Ferdinand Porsche
(1875 – 1951)
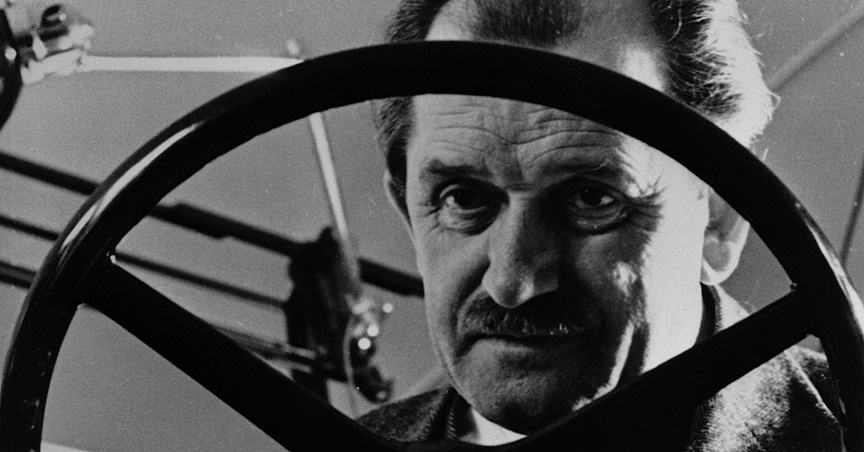
Ferdinand Porsche was an Austrian-German automotive engineer and founder of the Porsche car company. He is best known for creating the first gasoline-electric hybrid vehicle, the Volkswagen Beetle, the Auto Union racing car, the Mercedes-Benz SS/SSK and several other important automobiles and technologies. Most importantly though, for fans of the best sports cars in the world, Ferdinand Porsche is the founder of Porsche automobiles and his ambition and engineering prowess are why we get to enjoy Porsches so much today.
The Basics
Design engineer Professor Dr. Ing. h.c. Ferdinand Porsche, the third of five children, was born in Maffersdorf (now: Vratislavice/Czech Republic) on 3rd September 1875. His father, Anton Porsche, was the owner of a plumbing workshop. Anton’s son, Ferdinand, was expected to take over the family business, but he had other interests: at the age of 14 he was already performing experiments with electricity. However, his father was not very impressed with this. On the contrary, for a long time he tried to forbid his son from busying himself with “such nonsense”. Therefore, Ferdinand set up his own secret workshop in his parent’s house so that he could experiment unhindered.
No Subscription? You’re missing out
Get immediate ad-free access to all our premium content.
Get Started