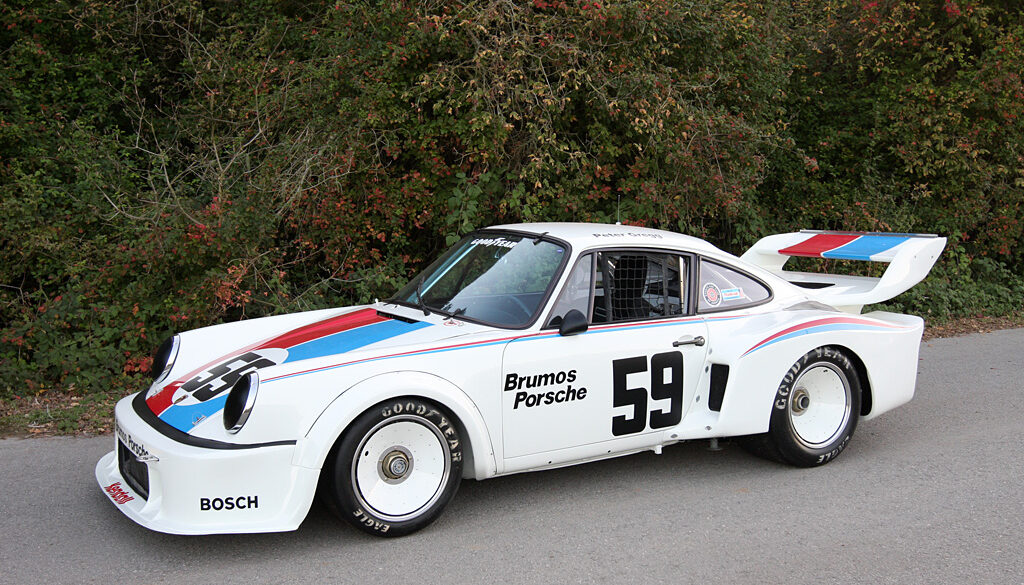
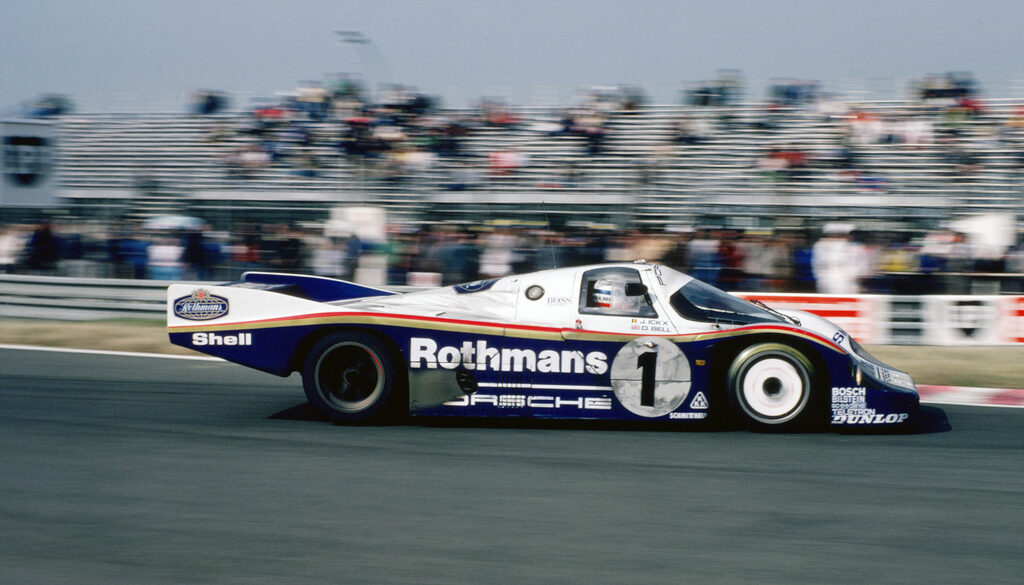
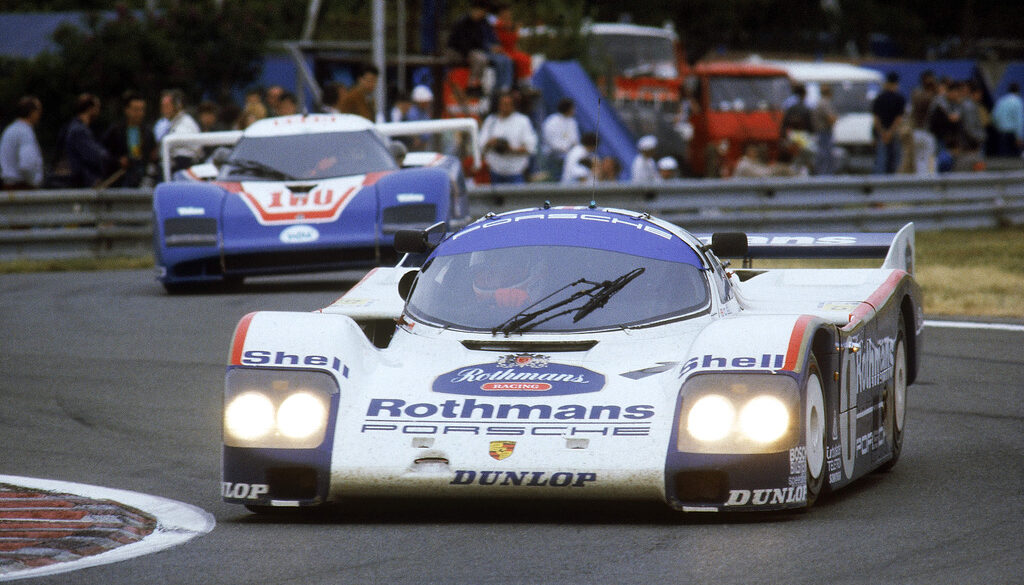
Jo Siffert was the first to take the 917 to Can-Am championship. The car he used in 1969, was the 917 PA Spyder. Although he participated in one Can-Am race in 1970 with a 917 K, that season he skipped. He was back from mid-season 1971 and now with the 917/10. Only two 917/10 were created in 1971. The chassis 001 was used for testing and the 002 by Siffert. He took part in six races out of ten, managed podium finishes three times and scored 4th in the season, like in 1969.
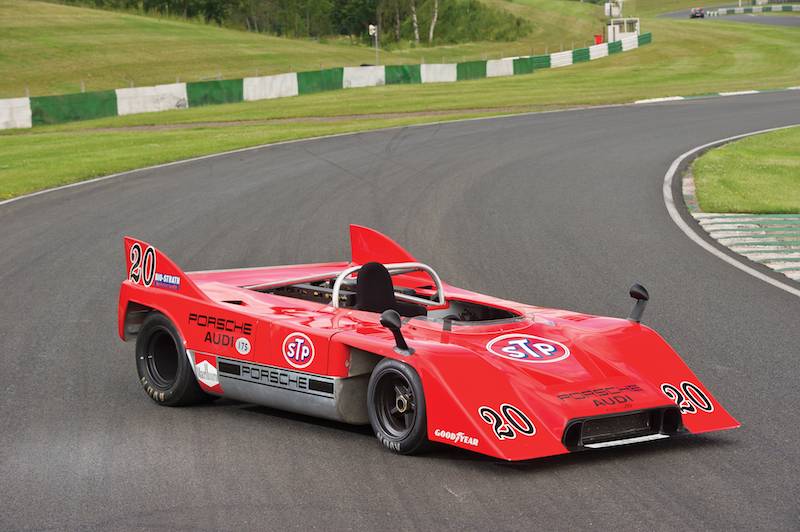
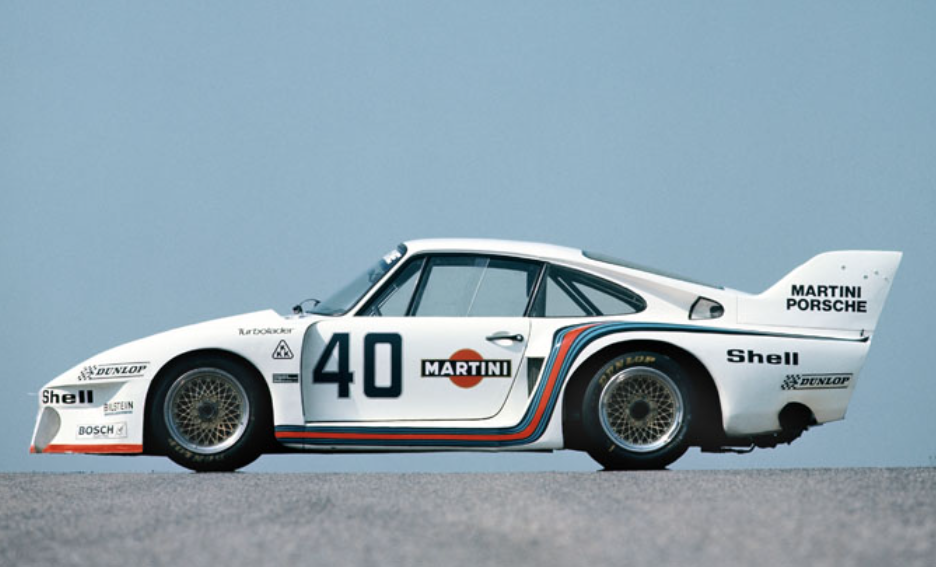
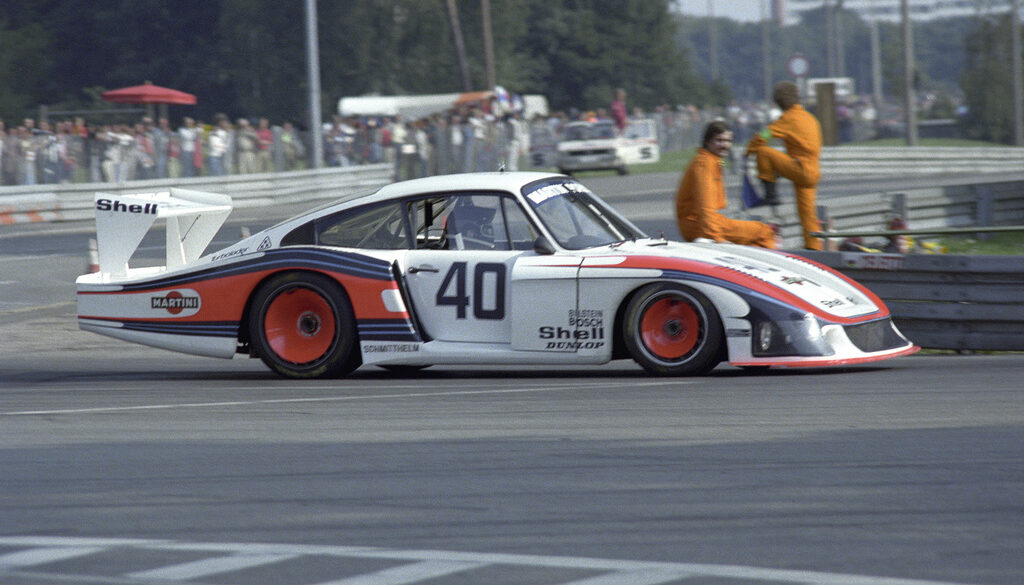
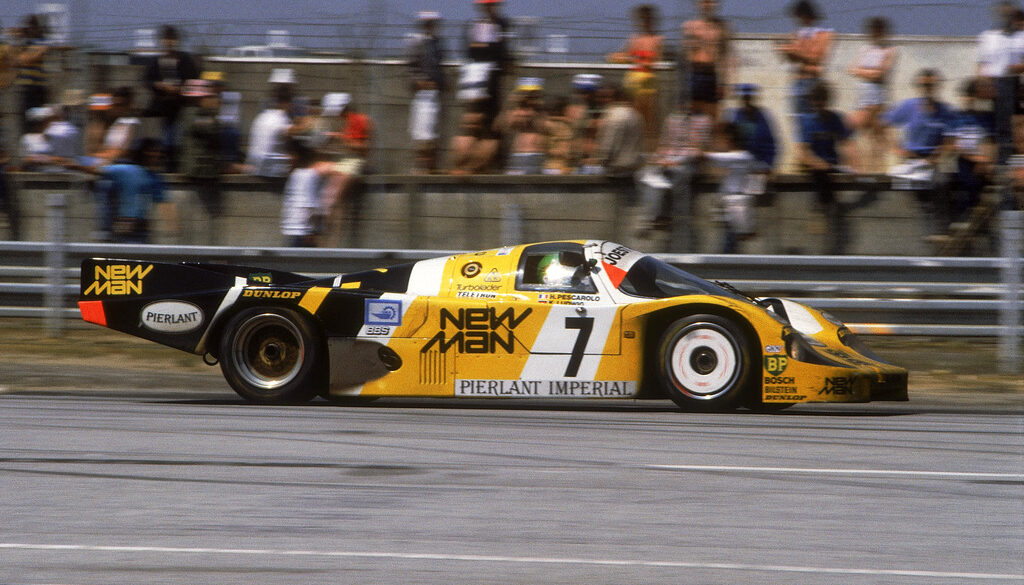
The 1972 917/10 was similar in its design to the 908/03, but, of course, had the 12-cylinder engine instead of the 3-litre flat-8. The 917/10-72 was first seen at the Interserie Nürburgring race on April 3. It was the chassis 004 car of Leo Kinnunen and Keimola Racing Team AAW. Kinnunen scored 4th in the first race, but would win the championship by the end of the season. The second Interserie race was at Monza on May 1st and that race was won by chassis 917/10-002 and Willy Kauhsen.
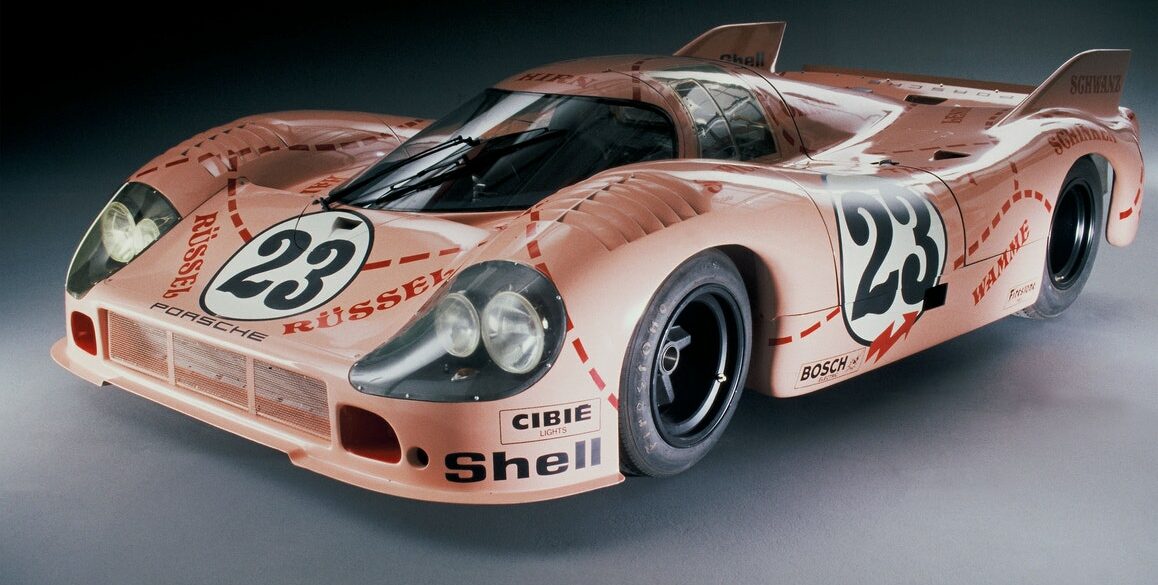
An attempt to blend the best aerodynamic characteristics from both the short-tailed 917 K and long-tailed 917 LH led to the the 917/20, otherwise known as the Pink Pig. The car's combination of a long body, stubby face, and wide hips gave it a pig-like look, which inspired Porsche designer Anatole Lapine to give the car a pink paint job with butcher cut lines covering the exterior. It was hugely popular at the 1971 Le Mans race, and was the fastest in qualifying and nearly came in fifth place, before a brake failure caused it to crash before the finish line.
The 917/20 Turbo is a confusing car - its chassis number reads 917/30-001, but it is not the real 917/30. In its first race it was called as the 917/10 Turbo. Sharp eye can detect that it was not just the 917/10 Turbo, but an evolution of it. At the same time it was not the evolution of the 1971 Le Mans 917/20. Still, the car should not be called as the 917/30 to distinct it from the "real" 917/30 Can-Am racers and in 1974 it was decided to call it as the 917/20 Turbo.
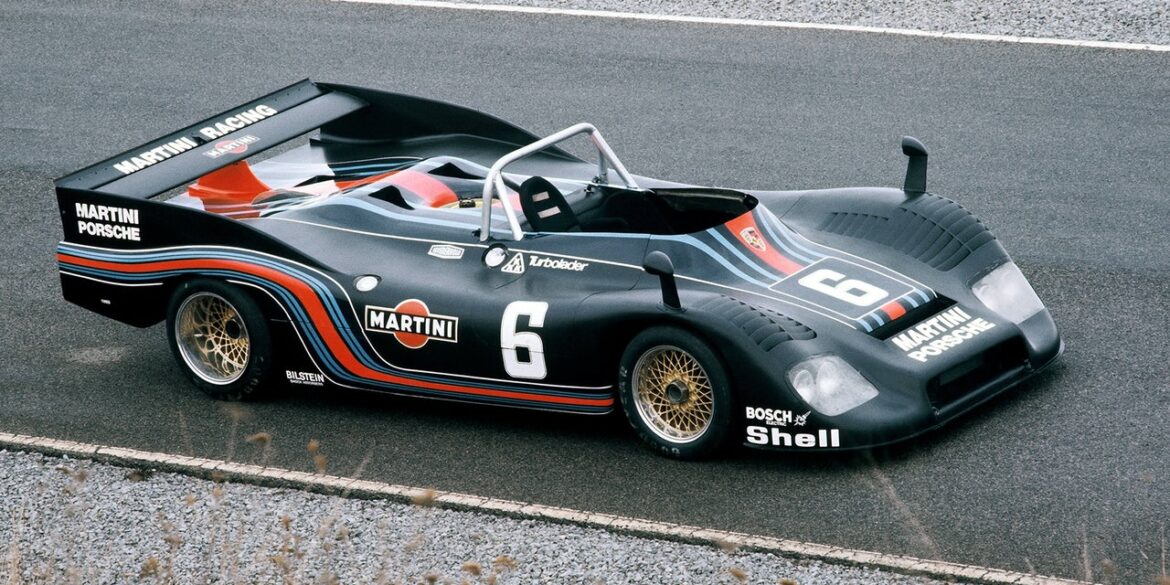
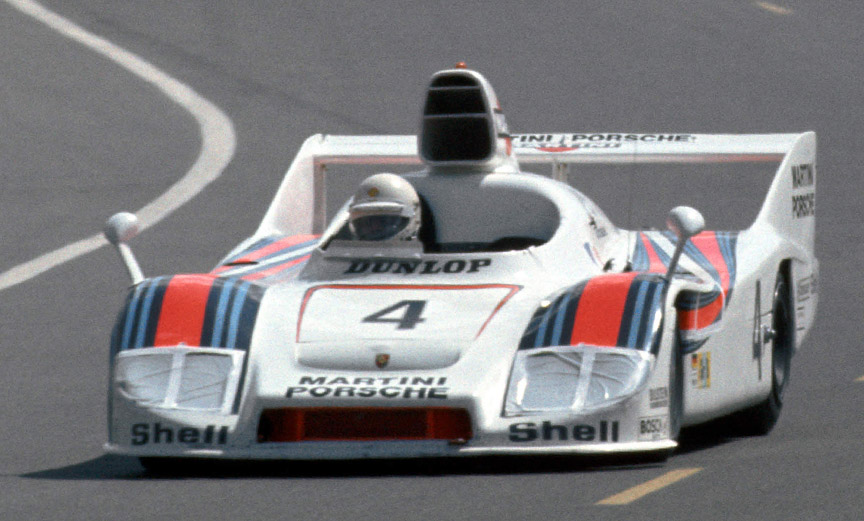
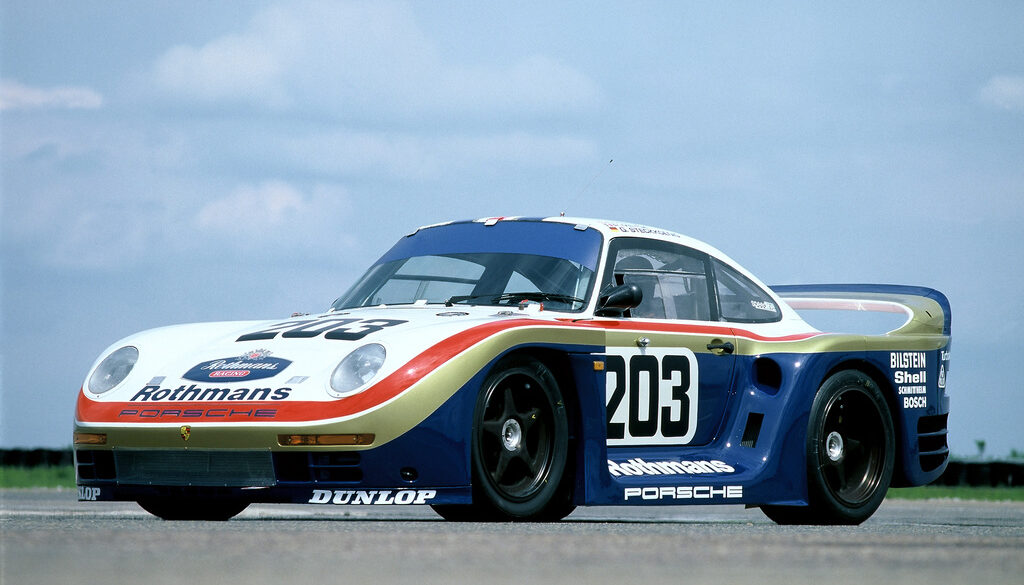
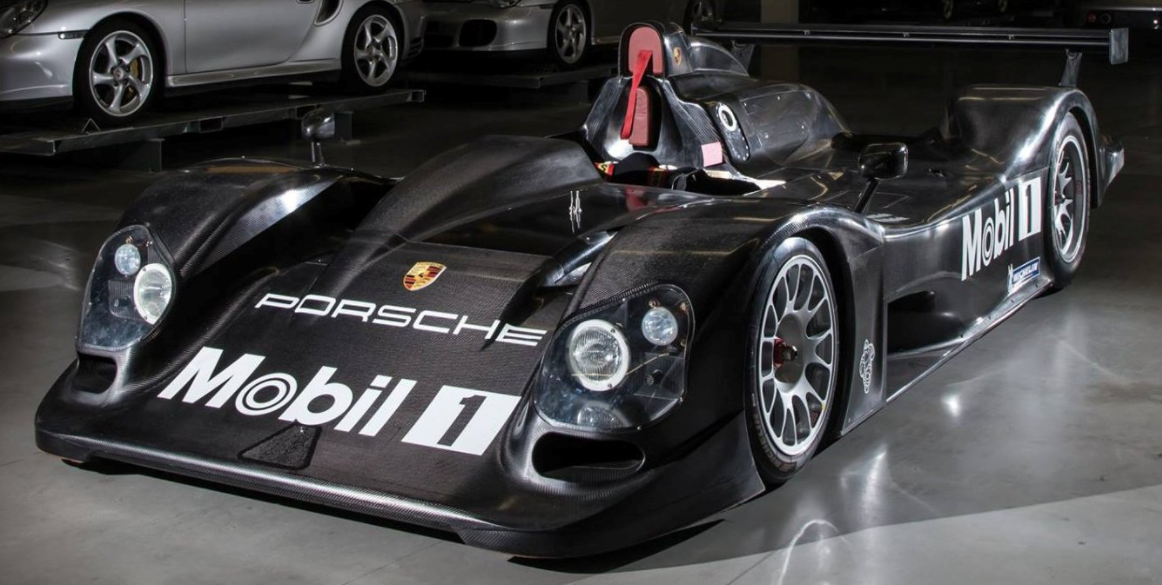
The final evolution of the 917 was created after Ferdinand Piëch had left the Porsche company in 1972. Two complete 917/30 Can-Am cars with 2500 mm (98.4") wheelbase were made for Roger Penske Enterprises racing team. They were chassis 917/30-002 and 003. The 001 car was not a real 917/30 and was raced in Europe at the Interserie. The Can-Am 917/30 had a 5.4-litre flat 12-cylinder twin-turbo engine which produced so much power that nobody really knew how much.
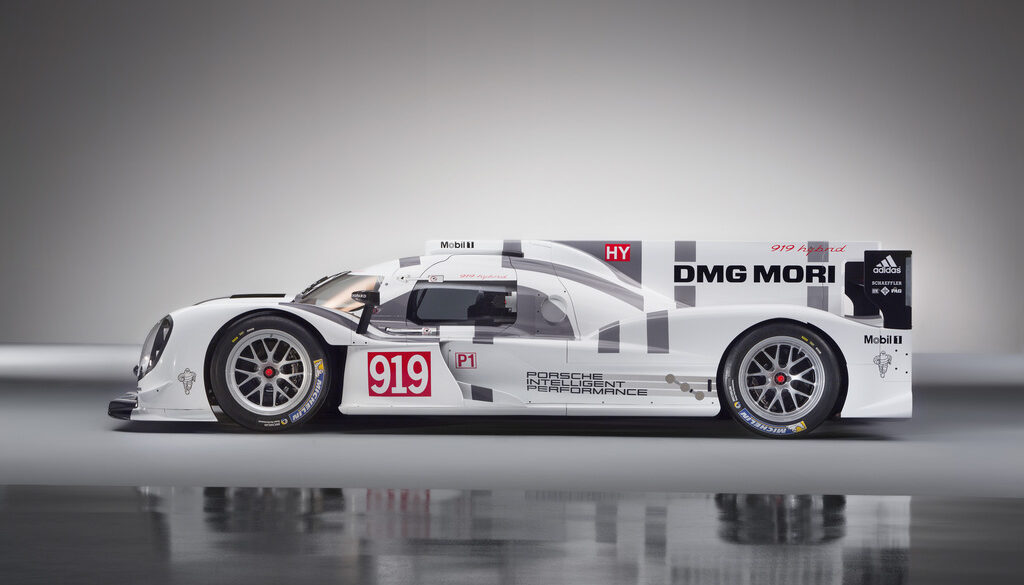
The Porsche LMP1-H (Le Mans Prototype Class 1, Hybrid) race car featured a hybrid system that consisted of a turbocharged 2.0V4 petrol engine at the rear axle and an electric motor at the front axle. The electric motor/generator unit (MGU) collected the energy from the front axle under braking and the AER exhaust energy recovery system operated on the exhaust gas - a separate turbocharger ran an alternator.
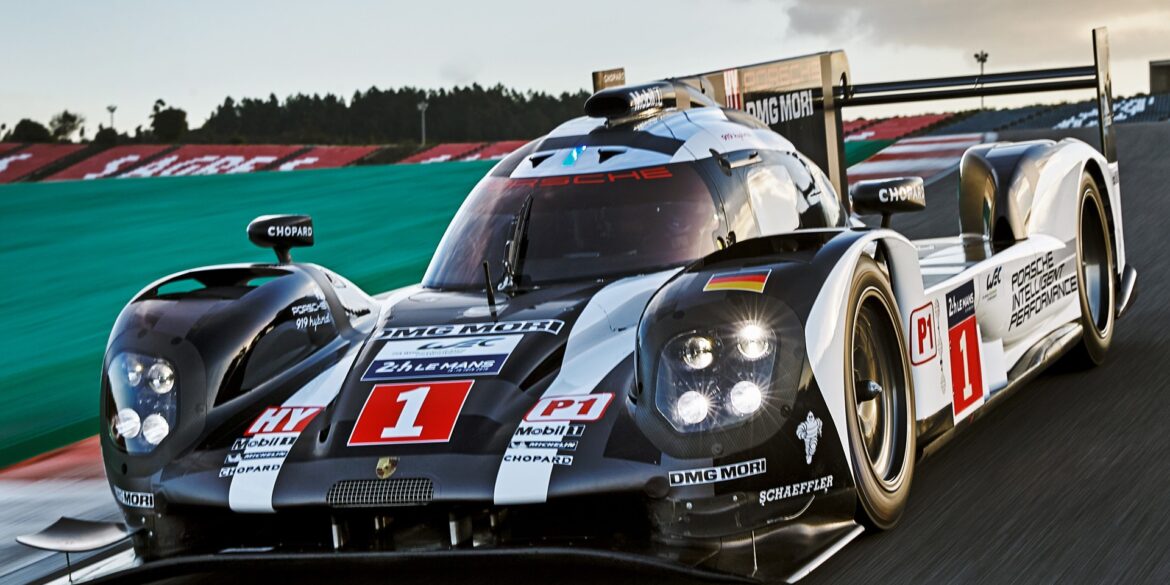
The 2015 season Porsche released a new version of their 919 LMP1 prototype which was reshaped and significantly upgraded to the Premiere class which uses an 8 megajoule hybrid electric system. It follows the 2014 car which had competitive but lackluster year against Audi and Toyota. Combined with a 2 litre, twin turbo V4 gasoline engine is the 8 megajoule lithium-ion battery which powers the front electric engine for a total power output nearing 900 to 1000 bhp.
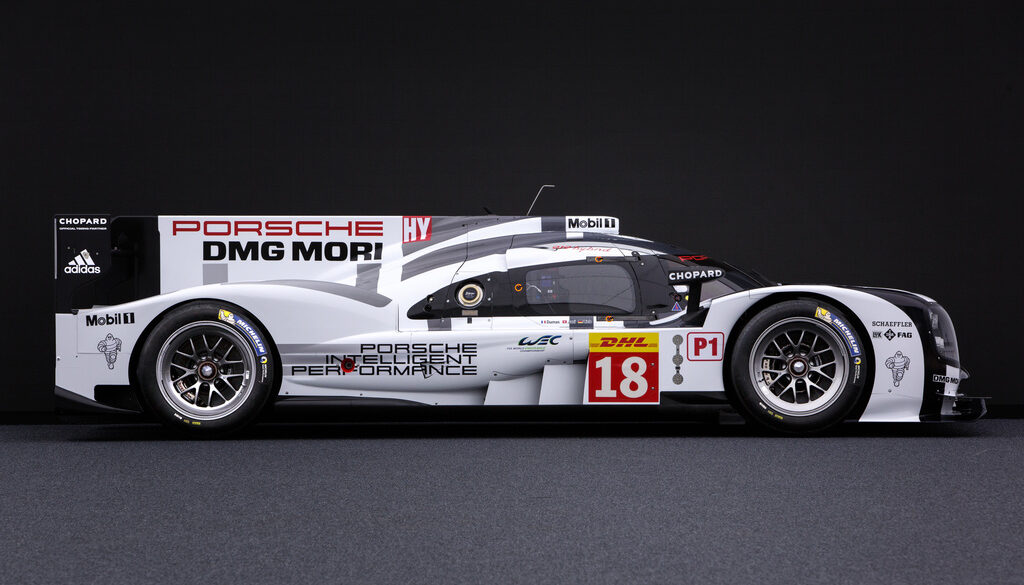
The third-generation 919 Hybrid (2016 MY) is powered by a turbocharged four-cylinder, two-litre petrol engine delivering almost 500 hp that drives the rear axle. The V4 engine, which is fully load-bearing, is turbocharged and features 4-valves per cylinder, DOHC, a Garrett turbocharger, direct fuel injection and an aluminium cylinder crankcase. In addition, the electric motor delivering more than 400 hp to the front axle. The latter is fed by two energy recovery systems.
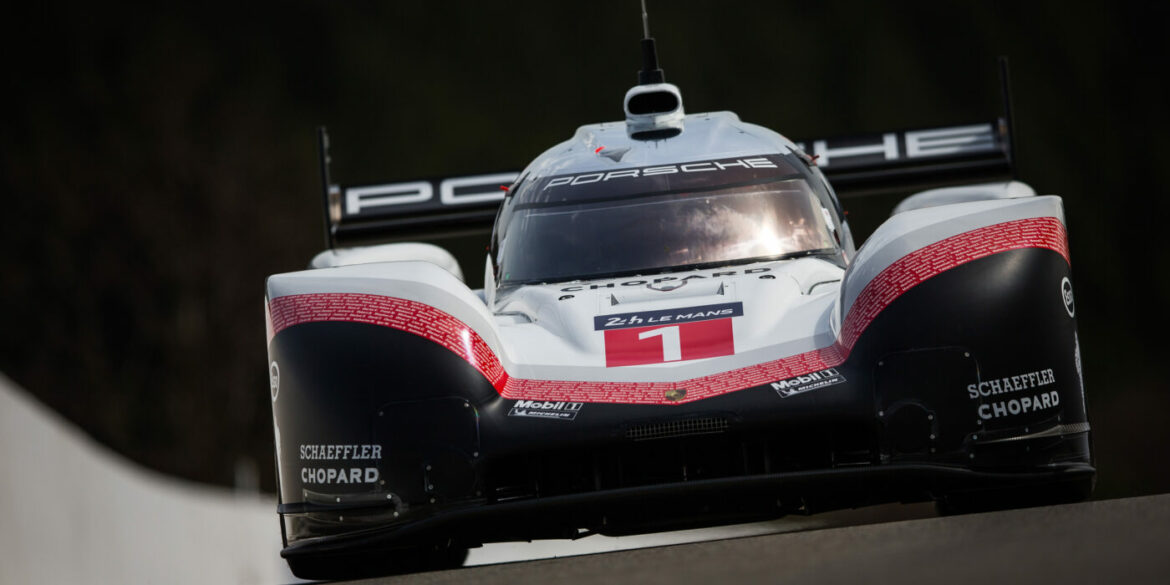
According to Porsche, it retained the monocoque from 2016, but 60 to 70% of the 2017 car was new, with the largest alterations being to its aerodynamic demands. This included a major redesign of the front of the 919 Hybrid with wider arches for the front wheels to make it less aerodynamically sensitive from small bits of discarded rubber from the track surface. Porsche remained in the 8 MJ (2.2 kWh) MGU category for the 2017 season. The engine was modified to be lighter and more compact, and Porsche stated that it was its most-efficient ever.
With the car retiring after the 2017 LMP WEC season, the Porsche team decided to throw it a truly memorable send-off. Freed from any restrictions brought upon by strict regulations in the class it competed in, Porsche threw out the rulebook and established a new benchmark. Amongst the notable parting gifts was a significant horsepower bump, increasing the turbo V4 to 720 horsepower from 500 horsepower. Additionally, the electric motor received a 10% boost, now generating 440 horsepower. In total this gave the 919 a remarkable 1160 horsepower.
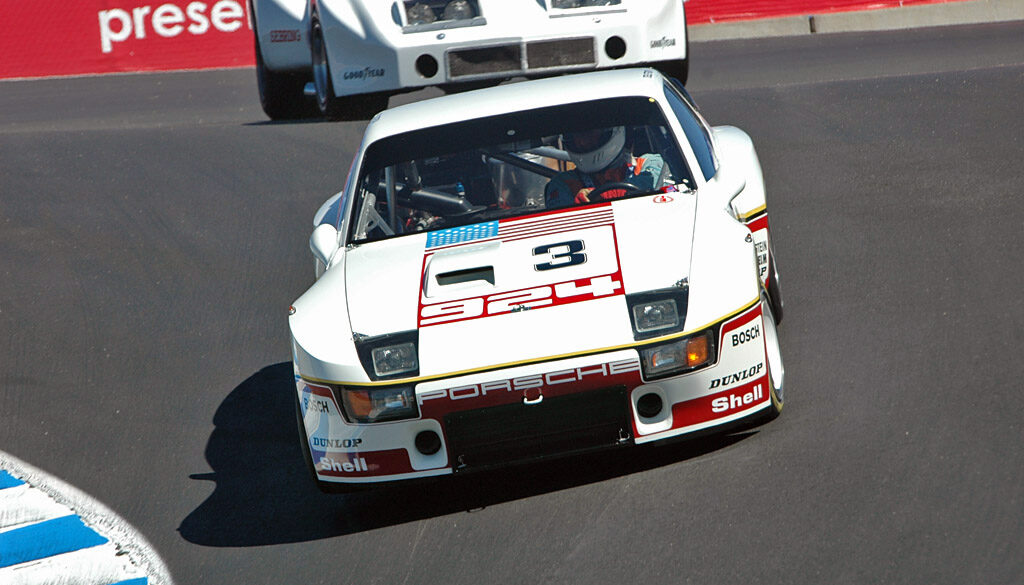
GTP cars were produced in 1980, three of which were special LeMans race cars. The cars had the 2.0L turbocharged 924 engine with a huge front-mounted intercooler and increased boost to increase output to 320 HP and 285 lbs/ft of torque. The engine used Bosch mechanical fuel injection and with a weight of 2050 pounds had a top speed of 180 mph. It was third in the GTP class, with an 6th place finish overall, and another finished fifth in class and 12th overall.
The Carrera GTR was the ultimate 924 Street/Race Car in 1981. The GTR had larger flares, larger wheels and tires, improved brakes and a whopping 375 horsepower from the 2.0L turbocharged dry-sump engine. At $75,000, the GTR would have cost over $200,000 in today’s money, but what you got was a 180 mph screamer for the street, but in full race trim.
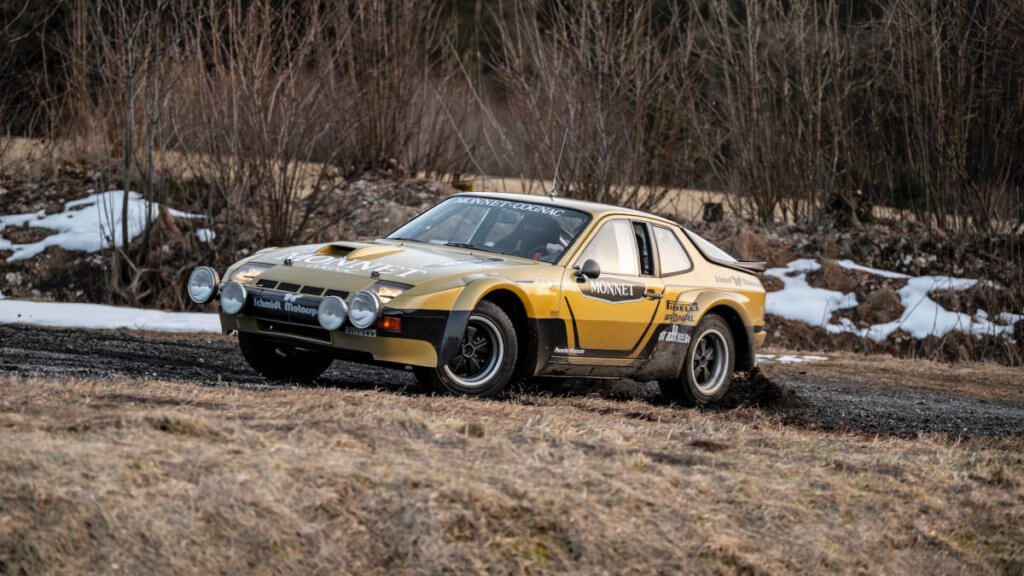
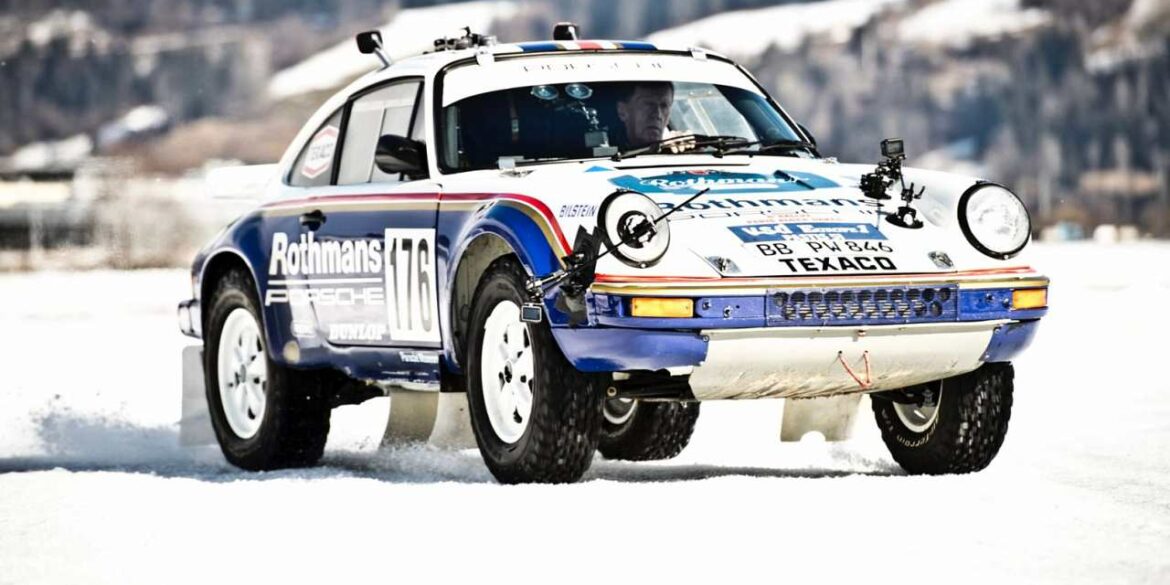
As a top-secret project, the Porsche Museum workshop and the Porsche Heritage department worked on a special front-engined sports car from 1981. 40 years ago, starting on May 15, this car competed in the Deutsche Rallye-Meisterschaft (German Rally Championship). Behind the wheel was non other than Walter Röhrl, with Christian Geistdörfer next to him.
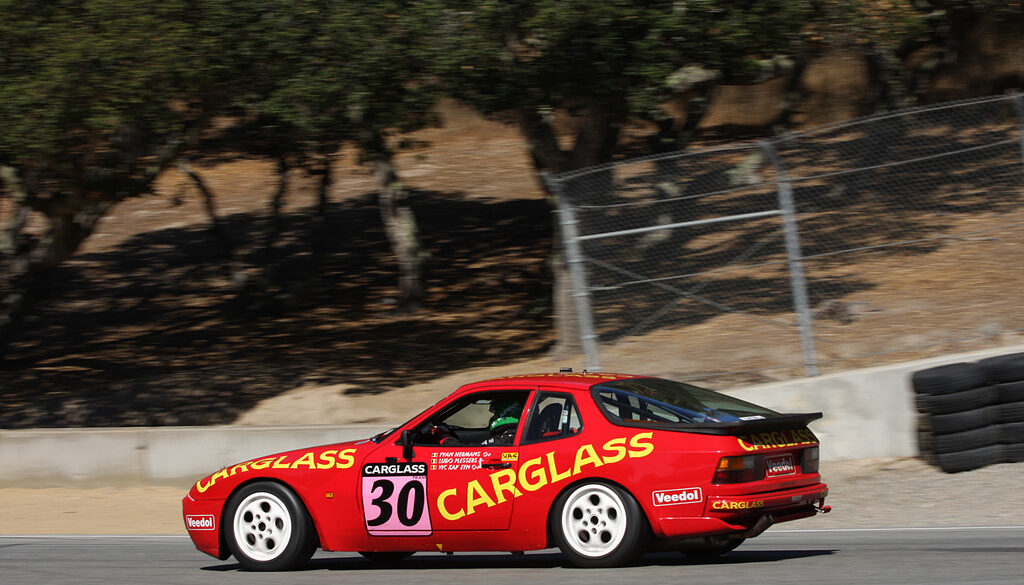
These cars were designed by the factory to race in SCCA D Production Championship starting in 1979. The Porsche project number of these race cars was 933. Only 16 were built by the factory. However, if you had the right connections, you "could" buy the parts as a kit from Porsche to convert your street car into a fully race-ready 924.
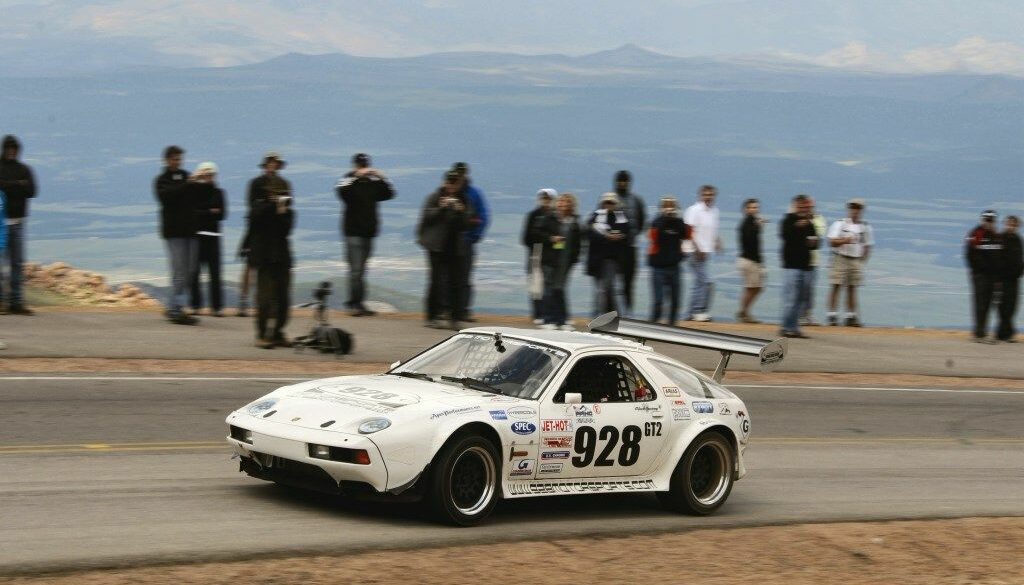
In 2007, 2008 and 2009 American racing driver Carl Fausett took his specially prepared and supercharged 1978 Porsche 928 to the Pikes Peak International Hill Climb and competed in the Open Division. Fausett placed third in the Open Division in both 2007 and again in 2009, where he was also the fastest 2WD car. At that time, much of the race course was gravel.
Using the 930 Turbo as a basis, Porsche built the 934 for Group 4 GT racing. It replaced the outgoing Carrera RSR while winning GT Championships in Europe and performing very well in America for Trans Am. Porsche built the 934 from a standard 930 bodyshell and production rear spoiler, but almost nothing else was left alone. The suspension was converted to solid mounts and nylon bushings with adjustable anti-roll bars.
In 1967 Porsche prepared a small number of 934 Porsches with 935 Group 5 parts for the Trans-Am and IMSA GTO series. In the end, the 934/5 dominated the Trans-Am series by taking to top five positions in the championship. Ludwig Heimrath became the 1977 Trans-Am champion in his 934/5 by protesting Peter Gregg's highly modified car. Together they humbled the Corvette C3s and the Group 44 Jaguar XJS.
The 935 tribute car was a non-street-legal collector's car built in a series of 77 cars. It was built from the 911 991.2 GT3 R racing car, fitted with the engine and transmission from the 911 991.2 GT2 RS street car and with the bodykit showing some design details from the 935 cars. The problem: it was not as powerful as the 1978 935 was with even smaller engine and the modern car is much heavier, so the power-to-weight ratio was almost 60% better 40 years earlier.
The 935 ‘Baby’, based on the successful 935 Group 5 race sports car, was created in 1977, after only four months of development,, specifically for entries in the small division (up to 2000cc) of the German Sports Racing Championship. Compared to the Group 5 car, this little 935 had a six cylinder turbo engine of 370bhp, reduced to a displacement of 1.4-litres. A thorough diet helped ‘Baby’ meet the minimum weight of 750kg as dictated by the rules.
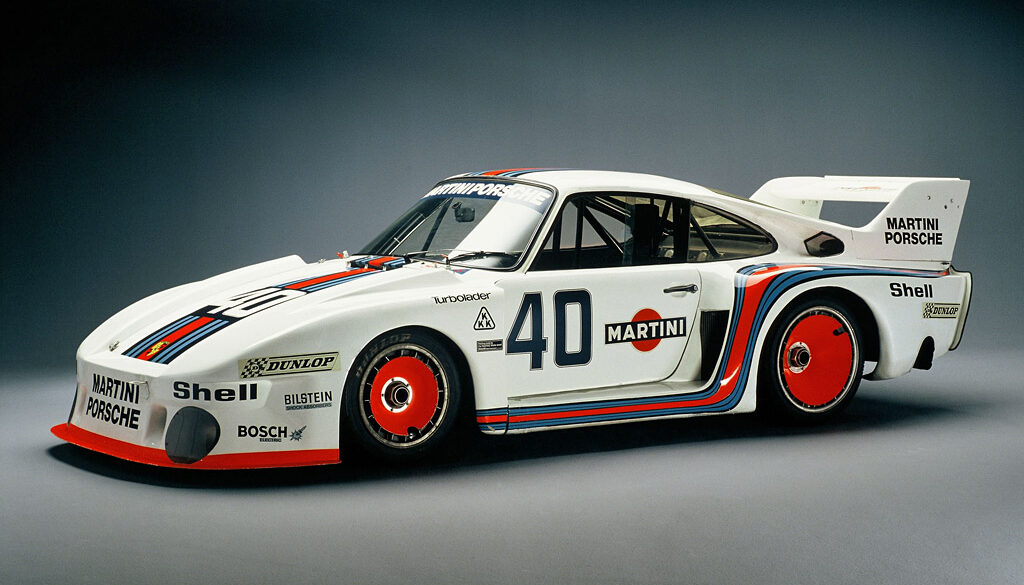
The Group 4 racer based on the 911 Turbo (930) was called 934 and the Group 5 Porsche was called 935. The first version of the 935 looked similar to the 911 Carrera RSR. The first customers for 935 were Martini Racing and Kremer Racing. The Martini car was a full factory development, while Kremer made its own enhancements already before the first race. By 1977, the 935 was sold as a customer car for these series to race against cars like the BMW CSL.
The 935/77 was a result of relaxed rules and the car got a completely new suspension. The mirrors were incorporated into the front fenders and the rear window had a new angle. The 935/77 was visually very pleasing. While the 935/76 had a single turbocharger, the 2.85-litre engine of the 935/77 had two turbochargers. There was also a "baby" 935/77 built with a smaller 1.4-litre turbocharged engine to compete in the national German DRM series under 2 liter class.
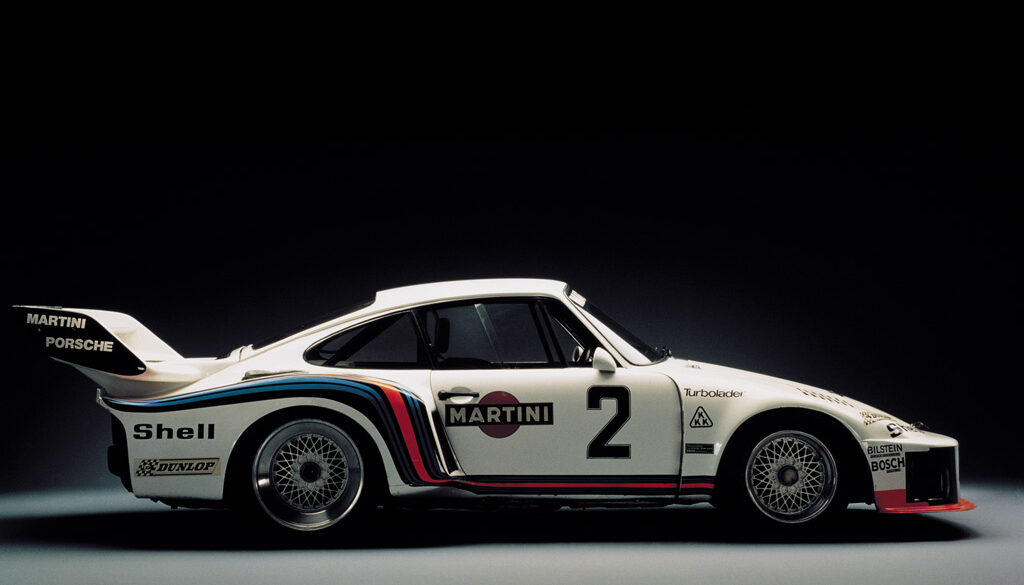
The 935/78 was the ultimate expression of the 911 factory race car before Porsche officially withdrew from motor sport. Raced under the Group 5 silhouette series, great liberties were taken with the design and the result was nicknamed ‘Moby Dick’ for its large size and huge overhangs. The 935/78 was built under Porsche's Chief Racing by Norbert Singer for high speeds at Le Mans. Due to the advanced shape of the car 227 mph or 366 km/h was possible.
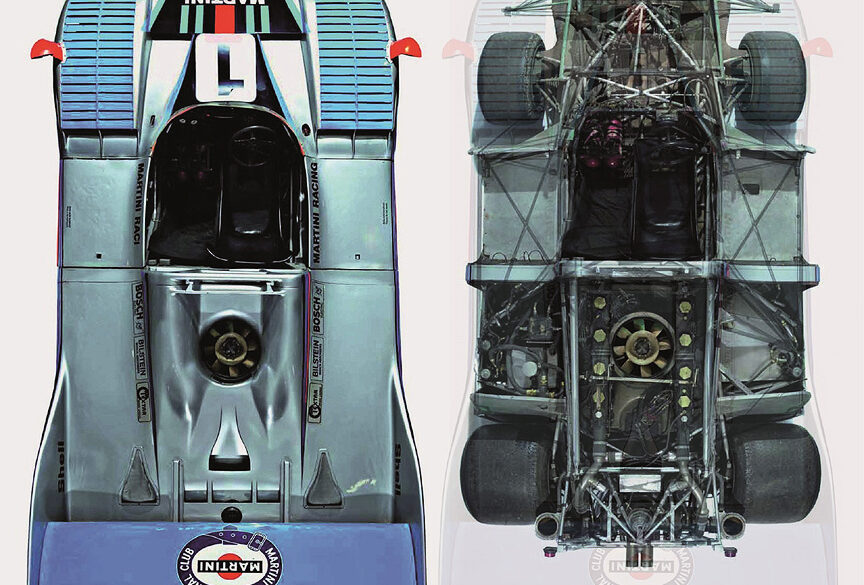
The Group 6 Porsche 936 was the successor to the 908/03 and the turbocharged 917. While the 917 had a 5.4-litre flat-12 biturbo engine, the 936 got a 2.1-litre flat-6 single turbo engine. The reason for the 2.1-litre displacement was to fit inside the 3-litre class (turbocharged cars had a coefficient of 1.4). Despite the small capacity, the engine developed more than five hundred horsepower. Imagine such power in a ~700 kg/1540 lb car!
In 1977, Porsche returned to Le Mans with the 936/77. Its body was smaller, lower, shorter and further refined aerodynamically. The engine now featured two turbochargers and delivered 20 more horsepower. At one of the most dramatic races in history, Jacky Ickx, Jürgen Barth and Hurley Haywood slayed the armada of four Renault works cars and two factory-supported “Mirage” with Renault motors. In the year 1981, the 936 celebrated a sensational comeback with another overall Le Mans victory.
For the 1978 Le Mans, Porsche created two new 936/78. The first one was built using chassis 936-001, which had already served for the 936/76 and 936/77. The second car was built on a new chassis and numbered 936-003. Because of the new water-cooled 24-valve engine, the 936/78 came with huge NACA ducts on the sides for the radiators and a new rear end with hanging spoiler.
Because the traditional pre-test is cancelled in 1981, Porsche is forced to start at Le Mans without testing. None the less, the race ends successfully: Jacky Ickx and Derek Bell win almost an hour ahead of the second placed competitor – right in time for the 50th anniversary of Dr. Ing. h.c. F. Porsche AG, and 30 years after Porsche’s first start at Le Mans.
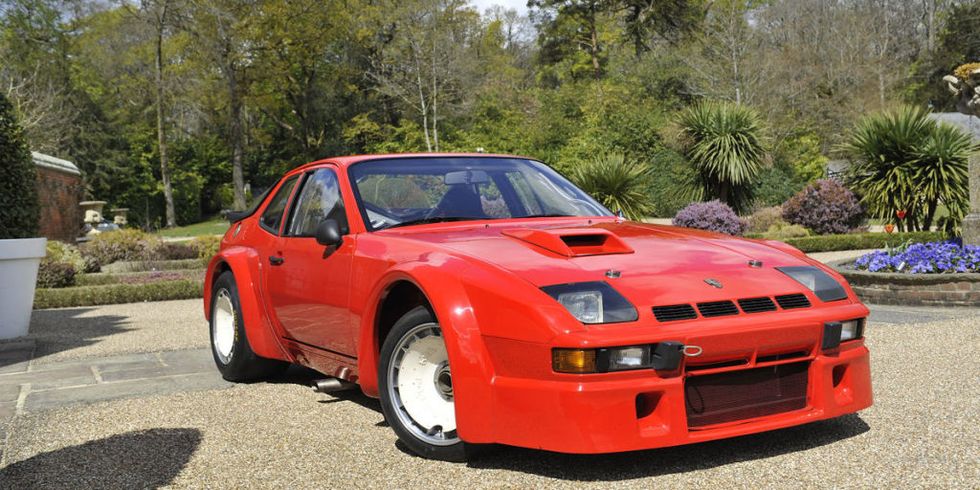
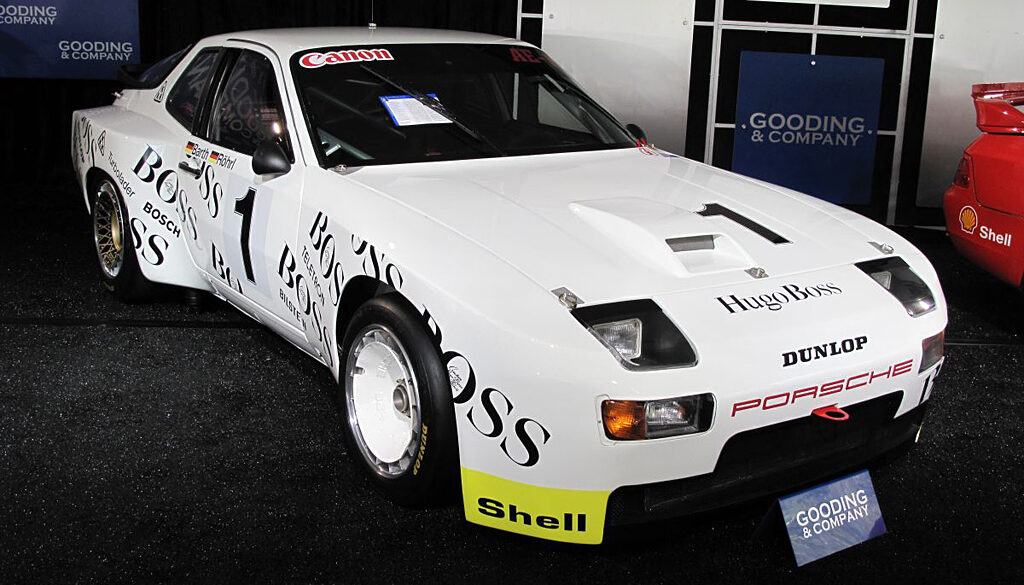
In 1981 Porsche developed two 944 prototypes to succeed the 924 GTPs which raced the 1980 24 Hours of Le Mans. To coincide with the release of the 944 in fall of 1981, Porsche prepared a GTP version to promote the car before the launch. The GTP was equipped with a special Type 949 cylinder block with dry sump lubrication, KKK K28 turbocharger and an air-to-air intercooler.
In late 1985 Porsche developed the 944 “Weissach turbo cup race car” to provide amateur enthusiasts with a cost effective entry into motorsports. Porsche initially designed to participate in a single-marque racing series run in conjunction with 1986 German ADAC Supercup races, but soon spread to Italy, Spain, Belgium, Austria , USA, Canada and even Czechoslovakia. The cars were modified extensively for racing duties, including taking out a lot of weight.
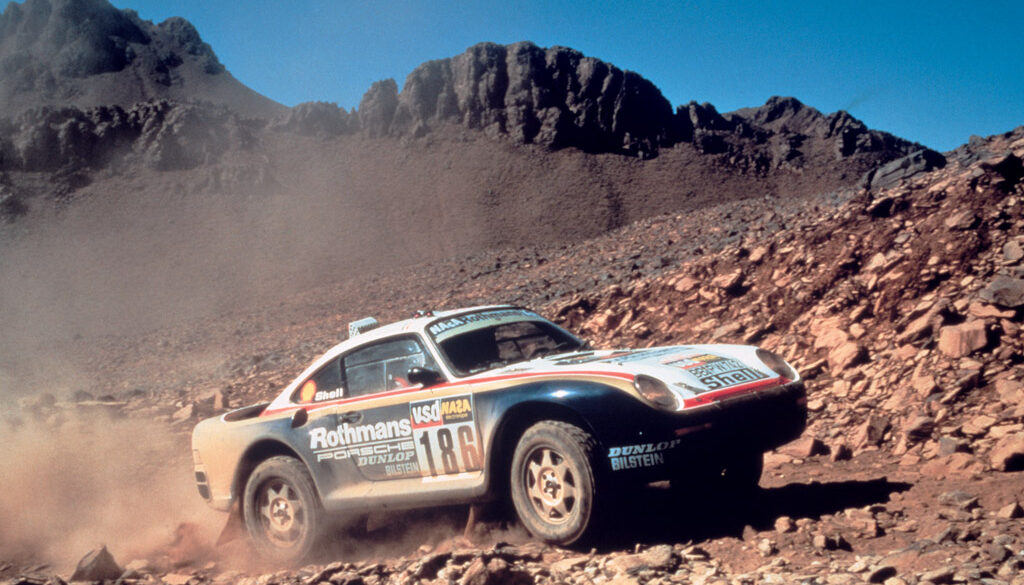
The Porsche 953 ranks as one of the finest off-roaders Porsche has ever made. It was basically a souped-up 911 designed specially to give Porsche an advantage in the 1984 Paris–Dakar Rally. Just a year later, it was replaced by the 959. Despite its brief run, it still managed to make quite the impression. Built around a massively enhanced suspension and a supremely powerful 300 bhp (224 kW), 6-cylinder engine, it showed Porsche knew more than just sportscars.
The Porsche 956 was a Group C sports-prototype racing car designed by Norbert Singer and built by Porsche in 1982 for the FIA World Sportscar Championship. It was later upgraded to the 956B in 1984. In 1983, driven by Stefan Bellof, this car established a record that would stand for 35 years, lapping the famed 20.832 km (12.93 mi) Nürburgring Nordschleife in 6:11.13 during qualifying for the 1000 km Sports Car race.
In 1984 Porsche offered a full works-specification car known as the 956B. This provided the New-Man Joest Racing team with a winning formula and they dominated the 1985 24 Hours of Le Mans with a resounding victory. One of the main differences between the customer 956 and the 956B was the Bosch Motronic engine management. This allowed more precise ignition and injection which in turn provided better economy and more power.
The 959 took both first and second place in the 1986 Paris-Dakar rally. For 1986, the Dakar Porsches finally got all the upgrades from the 959 project, including the active four-wheel drive system offering four driving modes adjusted by the computers. This gave Porsche a 1-2 finish, with supporting 959 Dakar engineer Unger Kussmaul crossing the line at sixth. Once the champagne had dried up, Porsche deemed its Dakar program accomplished.
The Porsche 961 was the racing version of the 959 supercar. While the 959 rallye car was also internally called 961, publicly only the circuit racer was called 961. Only one 961 was built. It had 959 prototype chassis number which in turn was from the 1985 911 Turbo chassis number sequence: WP0ZZZ93ZFS010016. The 961 was entered at the 1986 Le Mans 24 hour race. Uncommonly, the 24 hour race was scheduled for May 31-June 1 that year, two weeks earlier of the typical Le Mans weekend in the middle of June.
The Porsche 962 arrived on scene in 1984 as essentially a Porsche 956 for the IMSA/US market. A biturbo version was used in competition racing in Europe, while an IMSA version with a turbocharger featured in North America. The 962 C was based on the 956, with a 120 millimetre longer wheelbase and competed in LeMans. It differed from the IMSA version. The driver trio Stuck/Bell/Holbert was victorious at Le Mans in 1987. Porsche offered the 962 to privateers to race on their own and they were hugely successful.
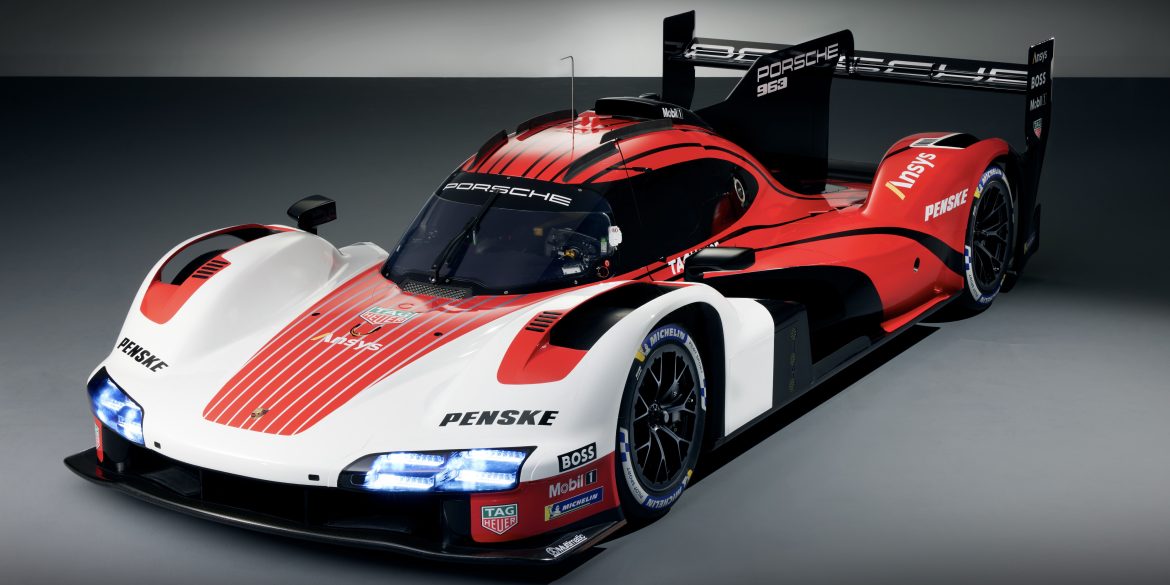
Porsche 963 LMDh – Reviews, Pricing, Specs & Buyers Guide Porsche’s first customer prototype in more than a decade comes with a $2.9 million price tag, making the 963 the most expensive model offered by the German auto manufacturer. Built by Canadian racecar constructor Multimatic, the LMP2-derived 963 chassis could become...
In 1992, Porsche introduced the 968 Turbo RS racecar which it developed to compete in the new ADAC GT racing series in Germany. The car was based on the 968 coupe with limited lightening due to the regulations of the series which had a 4kg/bhp power/weight ratio limit. The car featured a K27 turbo boosting the 3.0 litre, 4 cylinder engine and an 8V head, similar to the 944 Turbo S, rather than using the 16V 968 head.
The rear of the world’s most-produced GT racing car now houses a 4-litre, six-cylinder flat engine for even more drive. Thanks to thoroughbred motorsport technology, the compact engine with direct fuel injection delivers peak performance of 357 kW (485 hp). A range of innovative details also improve efficiency in addition to engine performance, ensuring even better durability of the naturally aspirated engine in racing mode and reduced maintenance costs.
The Porsche LMP2000 (also known as the Porsche 9R3) is a Le Mans Prototype racing car that was developed between 1998 and 2000, but never raced. One car was built, and it was designed around a modified version of Porsche's 3.5-litre V10 engine that was originally designed for Formula 1 in 1992. The project was canceled before the car was built, leading to various rumors about the reason for its demise.
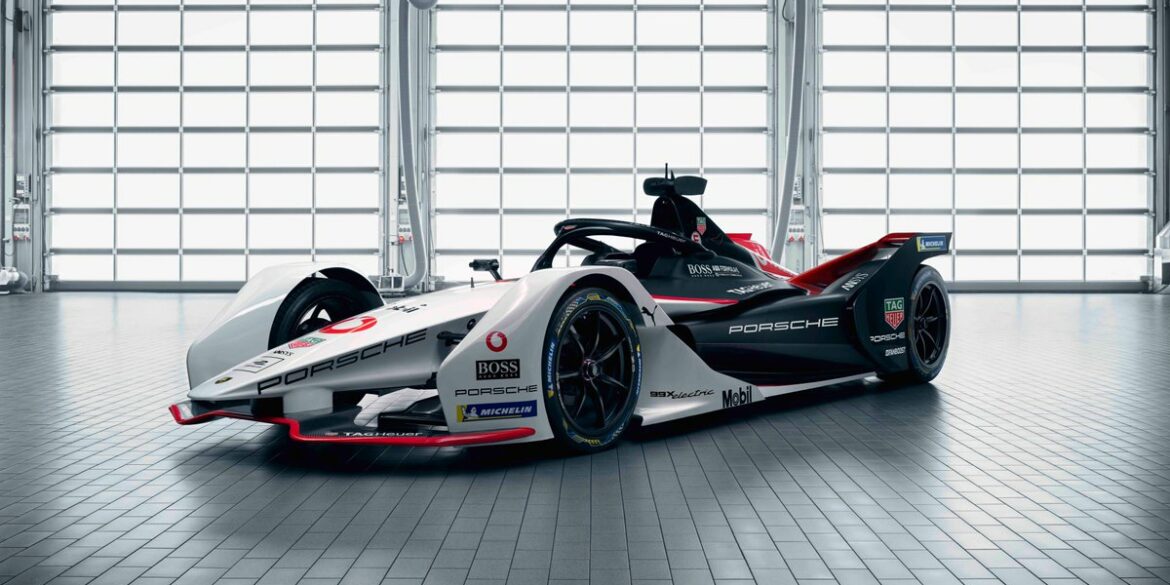
Spark Racing Technology is responsible for a big part of the Porsche 99X Electric. This is the racing car Porsche fielded in Formula E 2019 season. Maximum performance in qualifying mode? 335 horsepower and 174 mph. Zero to 100 kilometers per hour is doable in 2.8 seconds, and the minimum weight including the driver is rated at 900 kilograms of which the battery is responsible for 385 kilograms. In race and attack modes, the output is restricted to 272 and 320 PS, respectively. The useable battery capacity is 52 kWh while maximum recuperation is rated at 250 kW.
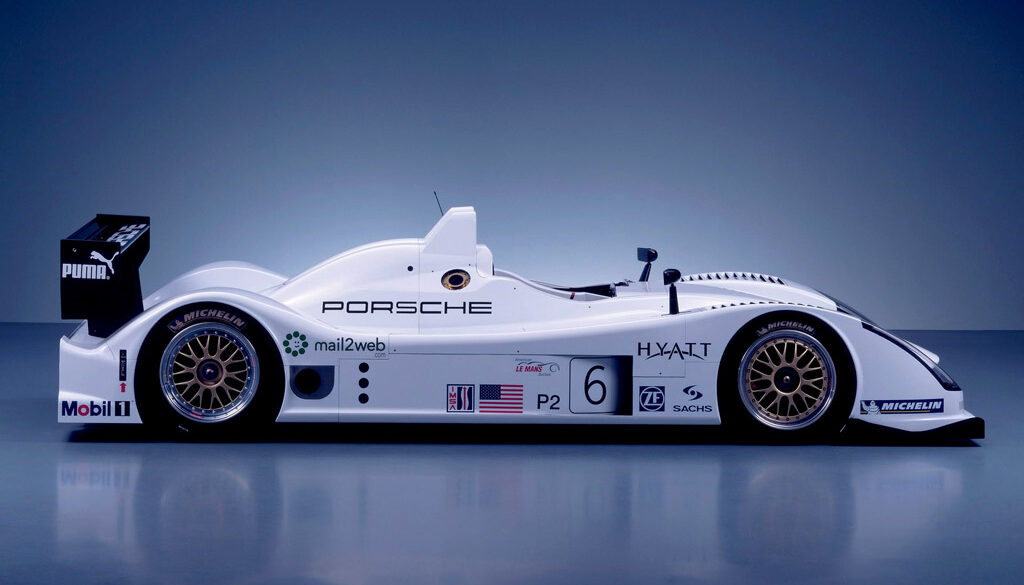
The Porsche RS Spyder, internally called 9R6, exists only thanks to a customer order made in 2004 by Penske Motorsports, a subsidiary of Penske Racing. The 9R6 was built according to the Le Mans Prototype class 2 (LM P2) regulations and to be raced at the American Le Mans Series (ALMS) in USA and Canada. The ALMS was created in the spirit of the Le Mans endurance races, hence the name of the series.
Following a development year with Penske Motorsports in ALMS, Porsche revealed the final version of their LMP2 contender for the 2007 season. Known as the 'EVO' model, it had a host of upgrades that made it suitable for customer-funded teams to successfully compete. This model dominated the P2 class at events like Le Mans and Sebring. It raced from 2007 till 2010 with strong results across the board.
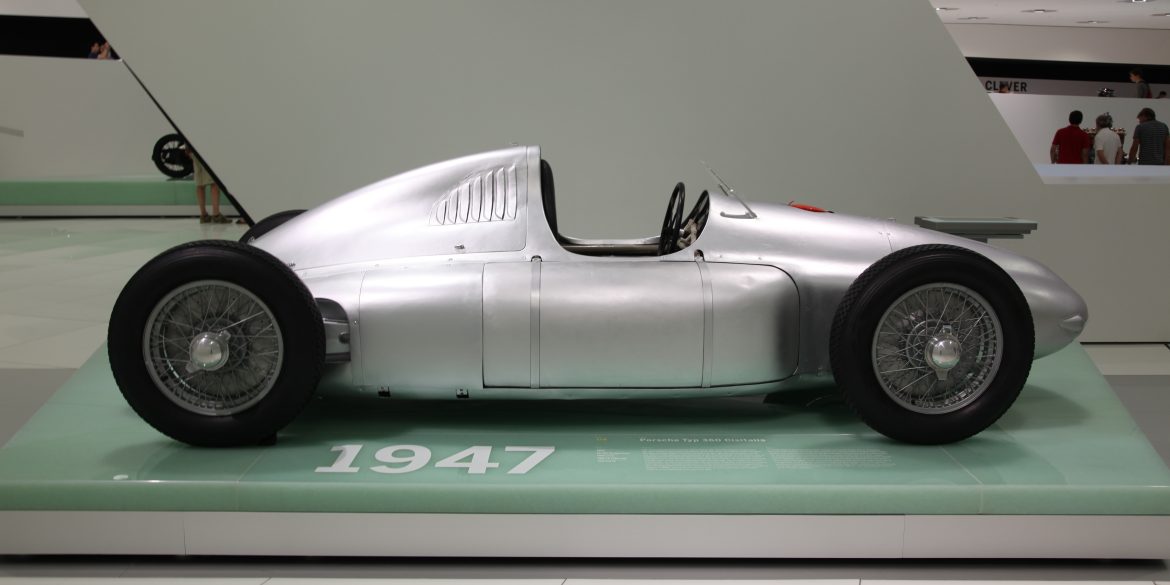
The Cisitalia Grand Prix is a single-seater car for the postwar 1.5-litre supercharged Grand Prix class, built by Italian sports car manufacturer Cisitalia and introduced in 1949. It was designed on behalf of Cisitalia by Porsche between 1946–47, and is therefore also known by its Porsche project number, Typ 360. An extremely advanced design, it proved too complex to build for the small Italian firm (and lead to the financial downfall of the company).
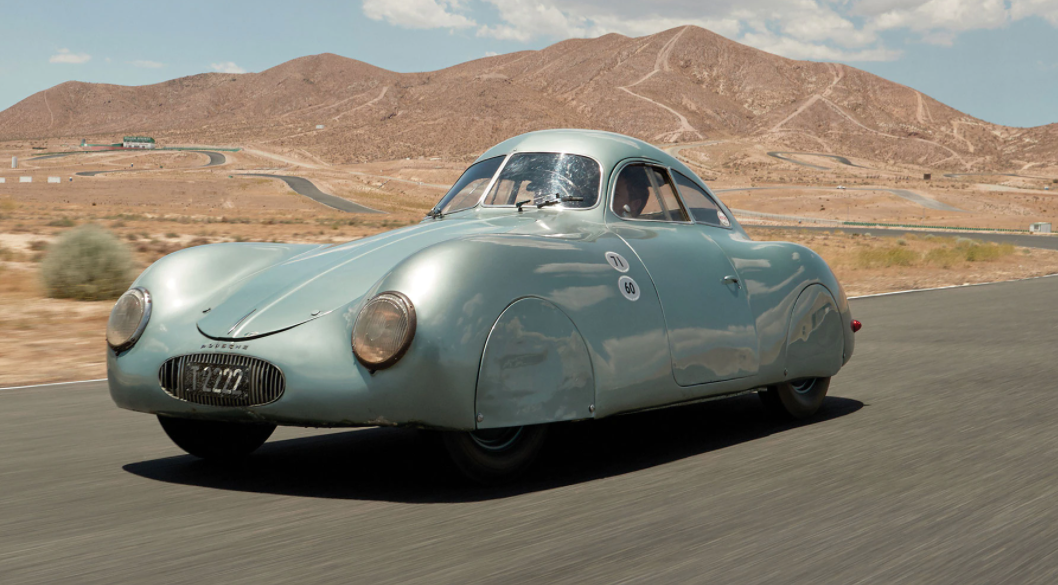
The Porsche 64, also known as the Type 64 and Type 60K10, is considered by many to be the first automobile from what was to become the Porsche company. The first KdF Berlin-Rome competition car, chassis number 38/41, was finished on August 19, 1939. It had a streamlined body and small 4-cylinder aircooled 1100 cc flat engine.
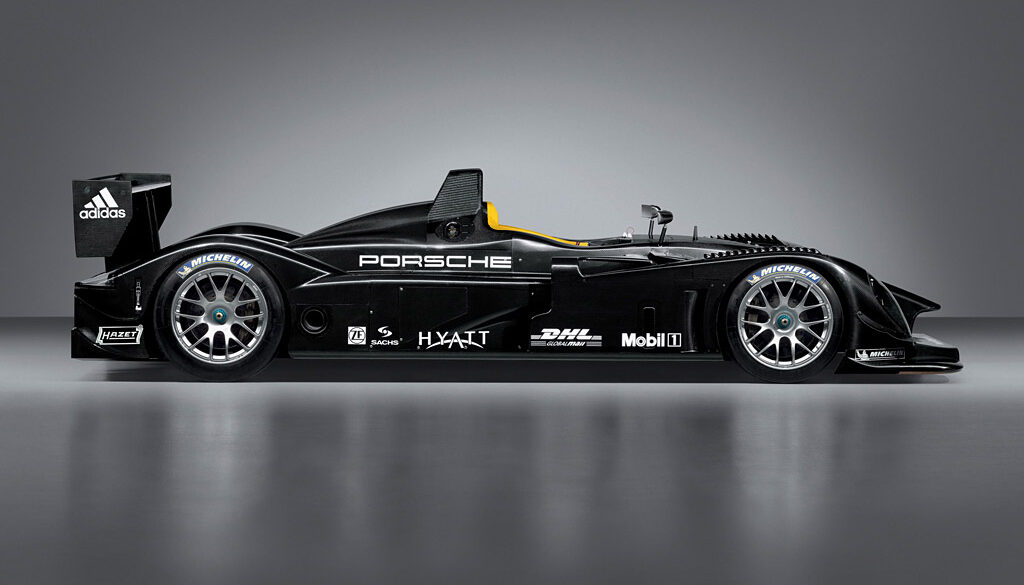
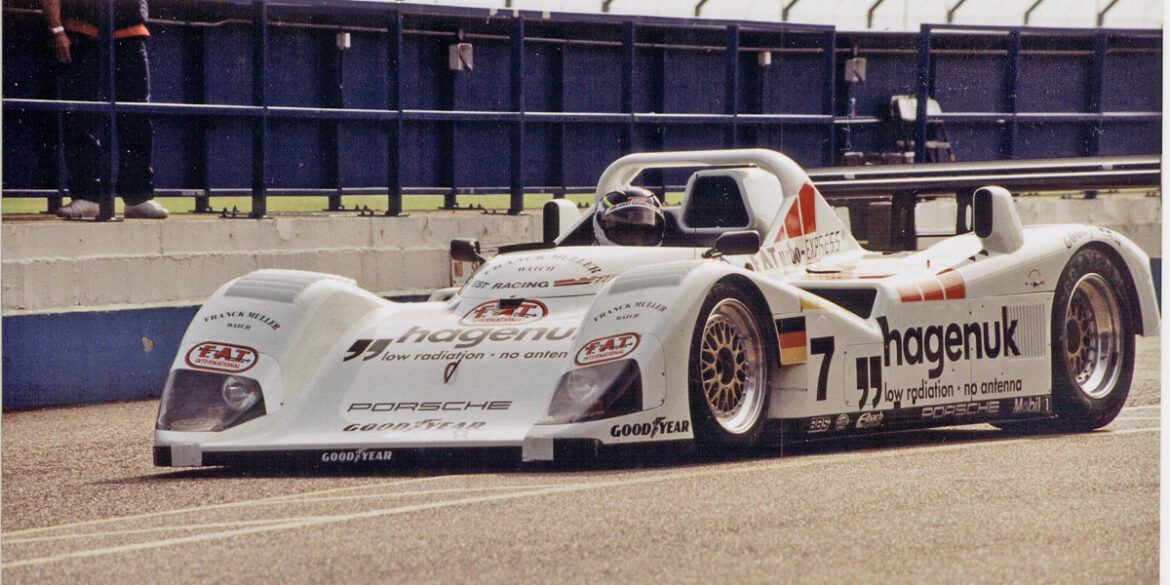
The Porsche WSC-95 (sometimes referred to as the TWR WSC-95) was a Le Mans Prototype originally built by Tom Walkinshaw Racing. It was modified by Porsche from the original Group C Jaguar XJR-14 from which it derived,[1] and run by Joest Racing. The WSC-95 saw very little race action even though it won the 24 Hours of Le Mans in both 1996 and 1997 without being acknowledged as a factory supported project. Later upgraded to the Porsche LMP1-98 before being retired. Only two cars were ever built.
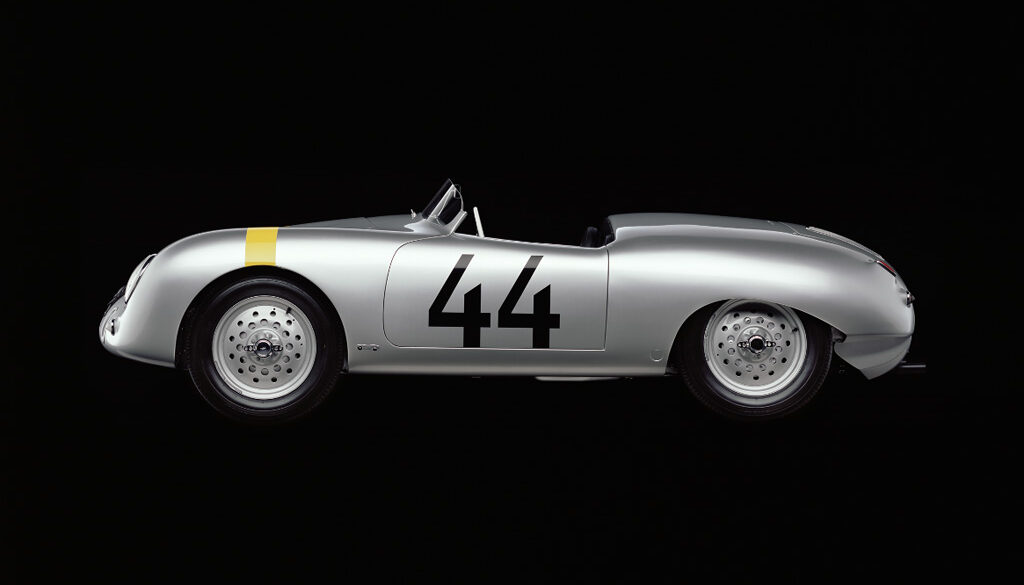
Successful VW Dealer and racer Walter Glöckler built several specials for the German Car Championship including this roadster. It was built with assistance from Porsche in Zuffenhausen and raced without its optional hardtop in the 1952 champion before being shipped overseas for SCCA racing. Weidenhausen created the body from aluminum with a nose that bore close resemblance to the 356 Porsche but had semi-skirted rear wheels and cutaway rear corners similar to Glockler-Porsche 1 and 2.
No More Content