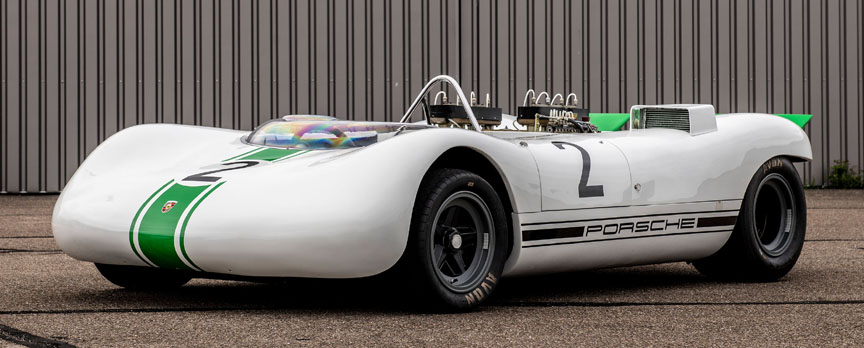
Porsche 909 Bergspyder (1968)
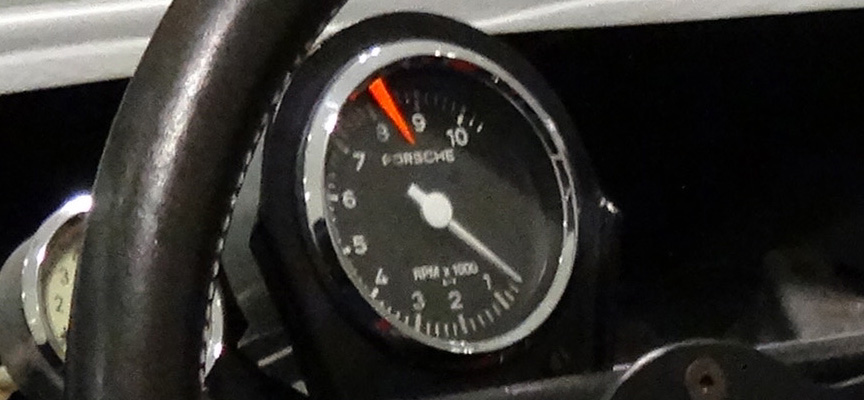
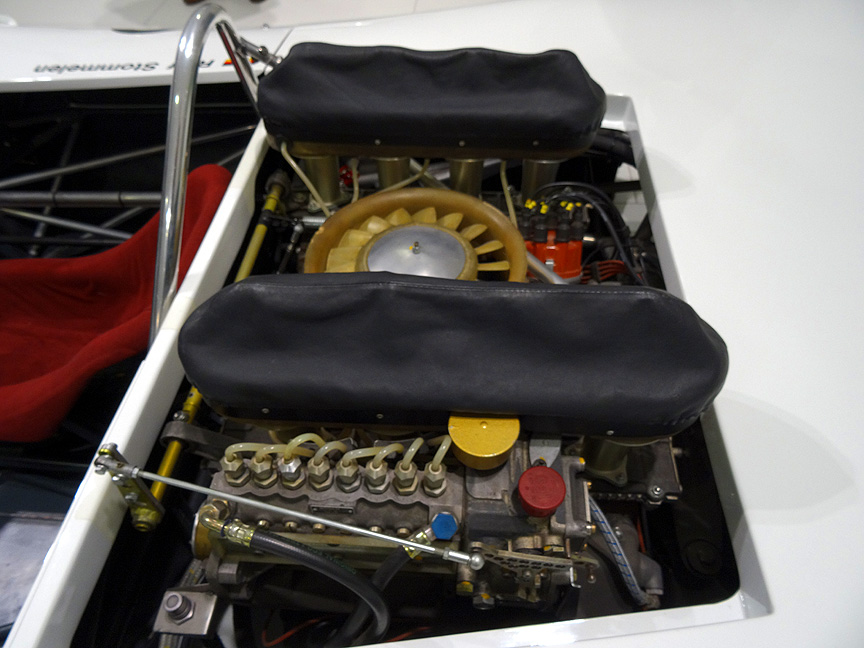
Year: 1968 / Engine: 2.0 L Type 771 flat-eight / Power: 270 bhp @ 8600 rpm 270 / Weight: 385 kg (849 lb) / Premiere: September 8, 1968 Gaisberg hill climb in Austria
In the 1960s hillclimbing was a big focus for automotive manufacturers and they would spend big money and goto extreme lengths to have the quickest cars racing up the hill. For Porsche this meant building the remarkable 909 Bergspyder. Built specifically for hillclimbing, the stop-gap race car may have had a short life, but it was a technical marvel that represented a watershed for Porsche, an object lesson in weight-saving like had never been seen before. At the time the 909 Bergspyder was claimed to be the most uncompromised racer Porsche had ever built and none had a greater singularity of purpose.
The 909 Bergspyder did not win a major event. It ended up being an awesome laboratory of ideas (not all worked). Thanks to timing and regulation changes that got rid of the minimum weight requirement and an ongoing battle between Ferrari and Porsche, these ideas also cemented the rise of Ferdinand Piëch as an original thinker and brilliant leader.
The Story
The 909 was developed using the know-how from the 910 Bergspyder. The total length of the car was only 344 cm/135″. The European Hillclimb Championship regulations stipulated 2-litre engine but didn’t stipulate minimum weight. This is something genius engineer Ferdinand Piëch could fully enjoy.
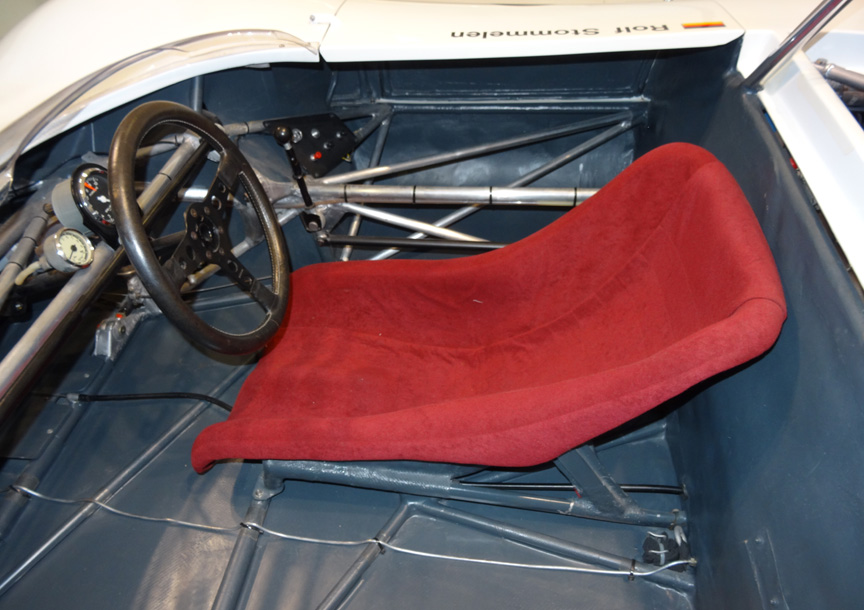
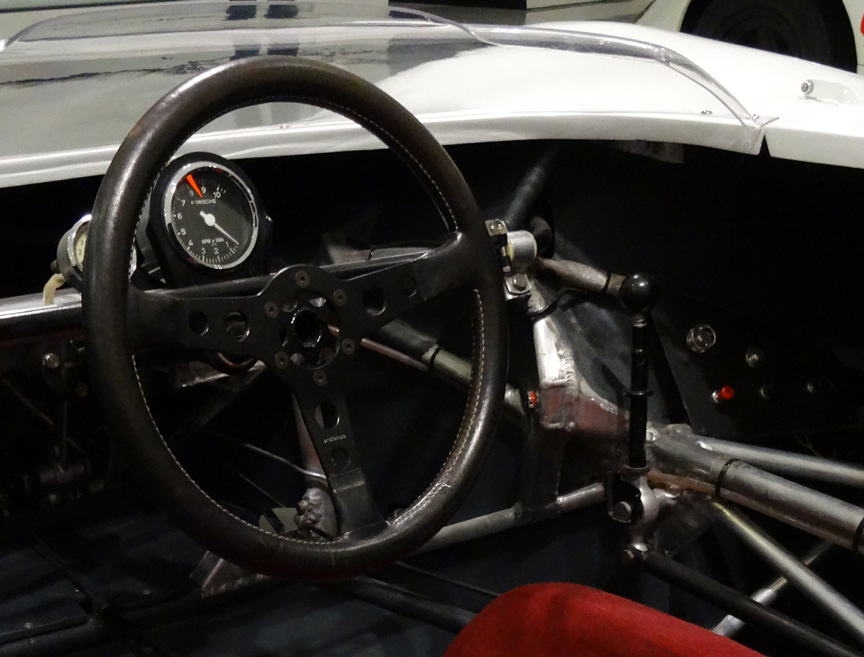
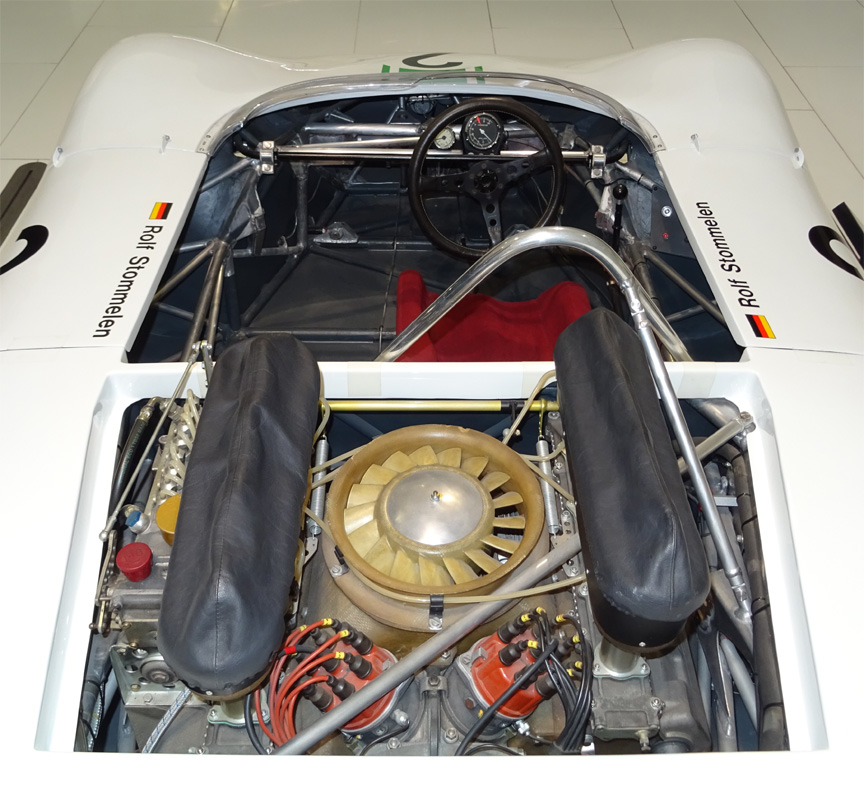
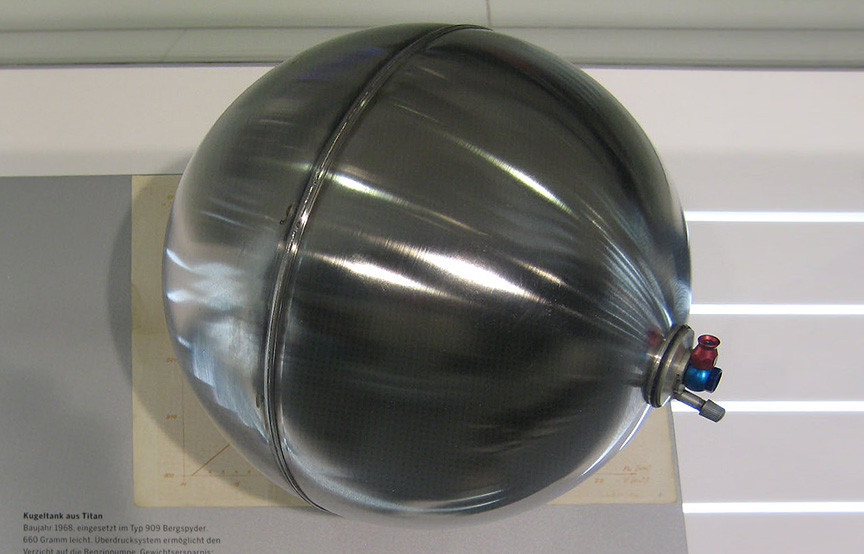
Safety wasn’t an issue these days, so the car was built on an aluminium spaceframe. Different diameter tubes were used, but the average diameter was only about 1″. Remember, the pipes were of aluminium, not of a high-strength material! Steel wasn’t used at all, not even for bolts. Light non-magnetic and sometimes even exotic and dangerous metals were used to save weight literally everywhere, even by grams. As the car was designed for short distances, the fuel tank could hold only 15 liters. A special pressurized tank was used to save the weight of the fuel pump. All this resulted in a car weighing only ~400 kg / ~900 lbs and with the 8-cylinder boxer this car was a mad thing to drive.
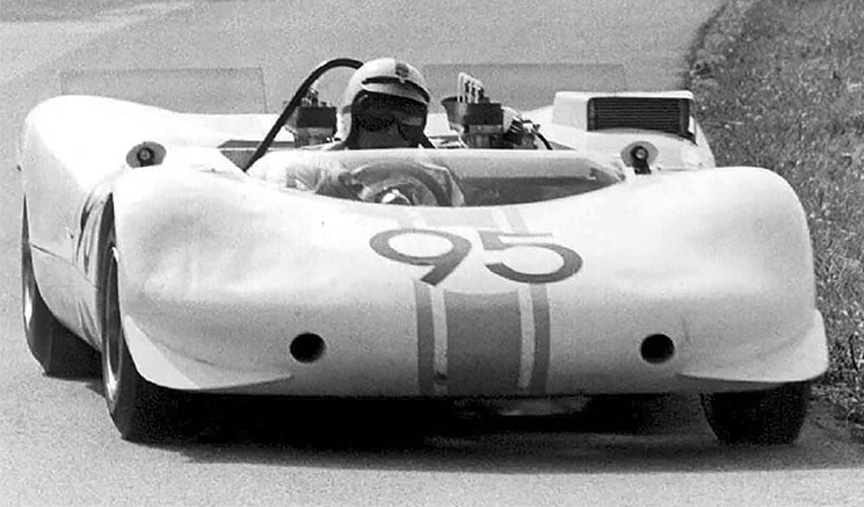
Two 909s were built by September 1968. On September 8, at the Gaisberg hill climb in Austria, championship leader and 1966-1967 winner Gerhard Mitter didn’t want to take risks with the new car although his 909 #95 was delivered to the event. Mitter decided to start with his 910 Bergspyder instead (remember, 910 came after 906 and before 907, 908 and 909).

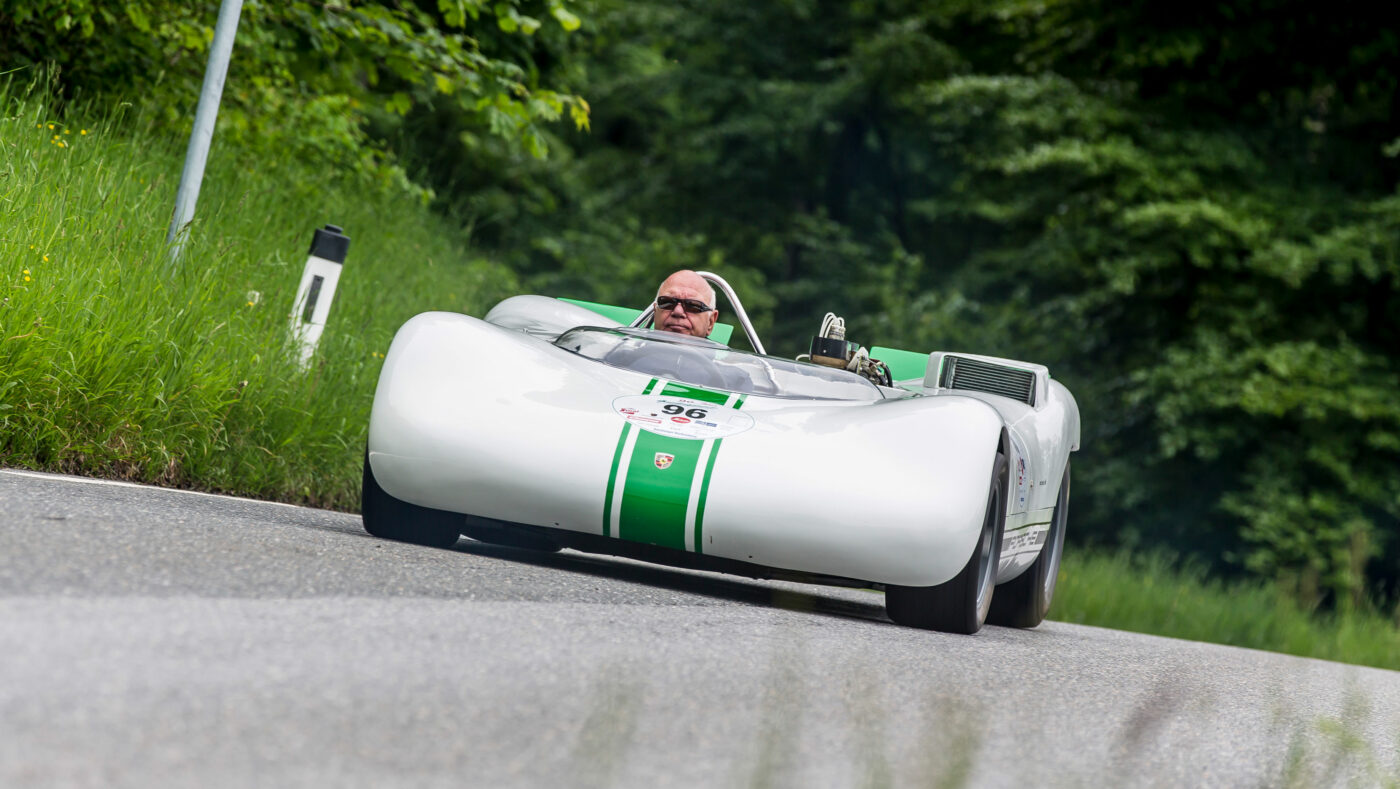
In the hands of Rolf Stommelen, the 909 #96 scored 3rd. Mitter had won the event with 910 and Dieter Quester with a BMW Monti scored 2nd.
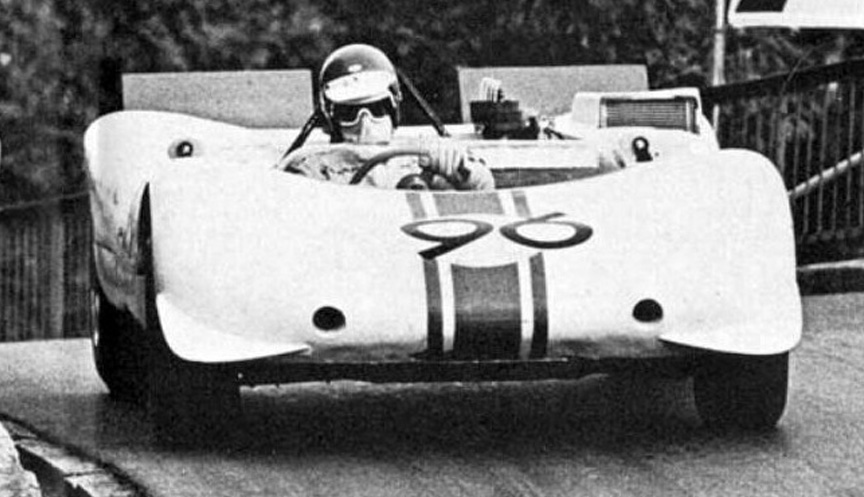

The second outing for the 909 was on September 22, 1968, at the season-ending Mont Ventoux event in France. Stommelen scored 2nd with the 909 #2. Mitter won again with 910 and didn’t use his 909 #1.
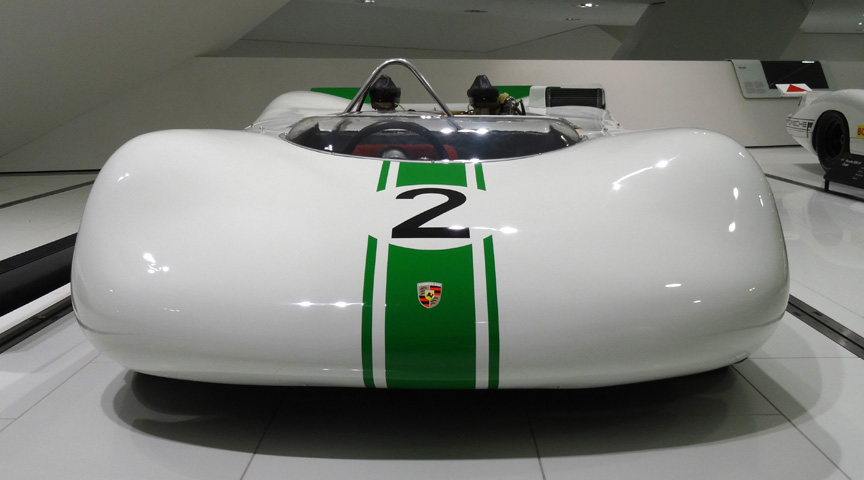
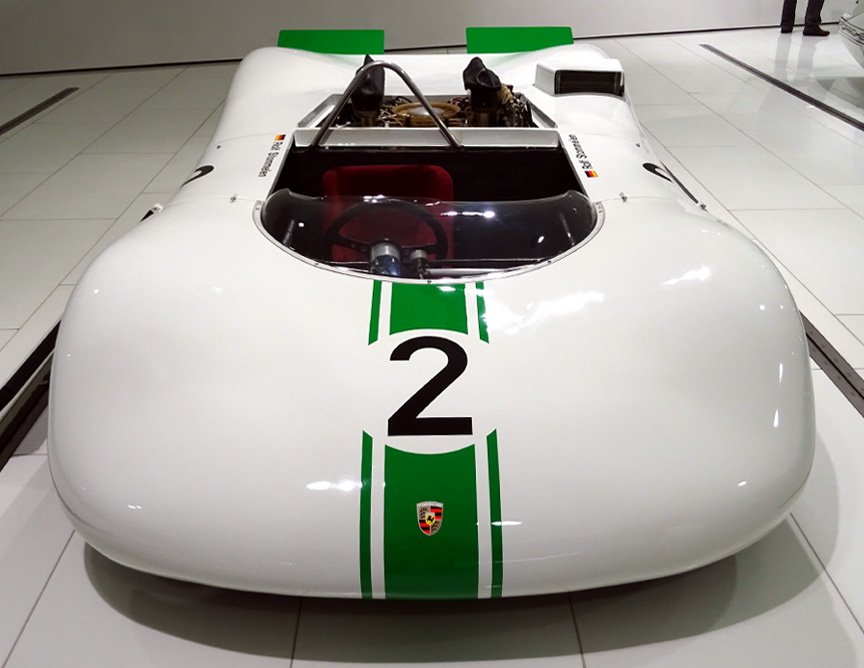
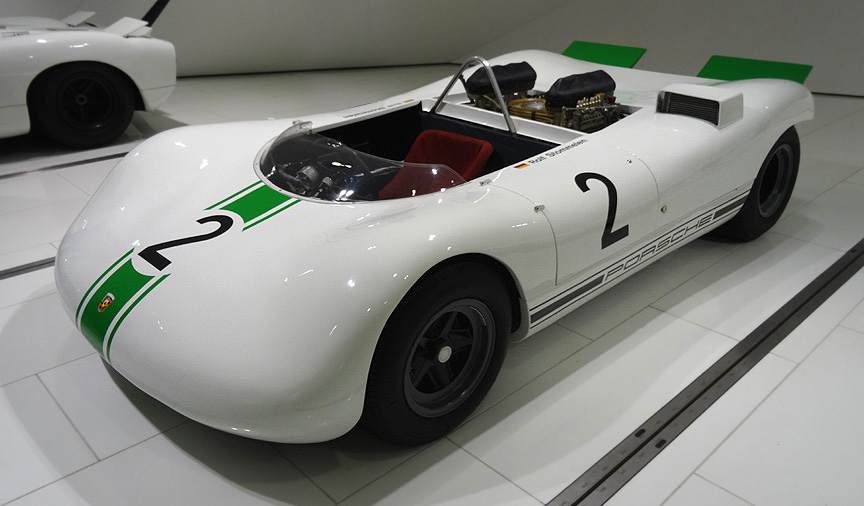









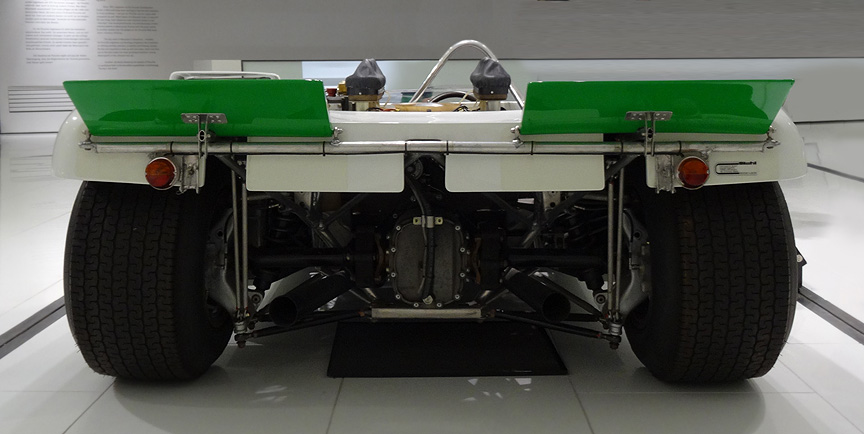

As Porsche decided to withdraw from the hillclimb championships after three consecutive championship titles and 8 championship titles during the last decade, the 909 wasn’t used again. Still, it was an absolutely amazing masterpiece and showcase, top of space-age engineering. Despite no racing victories, the information gathered in constructing it, made it one of the most important Porsches ever built – the know-how was extensively used in the racing cars to come.