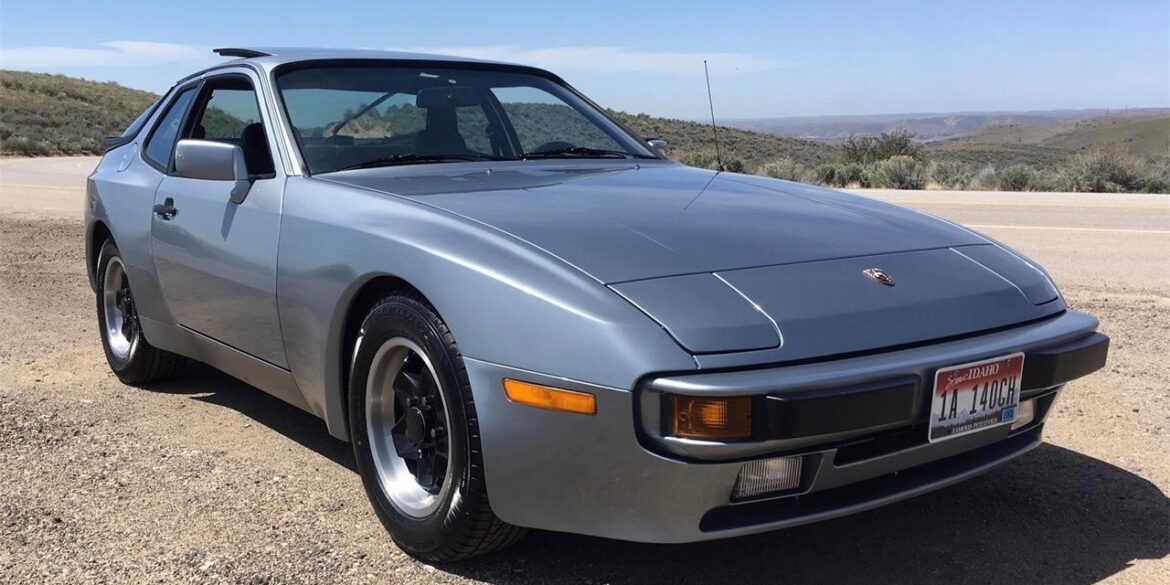
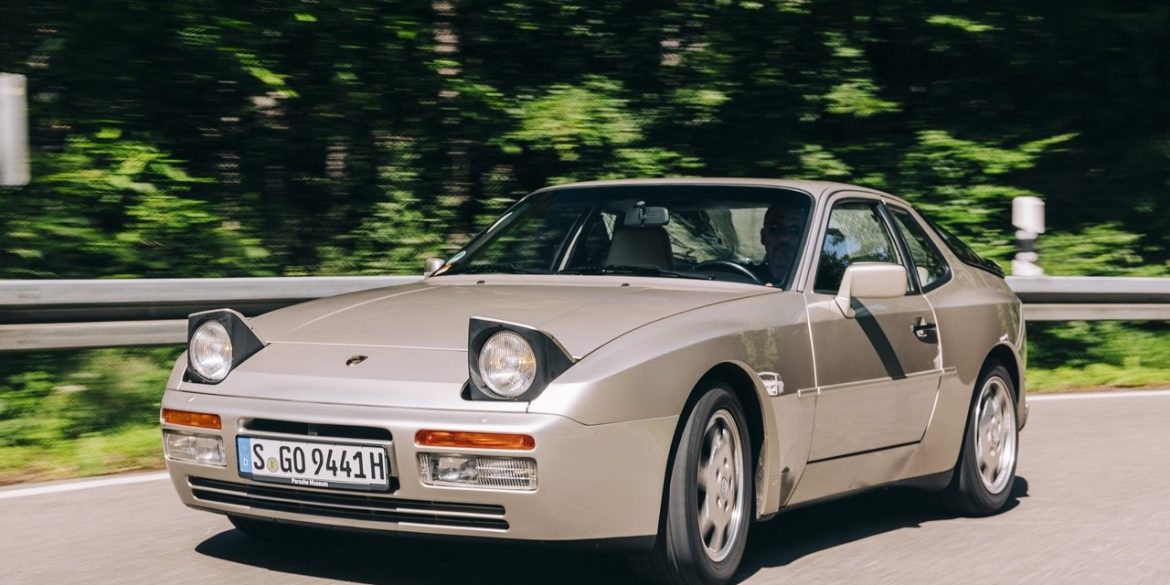
Porsche Option Codes – Porsche 944 (1984 Model Year) Looking to decode your 1984 Porsche 944 option codes? Want to know what those codes are in your 1984 Porsche 944 service manual? Then this is the post for you. We painstakingly researched all the Porsche option and equipment codes for...
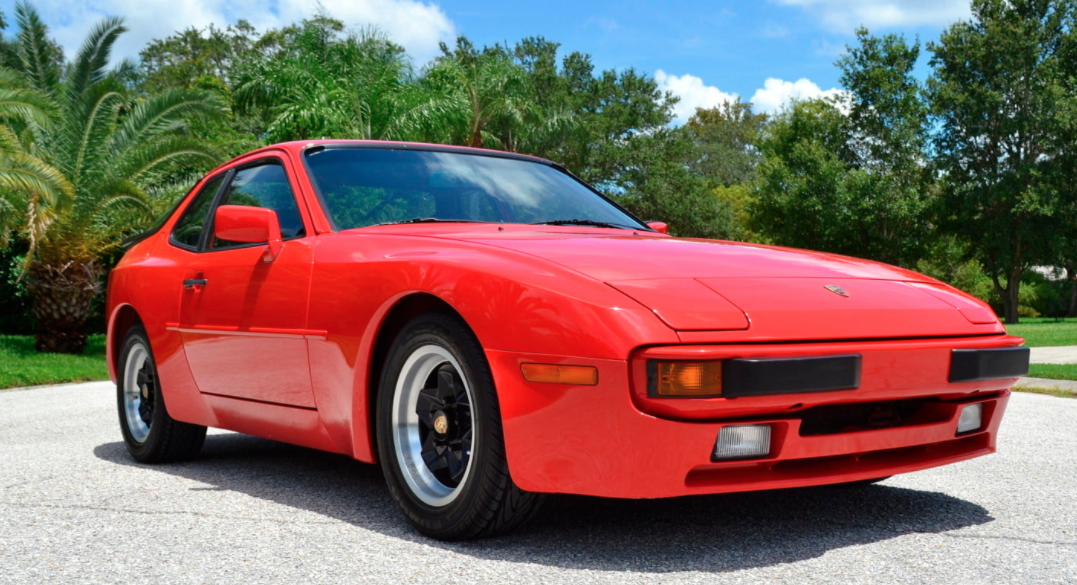
Porsche Option Codes – Porsche 944 (1983 Model Year) Looking to decode your 1983 Porsche 944 option codes? Want to know what those codes are in your 1983 Porsche 944 service manual? Then this is the post for you. We painstakingly researched all the Porsche option and equipment codes for...
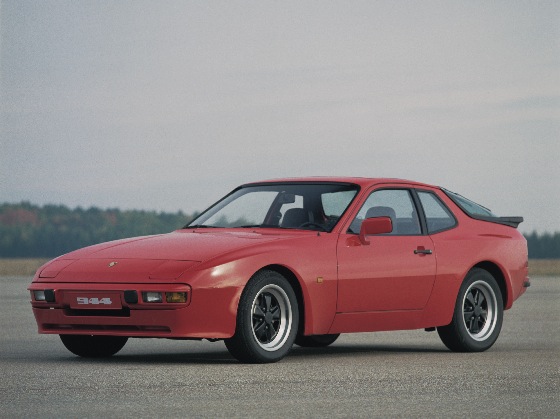
Porsche Option Codes – Porsche 944 (1982 Model Year) Looking to decode your 1982 Porsche 944 option codes? Want to know what those codes are in your 1982 Porsche 944 service manual? Then this is the post for you. We painstakingly researched all the Porsche option and equipment codes for...
1976 Porsche 924 Coupé It is a fact that most of us with an interest in roadgoing or race cars, will have a favourite model that holds a special place in our memory for some reason. That reason might be something significant that happened in your life where a certain...
#5 Porsche 908/3 – Juan Fernandez/Francesco Torredemer/Eugenio Baturone – NRF The 1972 season broke, ushering in with it a new era of racing. The Porsche 917 had reigned supreme for two years, but the race authorities (read FIA) had had their fill of Porsche interpreting the rules their way, and...
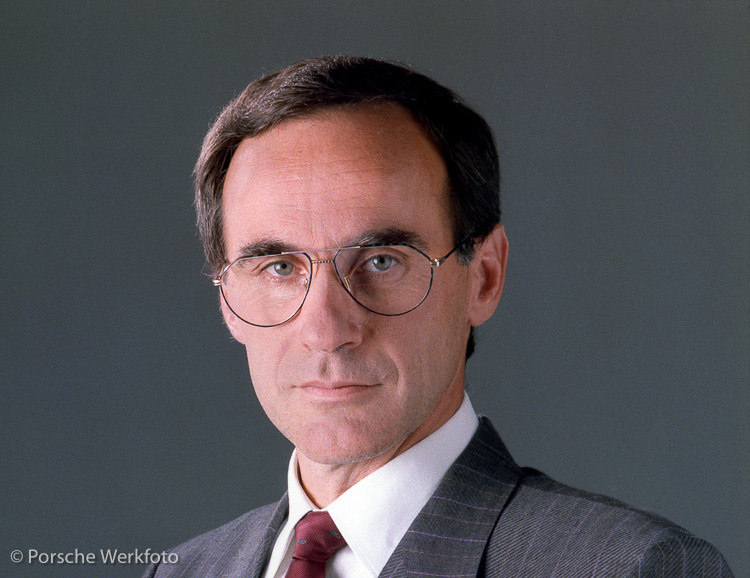
Dr. Ulrich Bez (1988) Hailing from the Bad Cannstatt district of Stuttgart, Ulrich Bez, who as Porsche Technical supremo hatched the 993, had two significant stints at Porsche. During the 1970s he worked in research and was responsible for establishing Porsche’s crash test programme; in the 1980s, he followed Porsche’s...
Autograph card signed by Jürgen Barth (ca. 1980) More books have been written about Porsche than any other car company so the publication in English of another tome is hardly headline news until you realise that the author, exceptionally, is a Porsche insider, but not just any insider. Jürgen Barth...
No Subscription? You’re missing out Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content. Get Started Already a Member? Sign in to your account here....
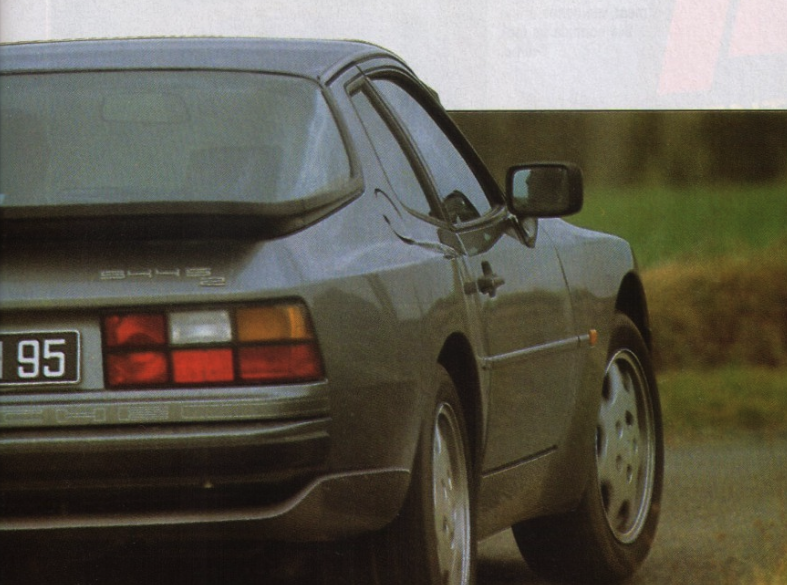
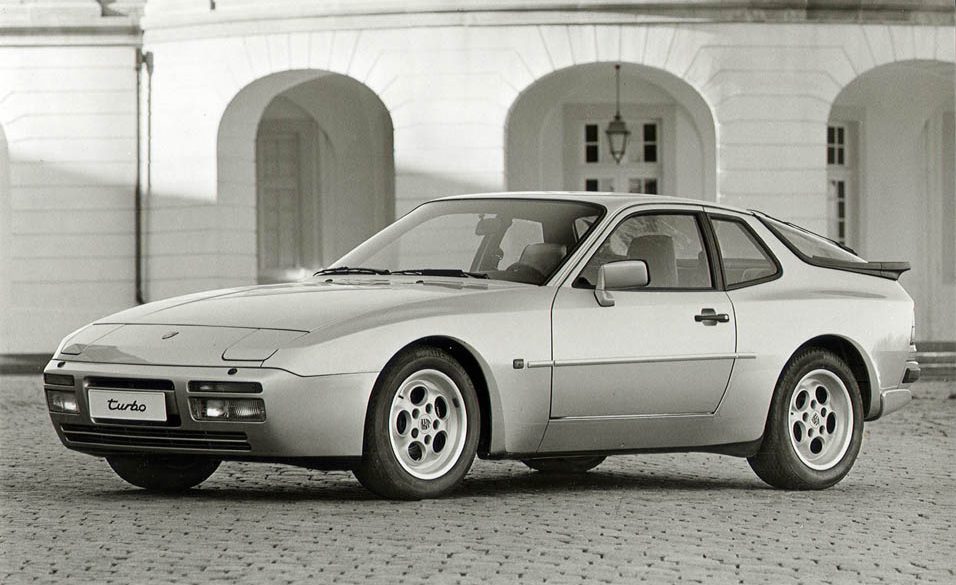
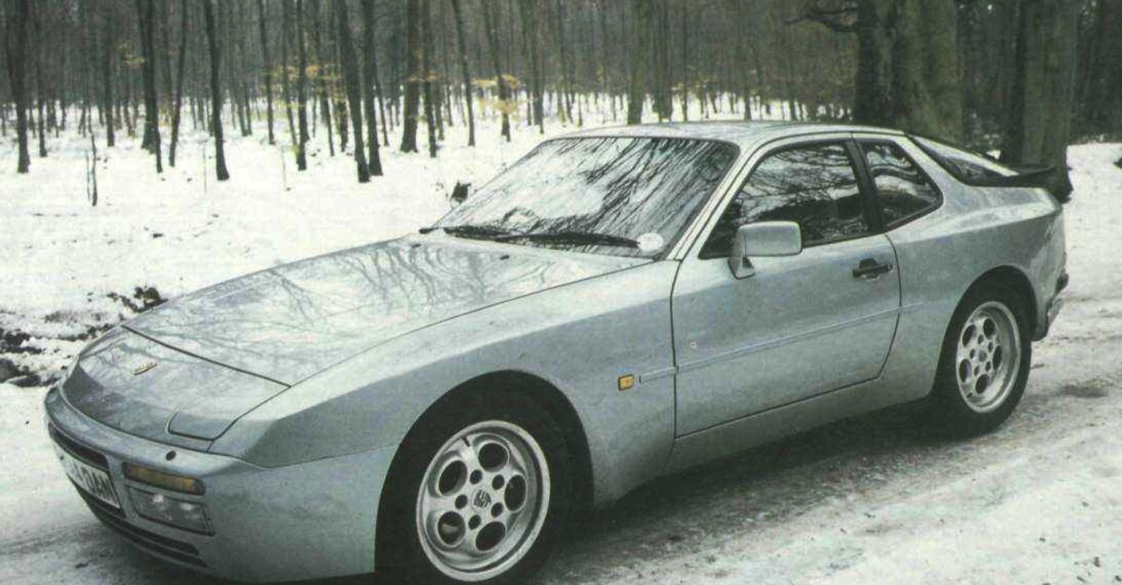
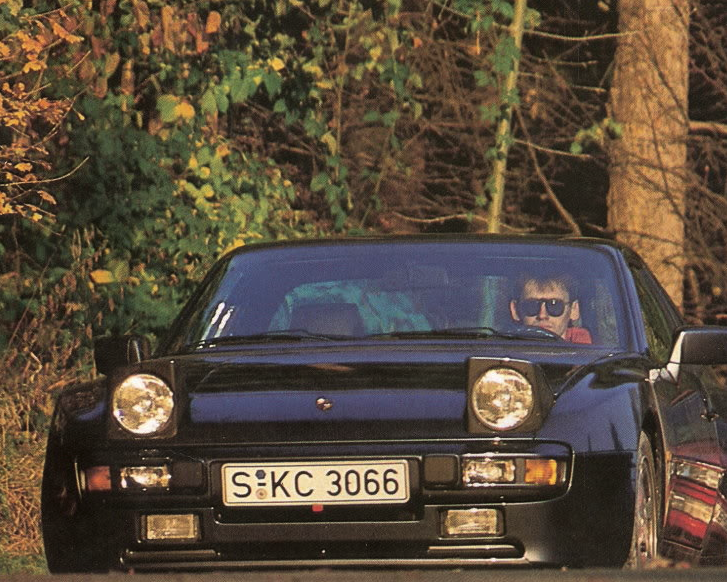
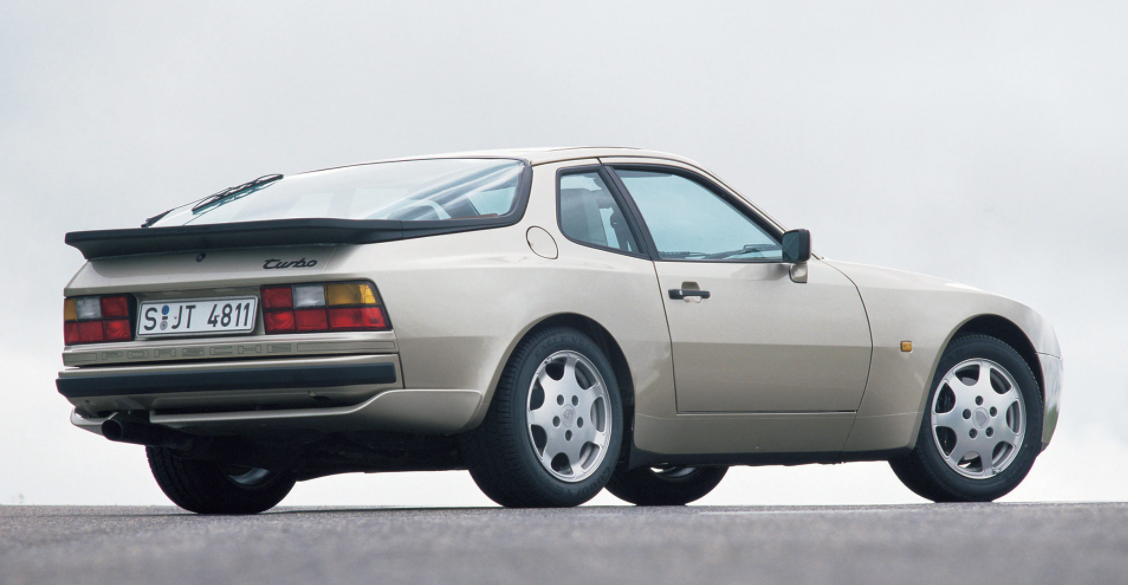
In 1988, Porsche introduced the 944 Turbo S with a more powerful engine (designation number M44/52) rated at a maximum power output of 250 PS (184 kW) at 6,000 rpm and 350 N⋅m (258 lb⋅ft) of torque at 4,000 rpm (the engine in the standard 944 Turbo generated 223 PS (164 kW) and 243 lb⋅ft (329 N⋅m)). This higher output was achieved by using a larger KKK K26-8 turbocharger housing and revised engine mapping to maximize boost for longer.
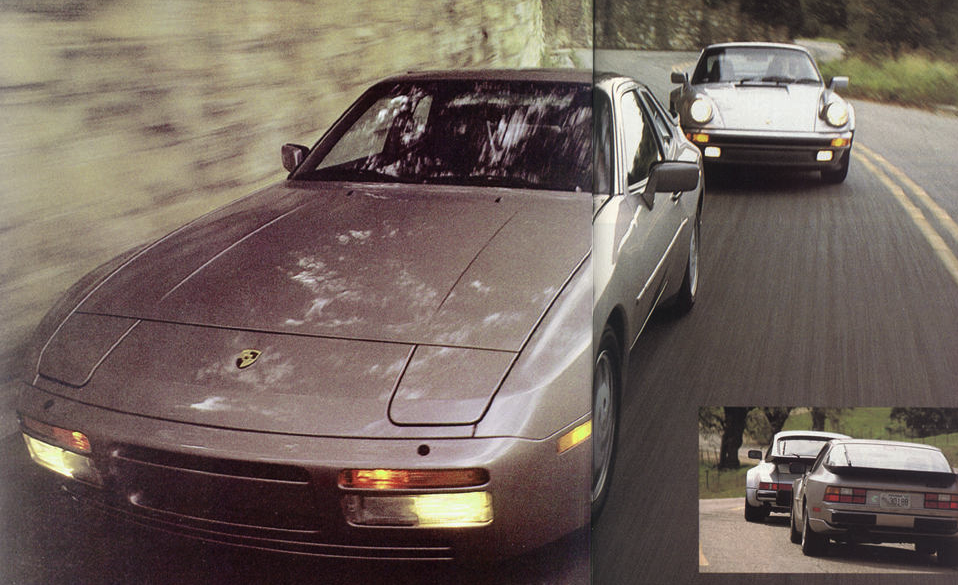
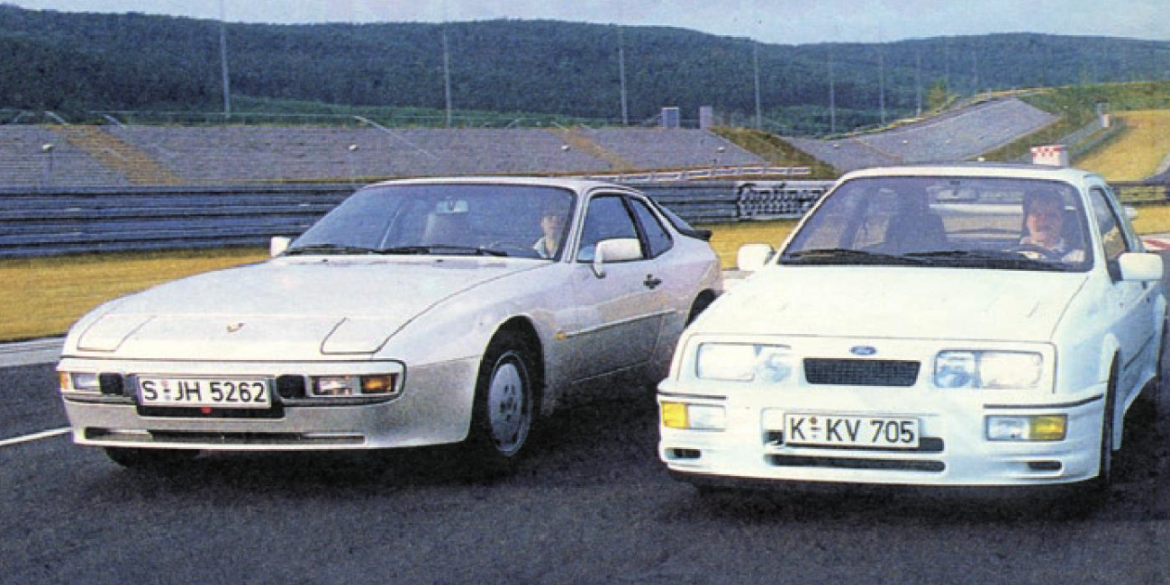
It didn’t take Porsche’s engineers long to significantly improve on the base 944’s performance by doing the obvious and adding a turbocharger to the engine. The 944 Turbo entered production in 1985 for the 1986 production year and it made a significant difference to the stock 944’s performance. Power of the new turbocharged engine was 220hp and torque was 243lb/ft, a significant increase over the naturally aspirated standard 944.
In spring of 1984 Rothmans cosmetic edition 944 was made, a batch of 100 numbered cars ordered by the French importer Sonauto (the subsidiary of Porsche AG) to celebrate the victorious Rothmans-sponsored Porsche 956 that had won Le Mans 24 hour race in France in 1982 and in 1983. At the time when the Rothmans 944 was sold, Rothmans-Porsche factory team decided to boycott the 1984 Le Mans race. Only 100 were produced.
The Swiss Special 944 was a very limited edition 944 Special produced in 1984. Only 200 944 Swiss Specials were produced and it was largely a design exercise, with several upgrades to the normal 944. The changes included, Red-colored stickers on the back of "Porsche” “944", Special size teledial rims, Seats , rear bench and door panels in 924 Carrera GT fabric and dashboard plastic parts in black instead of the standard silver.
In 1983, American tuning company Callaway Cars began offering a turbocharged package for the US-Spec 944 in collaboration with Porsche. The standard 2.5 L inline-four engine was not suitable for forced induction because of the higher compression ratio of 9.5:1 which made the engine prone to failure when subject to forced induction along with the complex Bosch Motronic engine management system.
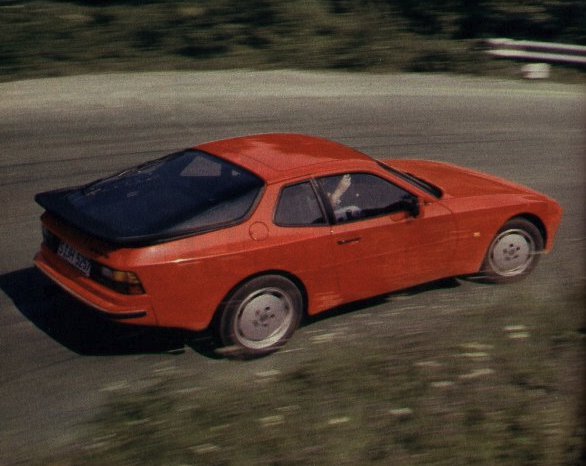
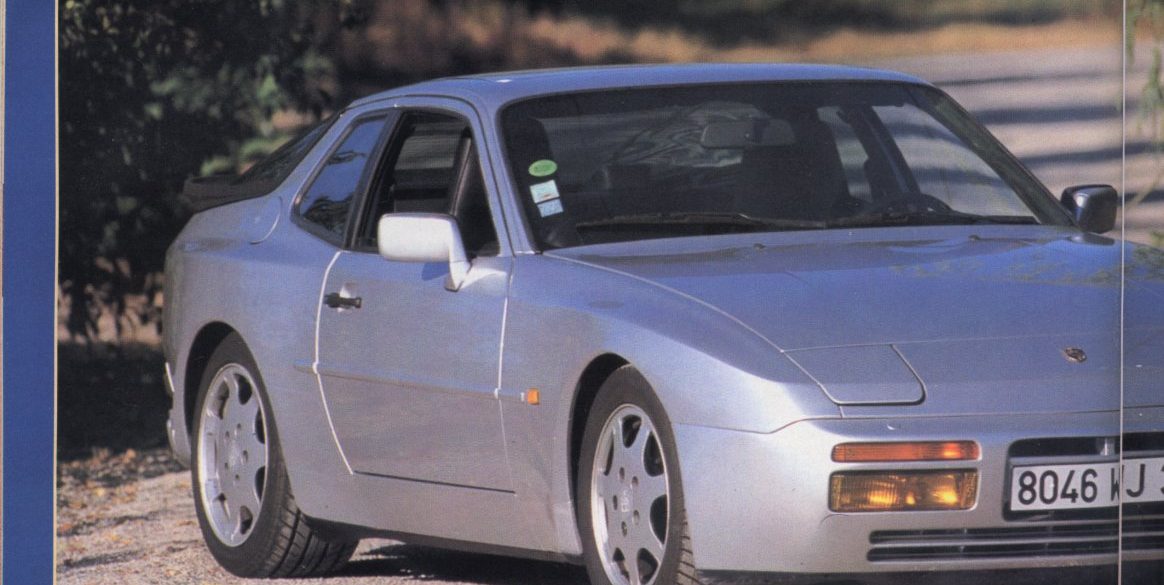
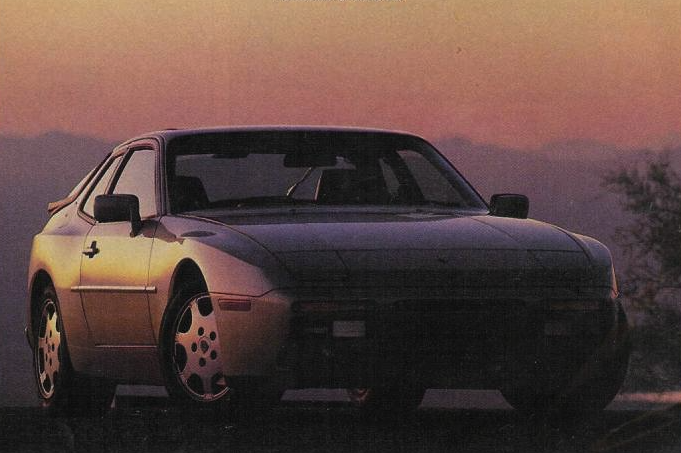
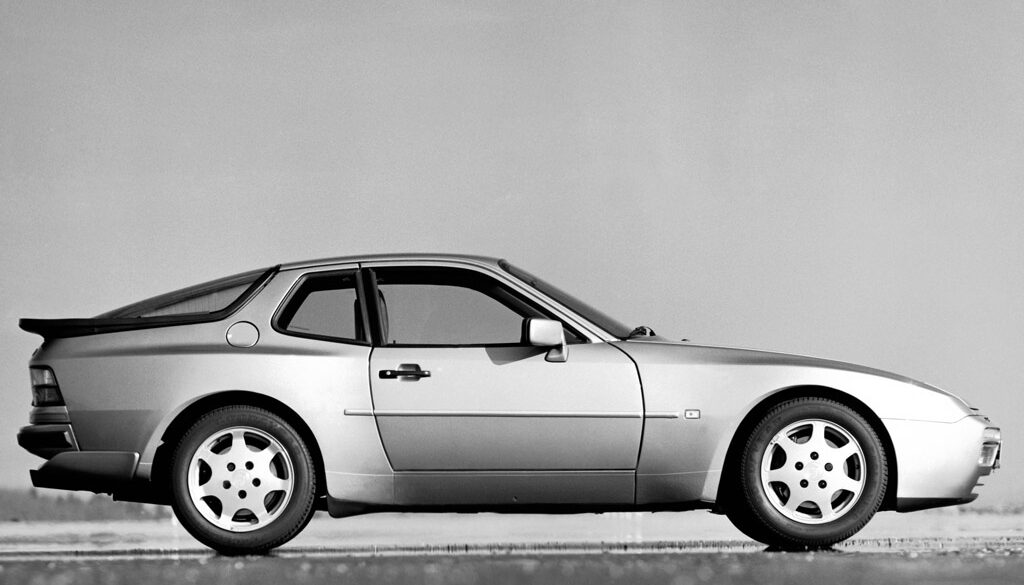
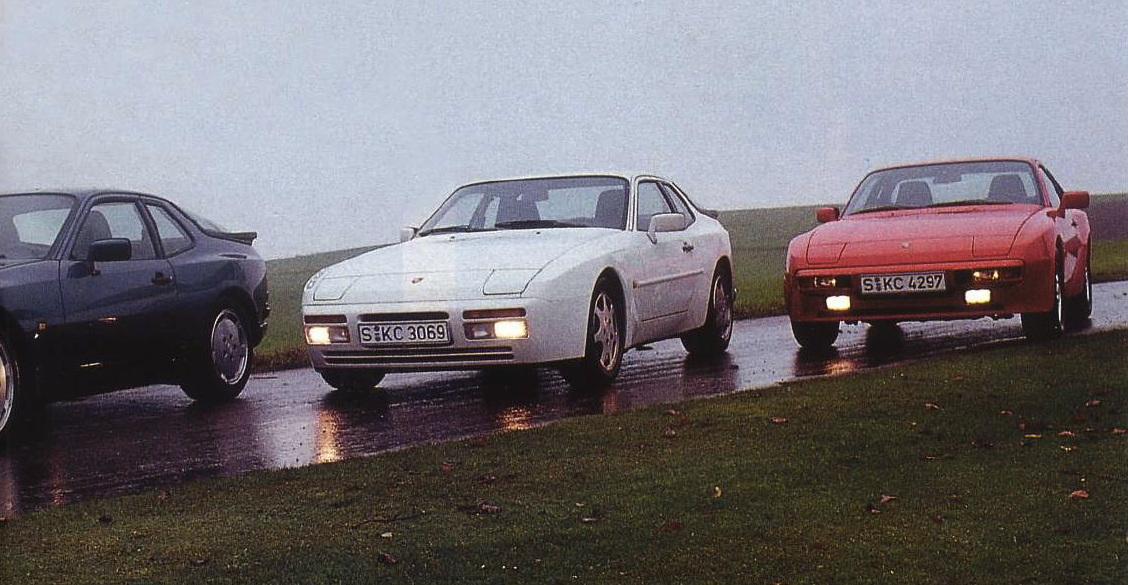
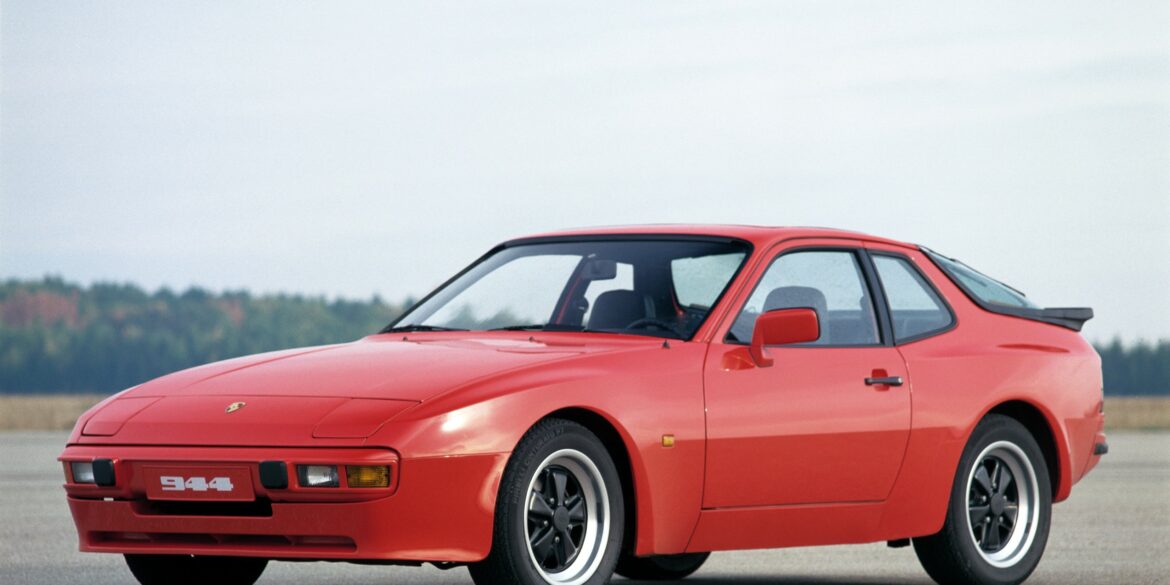
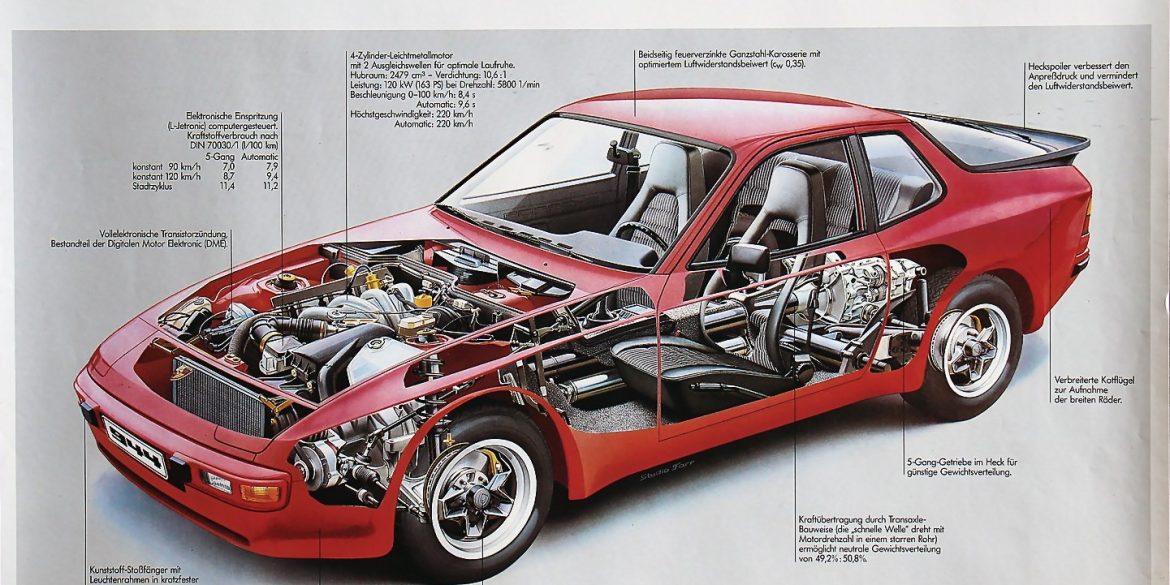
The base Porsche 944 coupe was built between 1982 and 1989, essentially the same platform as the Porsche 924 (there was some overlap as the 924 was produced till 1988). The 944 was intended to last into the 1990s, but major revisions planned for a 944 S3 model were eventually rolled into the Porsche 968 instead, which replaced the 944.
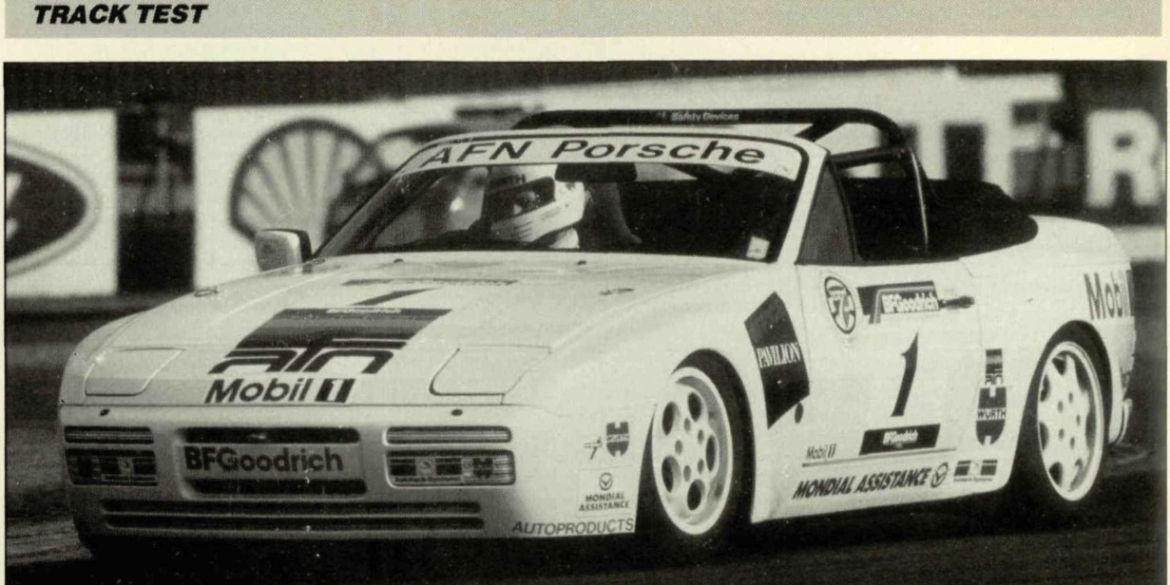
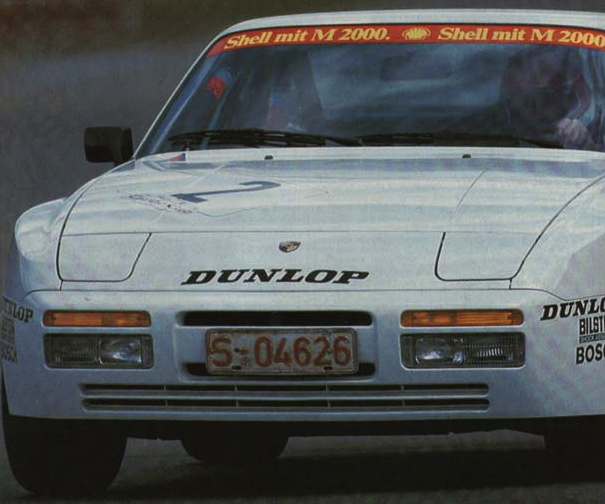
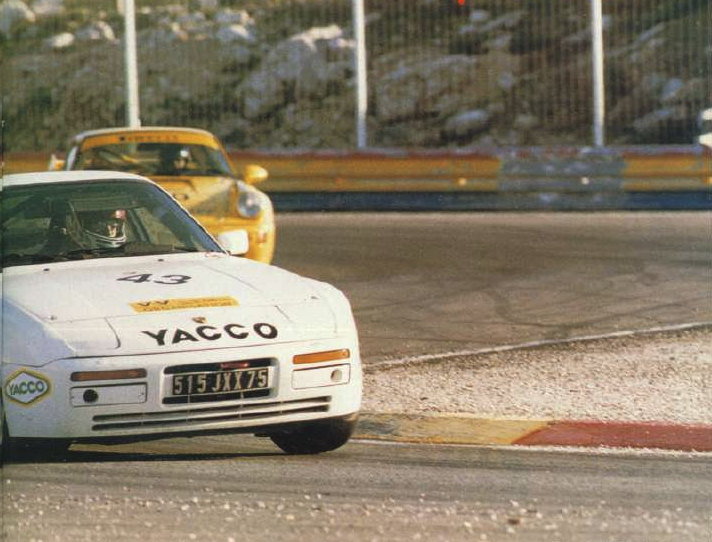
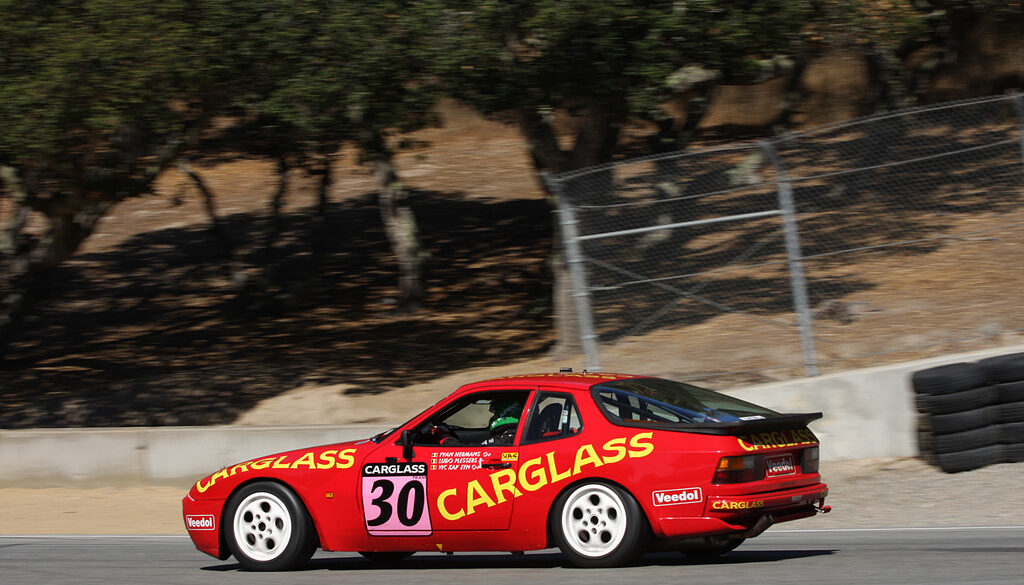
In late 1985 Porsche developed the 944 “Weissach turbo cup race car” to provide amateur enthusiasts with a cost effective entry into motorsports. Porsche initially designed to participate in a single-marque racing series run in conjunction with 1986 German ADAC Supercup races, but soon spread to Italy, Spain, Belgium, Austria , USA, Canada and even Czechoslovakia. The cars were modified extensively for racing duties, including taking out a lot of weight.
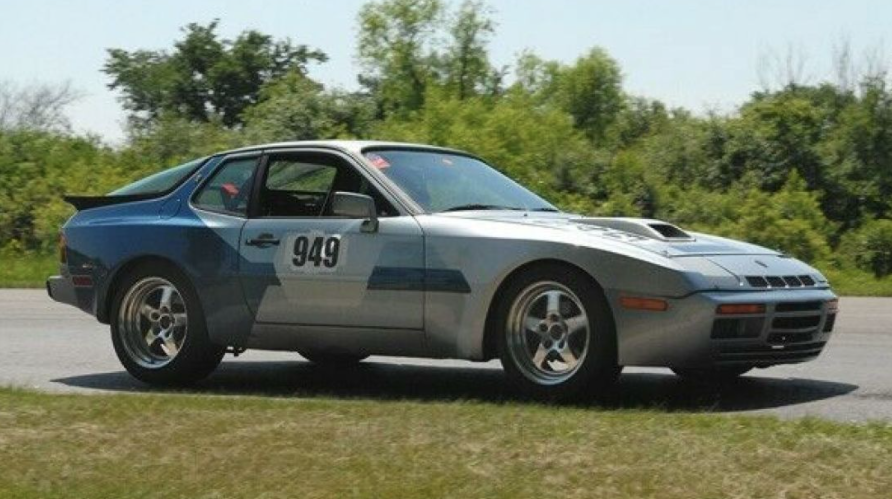
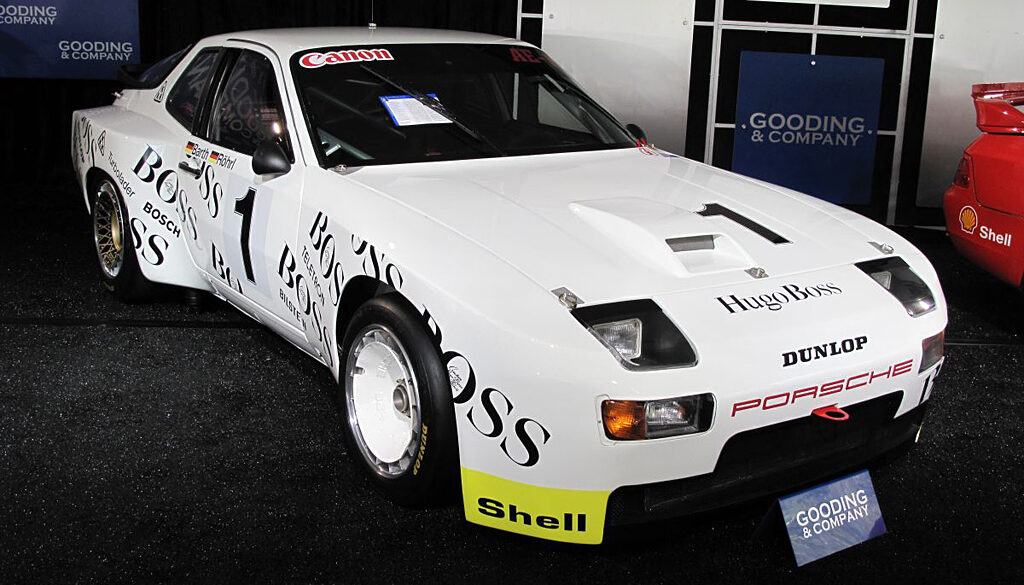
In 1981 Porsche developed two 944 prototypes to succeed the 924 GTPs which raced the 1980 24 Hours of Le Mans. To coincide with the release of the 944 in fall of 1981, Porsche prepared a GTP version to promote the car before the launch. The GTP was equipped with a special Type 949 cylinder block with dry sump lubrication, KKK K28 turbocharger and an air-to-air intercooler.
No More Content