevates them to a level above the rest of...
Bring A Trailer is offering two beautiful Porsche examples, a 2016 Porsche Cayman GT4 and a 1964 Porsche 356C Coupe. 2016 Porsche Cayman GT4 This 2016 Porsche Cayman GT4 was acquired back in December 2015 from Champion Porsche of Pompano Beach, Florida. Exterior features include a white finish and GT4-specific...
1951 – 1953 Porsche 356/1300 Split-Window Coupe (Pre-A) Pictures & Gallery...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 Roadster Gallery Porsche 356 B 1600 Roadster (T5) – Pictures & Gallery Porsche 356 B 1600 Roadster (T6) – Pictures & Gallery...
Four-Cam Coupe Porsche 356 Carrera GS/GT Driven The Porsche 356 brought the automaker into a new era. The model started the trajectory that would eventually lead to the venerable 911, and prototype versions of the car earned Porsche its first major achievements in endurance racing—namely a class win at the...
Emory Motorsports stands as the global benchmark for creating bespoke Porsche 356 vehicles, melding the essence of the Porsche brand with Rod Emory’s distinctive vision for its most iconic models. Renowned for their unparalleled craftsmanship, Emory Motorsports produces the most exceptional, meticulously crafted 356 custom cars in the world. Going...
1962 – 1963 Porsche 356B/2000GS Carrera 2 Pictures & Gallery...
1954 – 1955 Porsche 356/1300 Super Cabriolet (Pre-A) Pictures & Gallery ...
Of all the Carreras, the 1959 de Luxe was best suited for the road. Not only was it the most luxurious 356, but it was also was the only year to get the large 1600cc 4-cam engine. The Type 692/2 engine was a much different engine than the 1500cc unit it replaced. The newer unit used plain main bearings instead of roller bearings. Furthermore, the distributors were moved to the end of the crankshaft and the engine shroud was better attached to the 356A body. With twin Solex carburetors, the somewhat detuned version offered 105 bhp @ 6500 rpm.
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
Around 20 Super 90 Coupes were ordered with the lightweight GT package for racing. They used aluminum panels, a lightweight interior and plexiglas windows to shed over 200 lbs off the standard production coupe. Inside the car came equipped with a roll bar, leather-strap window lifts and speedster seats. Aluminum exterior panels included the doors, hood, rear deck lid.
Issimi is currently offering for sale a 1963 Porsche 356 B Carrera 2 GS whose engine has been rebuilt by renowned 4-cam specialist Baumann. Back in the 50s, in their desire to become a world-class sports car manufacturer Porsche created their first bespoke engine. Before then, Porsches used a Volkswagen...
A True Porsche Specimen The Porsche 356A Speedster is a beautiful car and an important part of Porsche’s long motoring history. There’s a 1958 version of the car for sale at Bring A Trailer right now. The current bid is at $205,000 and the auction ends in seven days. If...
With lessons learned from 356 No. 1, Porsche developed the 356/2 as a production-ready version. The biggest concession to useability was repositioning the engine back behind the rear wheels as the original VW design. Like 356 No. 1, 356/2 was built as two-seat roadster using VW parts.
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1957 – 1958 Porsche 356A/1500GS Carrera GT Speedster Pictures & Gallery...
Porsche & Le Mans Newly released “Racing with Giants” video features archival footage of Le Mans past and present, along with interviews with multiple drivers and Porsche team principals, including Allan McNish, Patrick Long, Jacky Ickx and Nick Tandy. Porsche has long competed at Le Mans, though recently solely in...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 S Notchback Coupe Pictures & Gallery...
A Drive In the Emory Outlaw Roadster This 1960 Porsche 356 Roadster is a rather unique example of the Emory Outlaw essence. It features a 205-hp, 2,650 cc FAT 914 engine, 911 rear suspension, 911 5-speed transmission, aluminum hood, tonneau cover & headrest fairing and a Speedster windshield. There are many...
Ferry Porsche had in fact requested Swiss technicians to make a less sporty and more elegant version of the 365 B and thus the 1600 Beutler Coupè was born. This project is a 2+2 based on a Porsche 1600. Like the Porsche, the car is built on a VW platform, but includes Porsche elements such as the brakes and the engine. It was built in 5 copies before production was stopped in 1957 due to a change in commercial strategies by the German company.
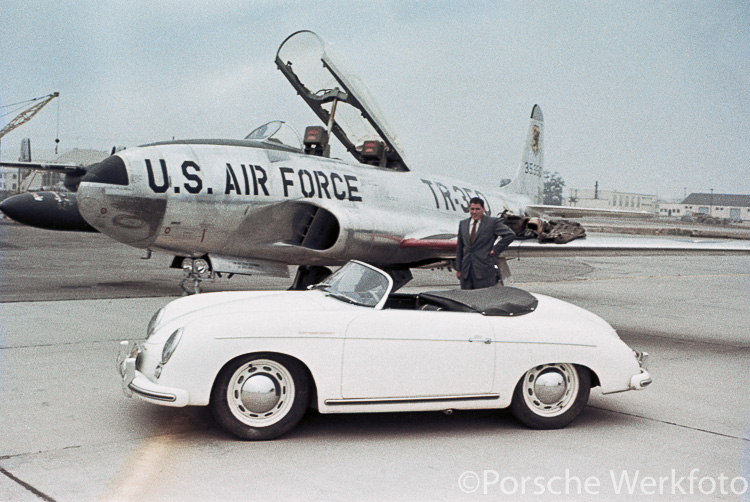
Porsche 356 Cabriolet competing at an aerodrome race in the USA, ca. 1952/1953 America has for decades been Porsche’s biggest market, and this was important for the young and growing company. In some ways, the importance of this market even influenced the development of certain models. In this feature, Porsche...
Celebrations for the #55 Porsche 550 Spyder after finishing third in the 1954 La Carrera Panamericana. Sitting on the #55 car is Herbert Linge (left and Hans Herrmann (right). Sitting on the #56 car is driver Jaroslav Juhan with Porsche PR supremo Baron Huschke von Hanstein standing between the drivers...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
1956 – 1957 Porsche 356A/1300 Super Coupe Pictures & Gallery...
1954 – 1955 Porsche 356/1300 Split-Window Cabriolet (Pre-A) Pictures & Gallery...
A Beautiful Piece of Porsche History The 1960 Porsche 356B Roadster is an automotive icon. The vehicle is one of those highly sought after cars by collectors. That makes this particular one that’s for sale on Bring A Trailer special. The car has low miles (about 6,000) and looks absolutely...
It’s rare for a car to be considered as a part of a family. But this Porsche 356 Speedster managed to become not just a car but a family member as well. Watch the video to know more about this interesting story. ...
1956 Porsche 356 C “When you’re out there in something like this, people just stop and…it might not even look like a car at first…it might look like a small spaceship floating around out there,” says Matt Hummel, adding, “this is my favorite car to get lost in”. A mis-spelled...
For decades, Porsche has established itself as a renowned car manufacturer, celebrated for its adaptability and agility. It has consistently catered to the desires of racing enthusiasts and discerning clients by creating special versions of their beloved cars. During the early 1960s, the 356s were no exception to this tradition....
1957 Porsche 356 A Speedster – looking chocolate box pretty! It was Max Hoffman, the New York-based Porsche importer, who was instrumental in getting the factory to produce a lightweight sports car for local competition in the USA. Hoffman’s clients were demanding a stripped-down factory version of the 356 to...
1959 – 1963 Porsche 356B/1600 Coupe Pictures & Gallery...
SportErfolge: by Tony Adriaensens – page photographs by © Virtual Motorpix/Glen Smale Simply titled, SportErfolge (English: Success in Sport), this book came my way quite by surprise. It is not a book I knew anything about until I spotted it on the internet, and decided to look for a copy....
Sorry, but you do not have permission to view this content....